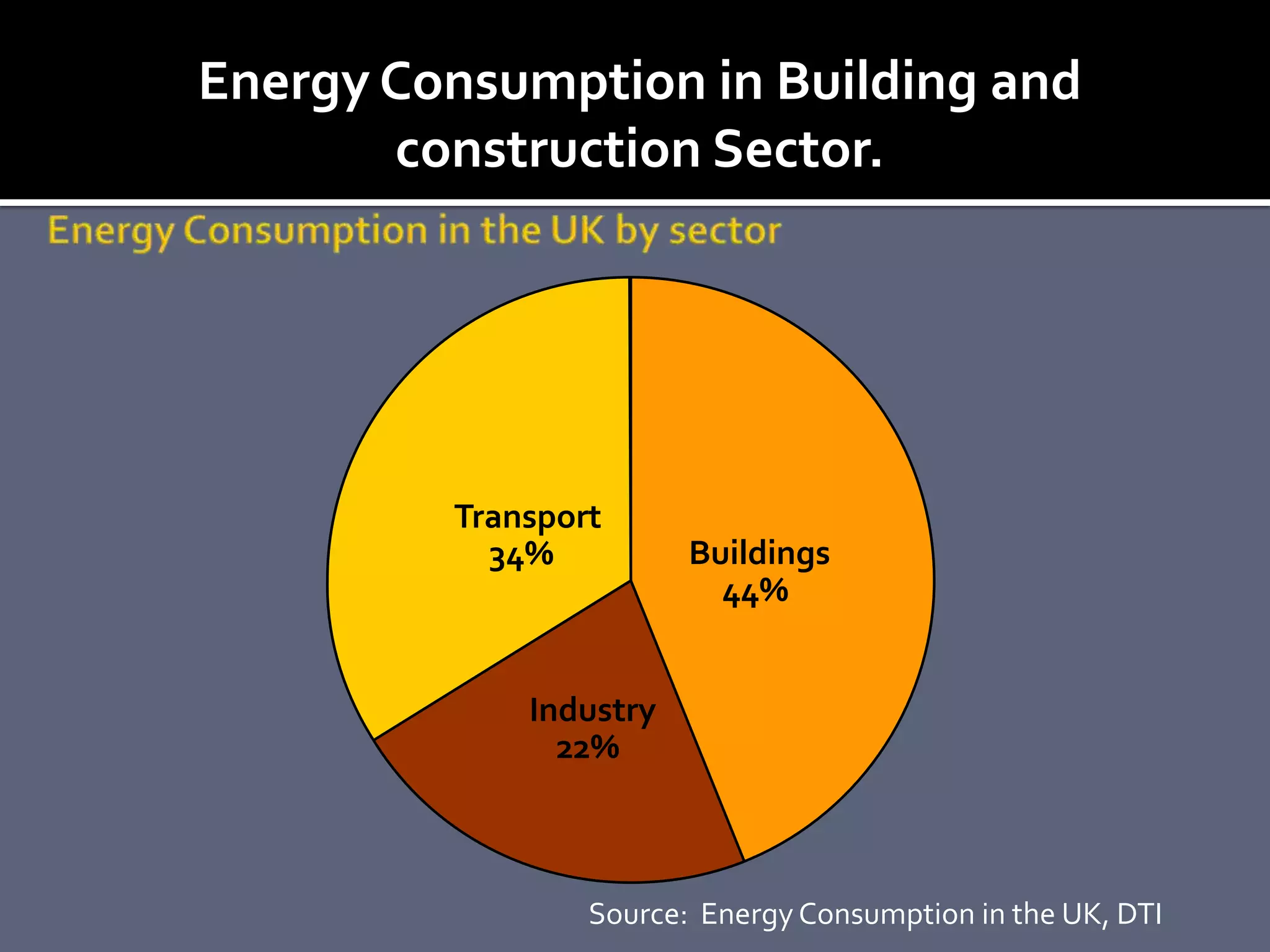
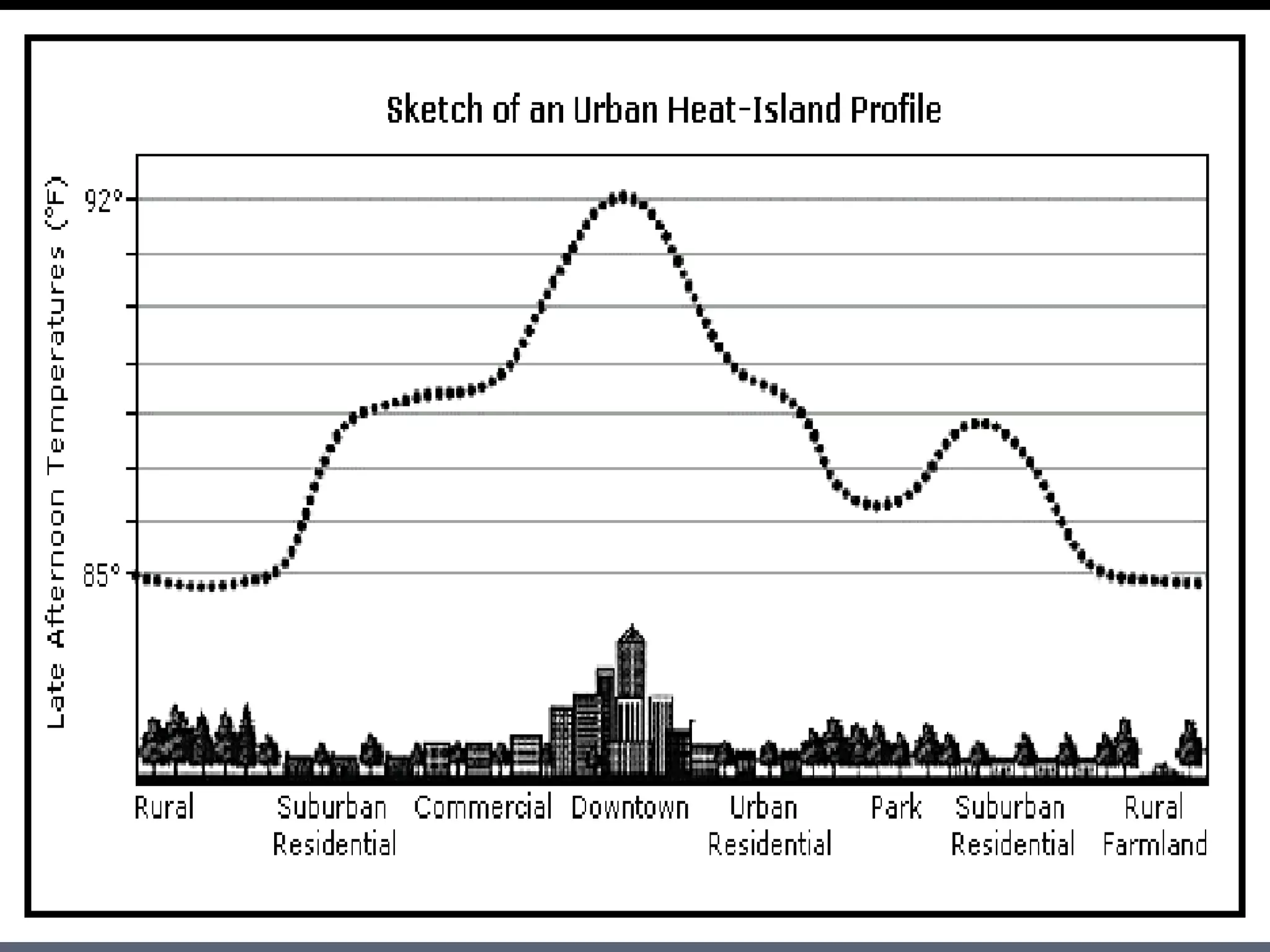
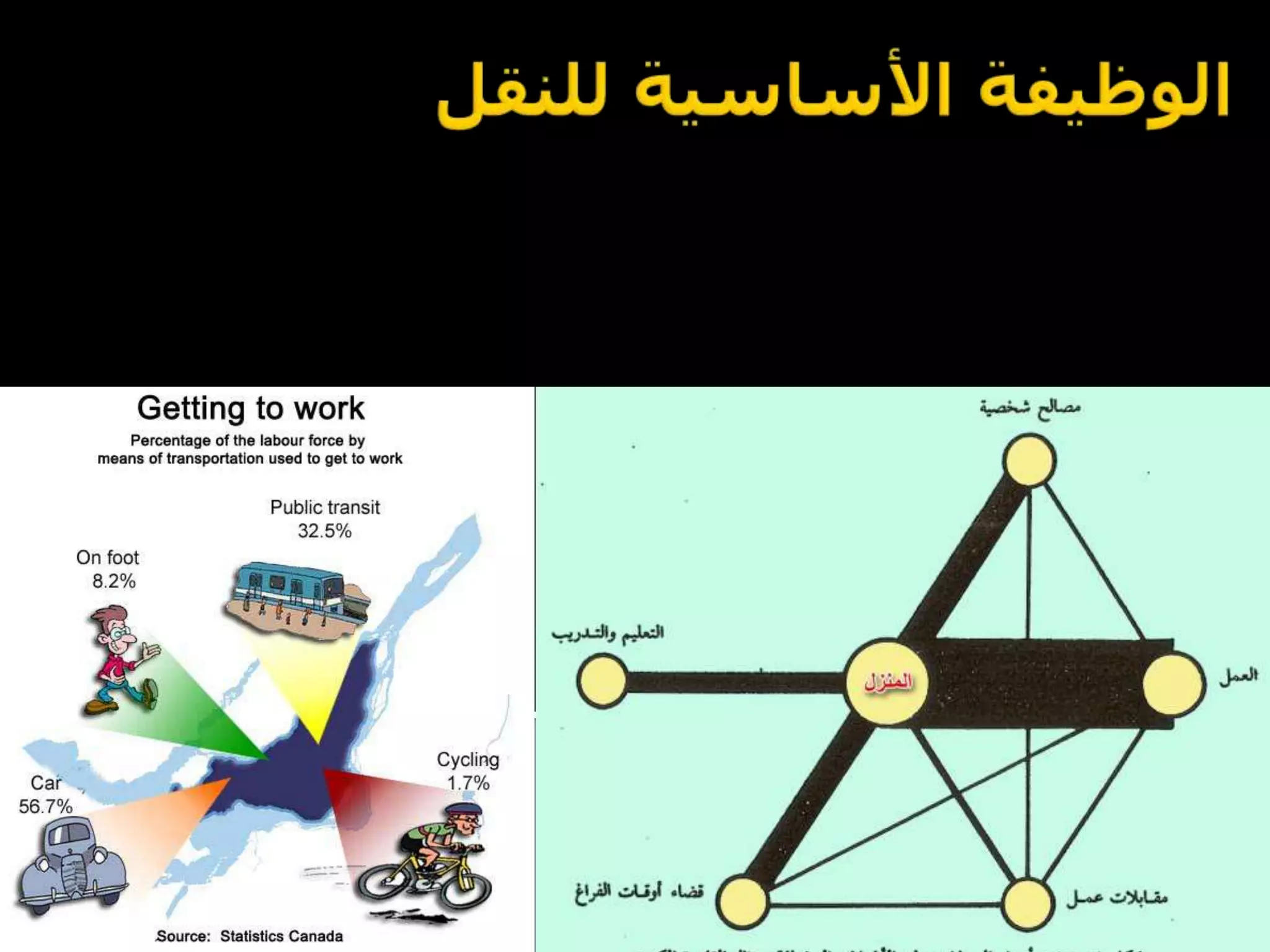
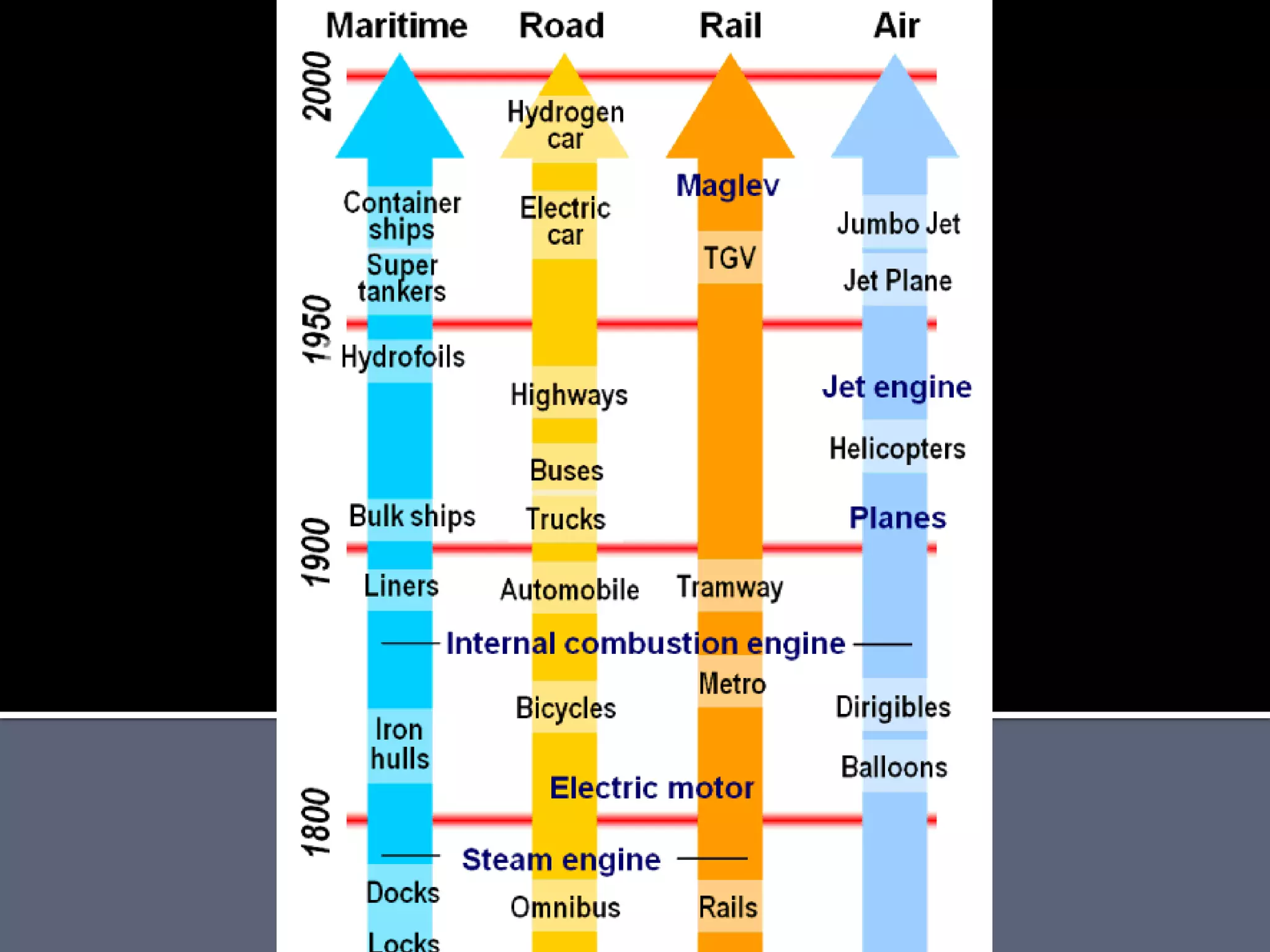
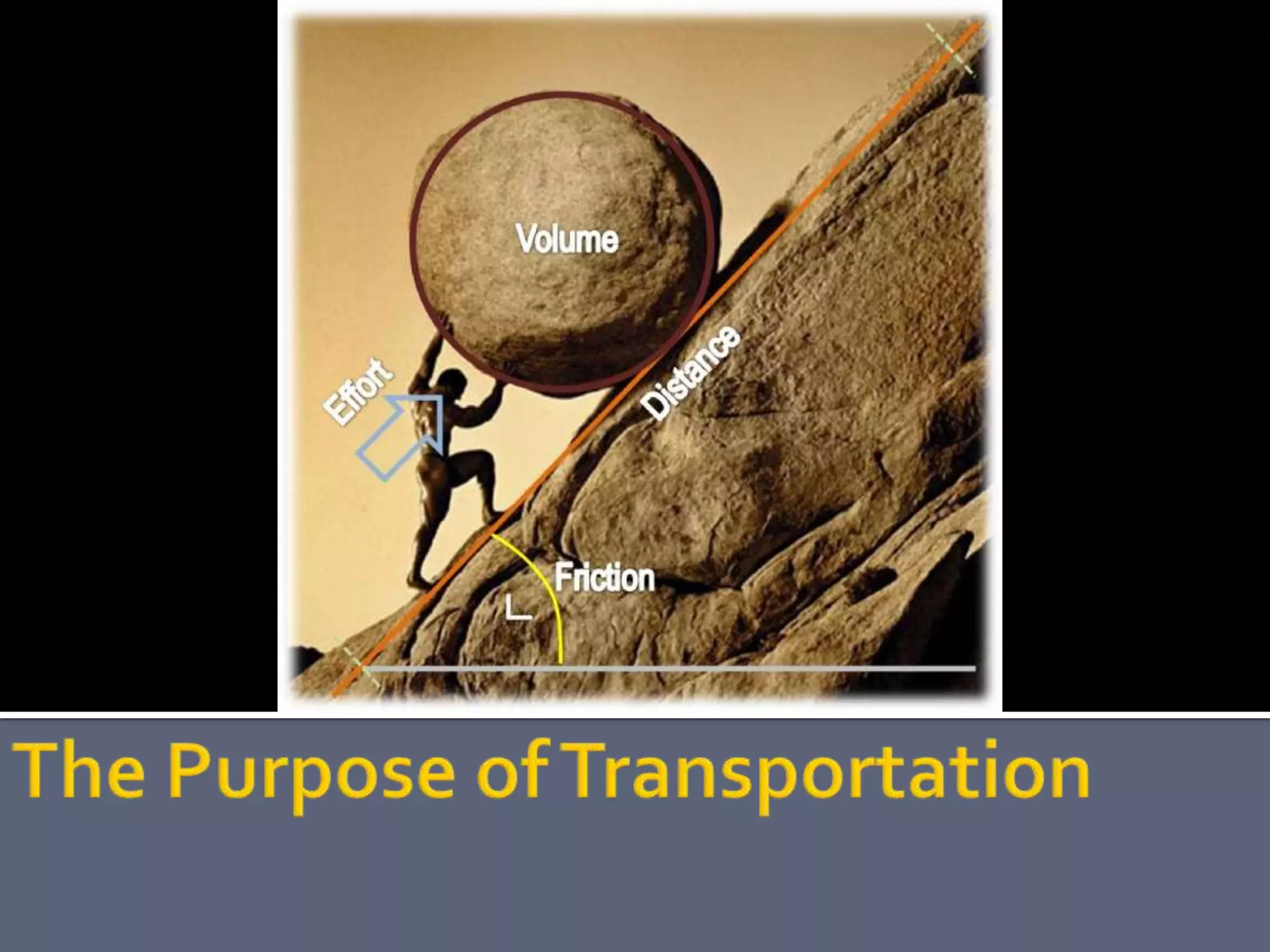
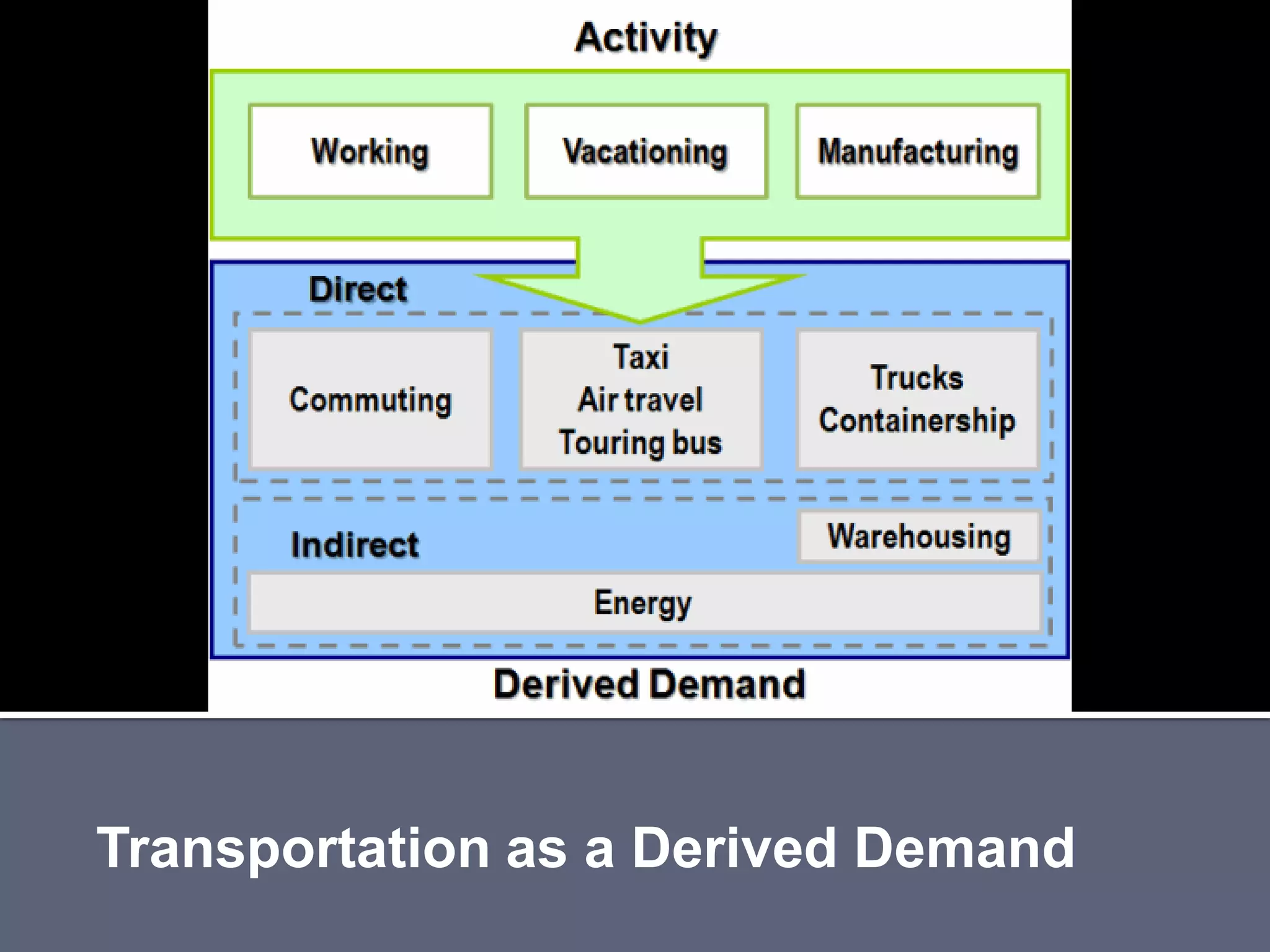
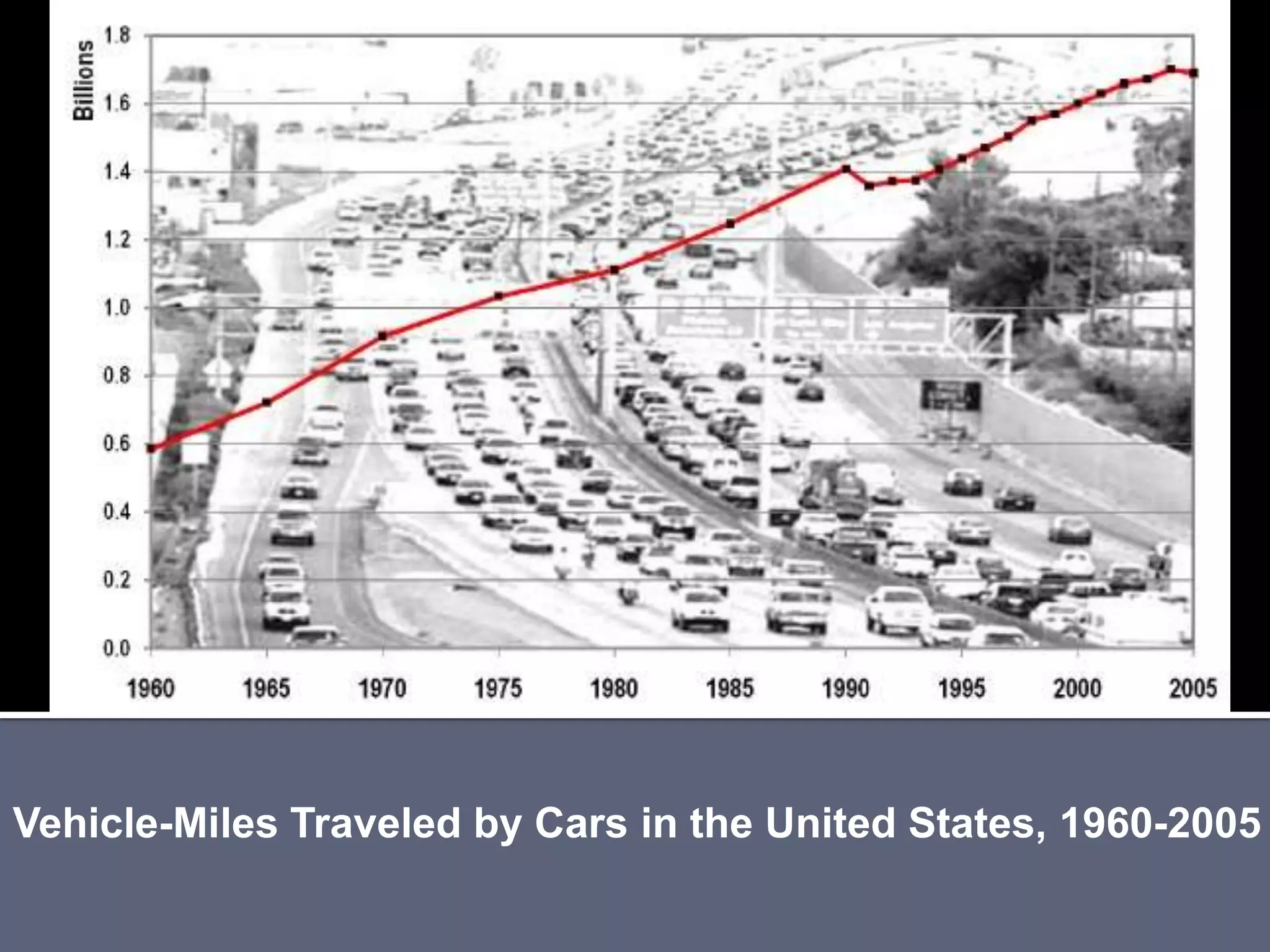
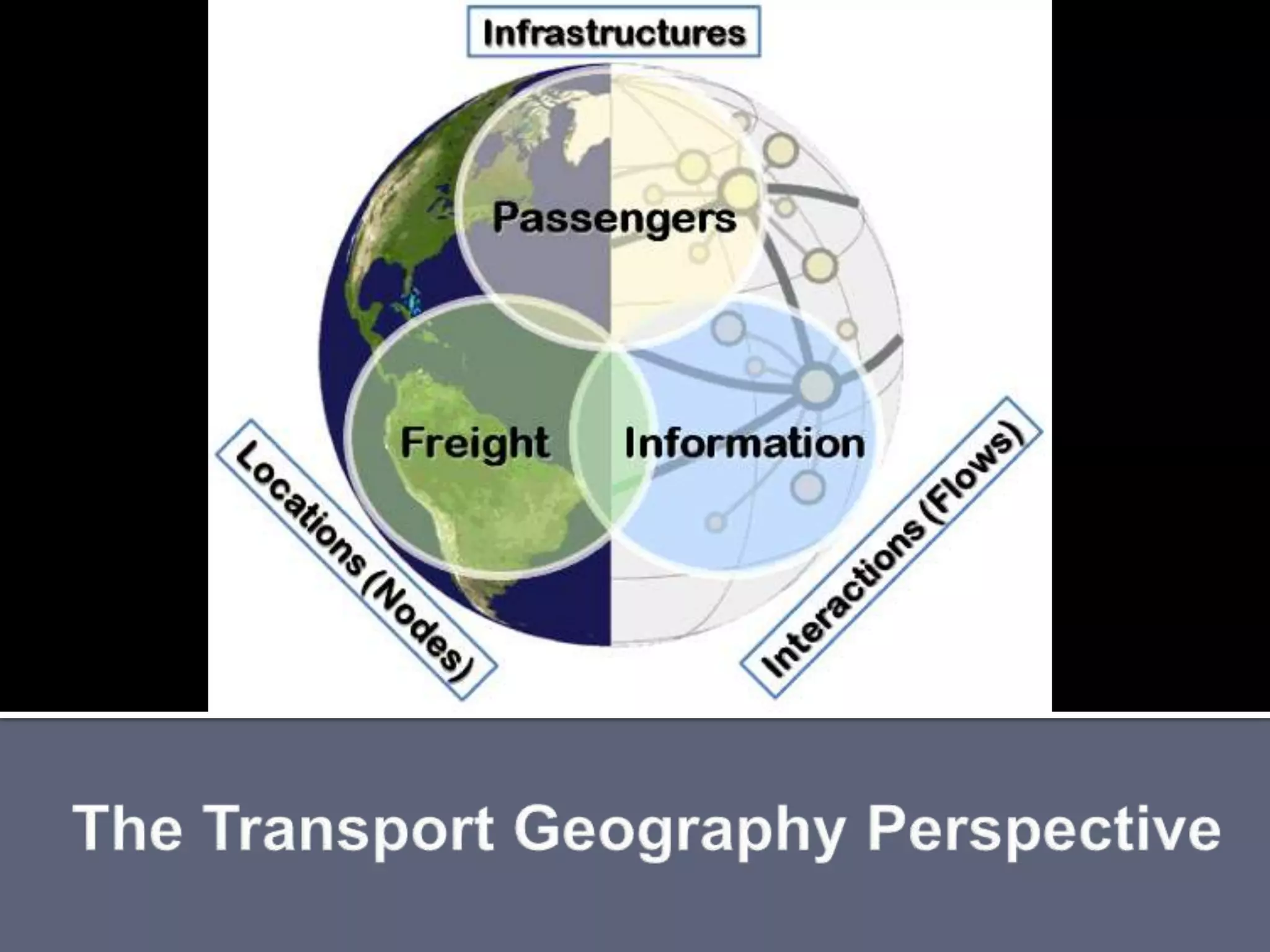
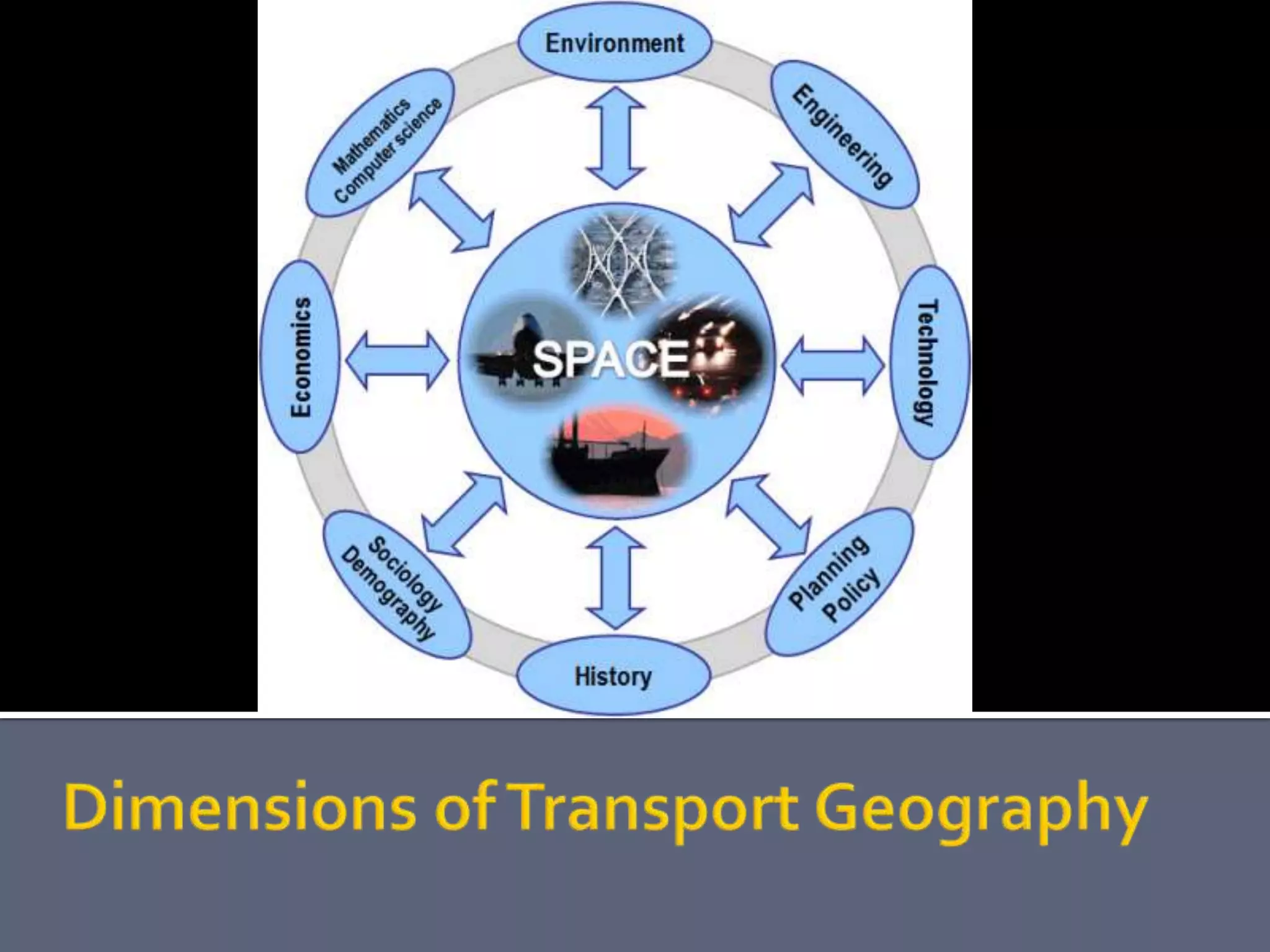
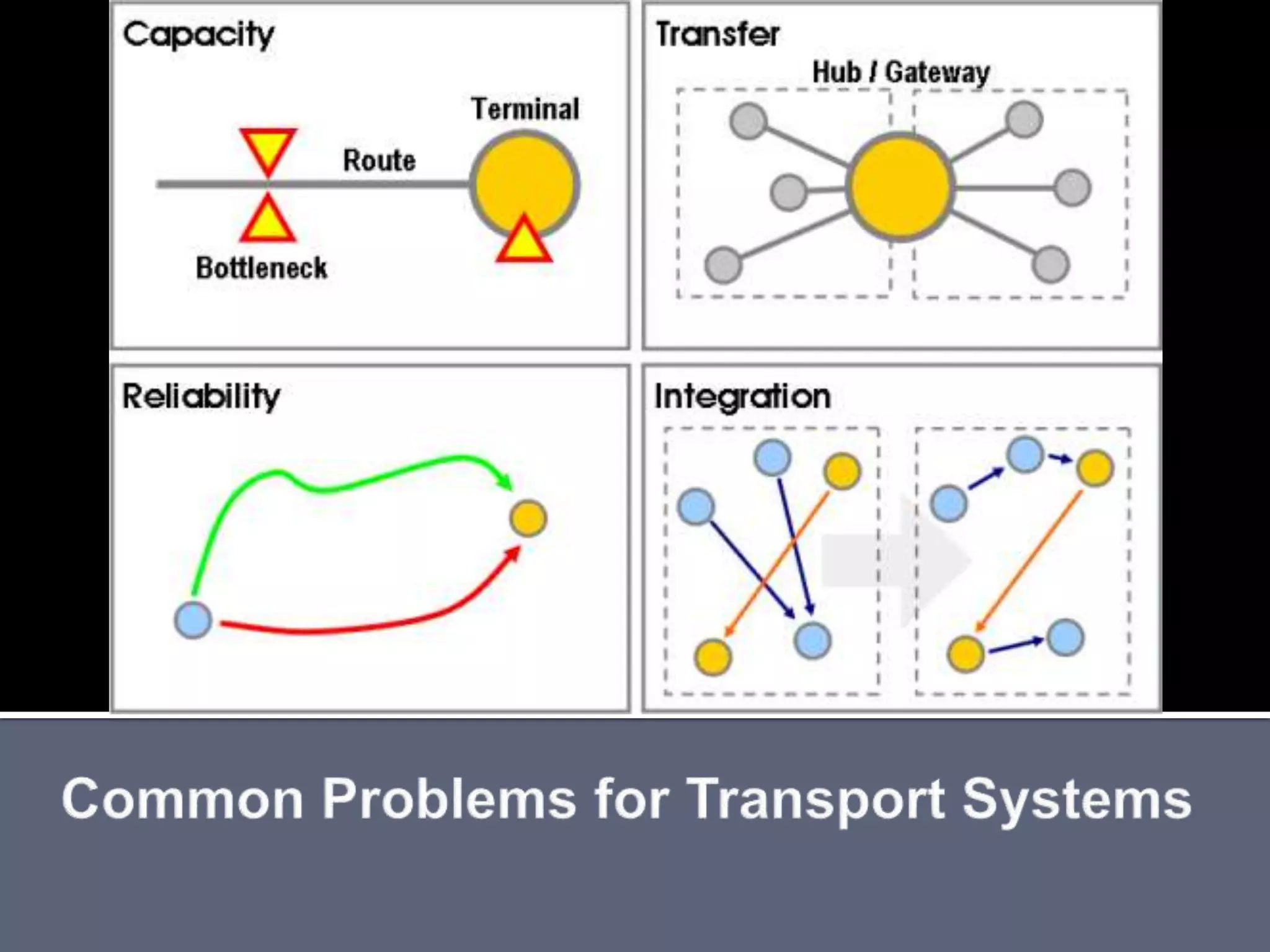
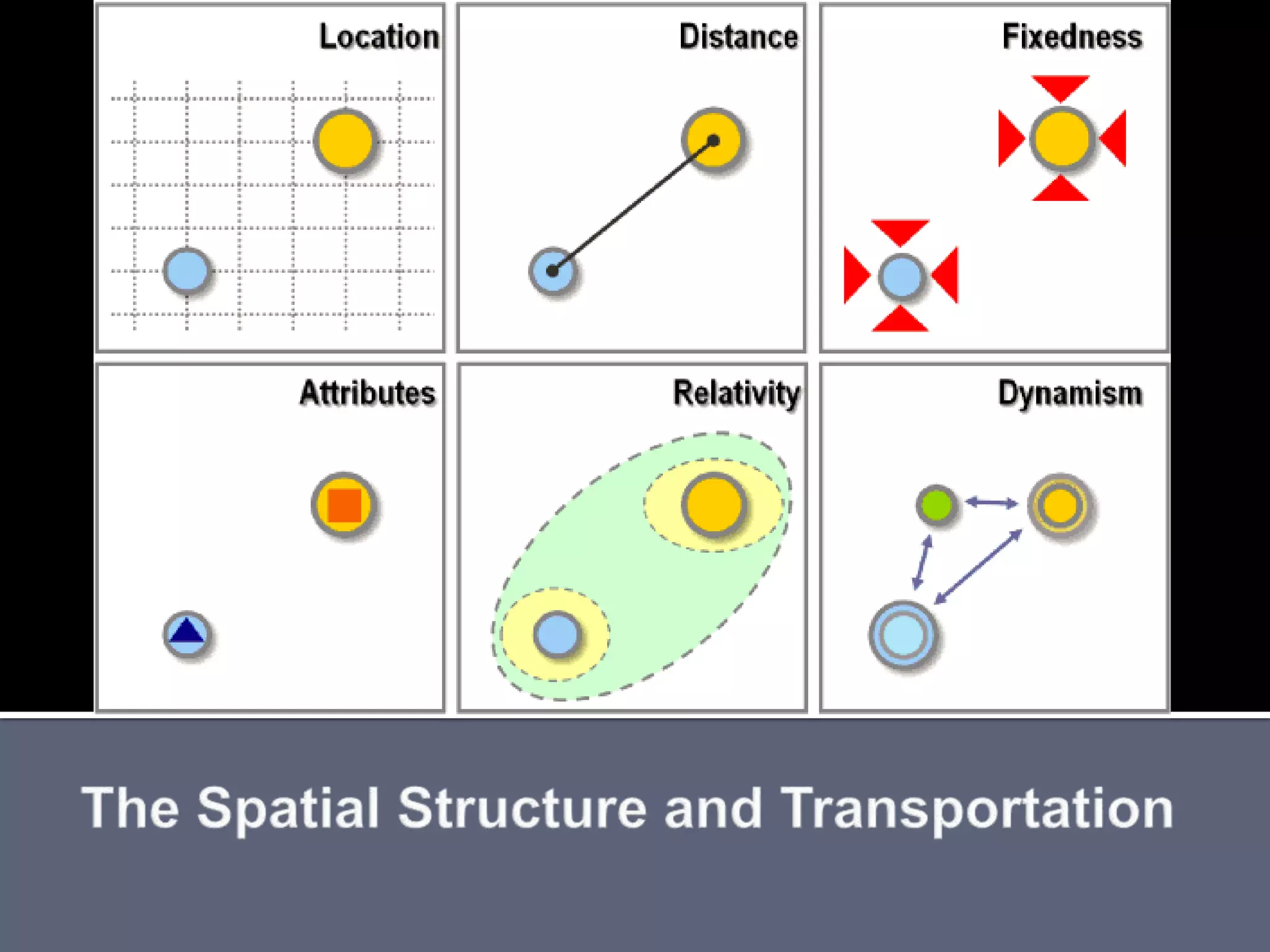
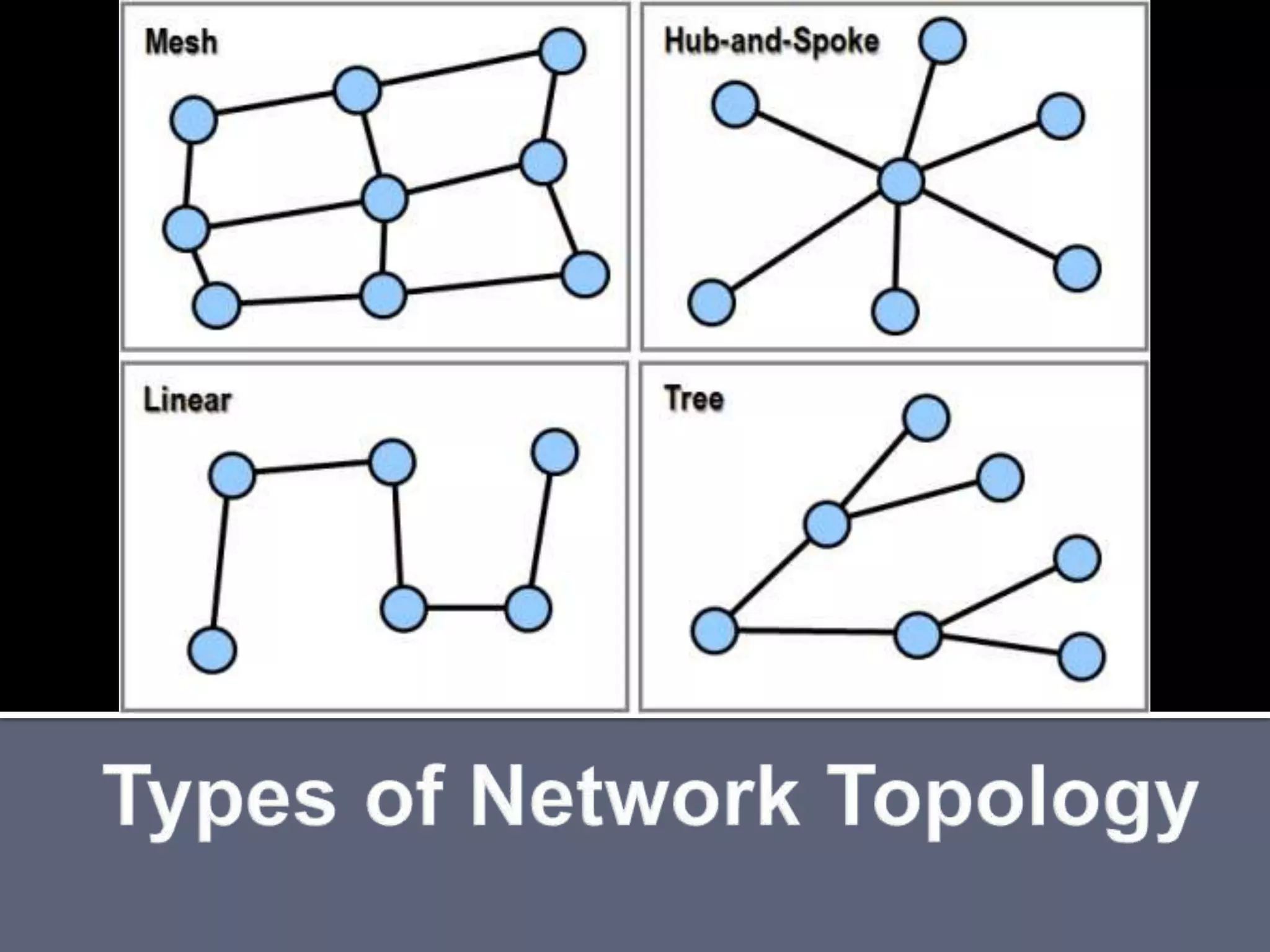
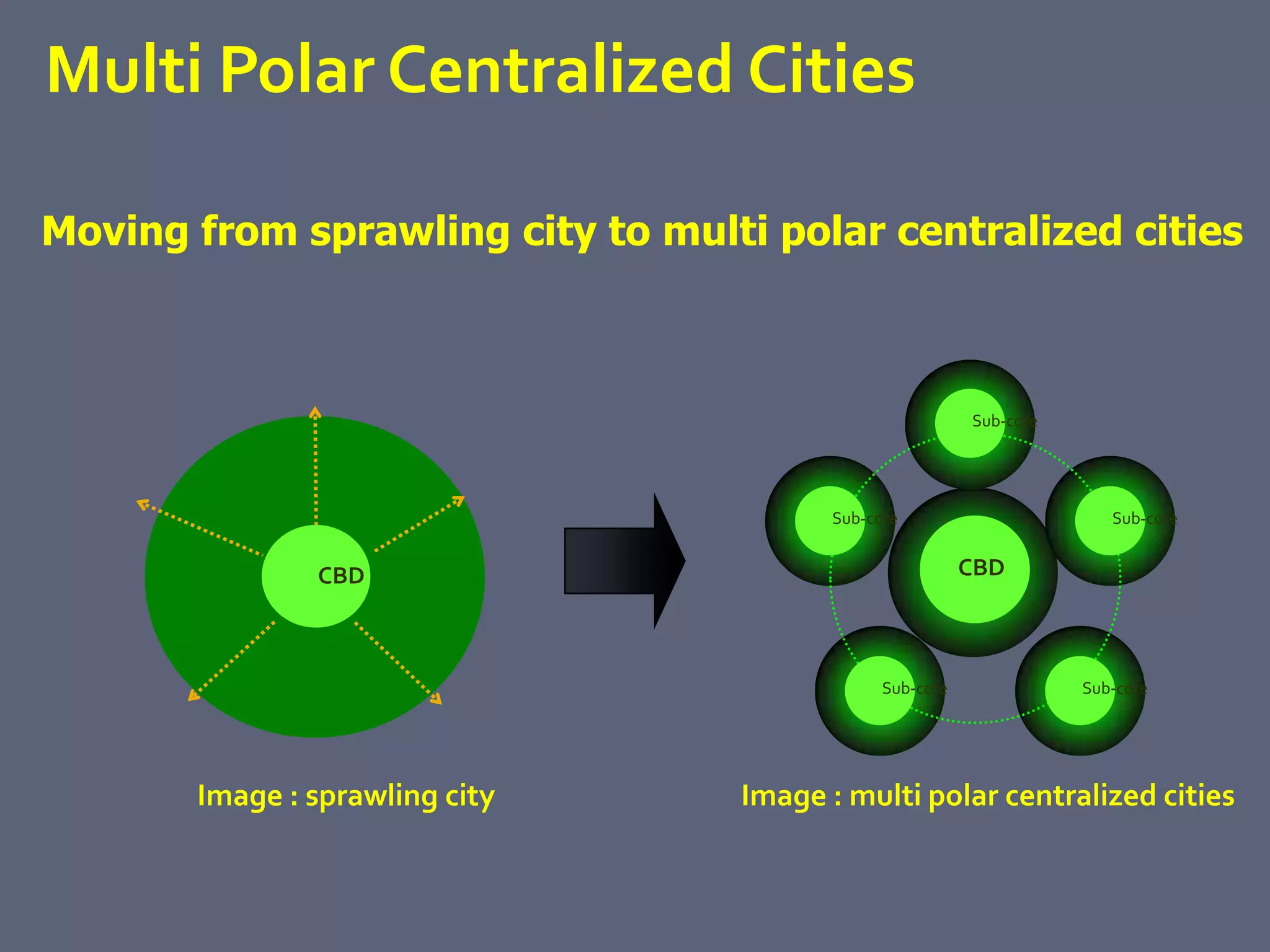
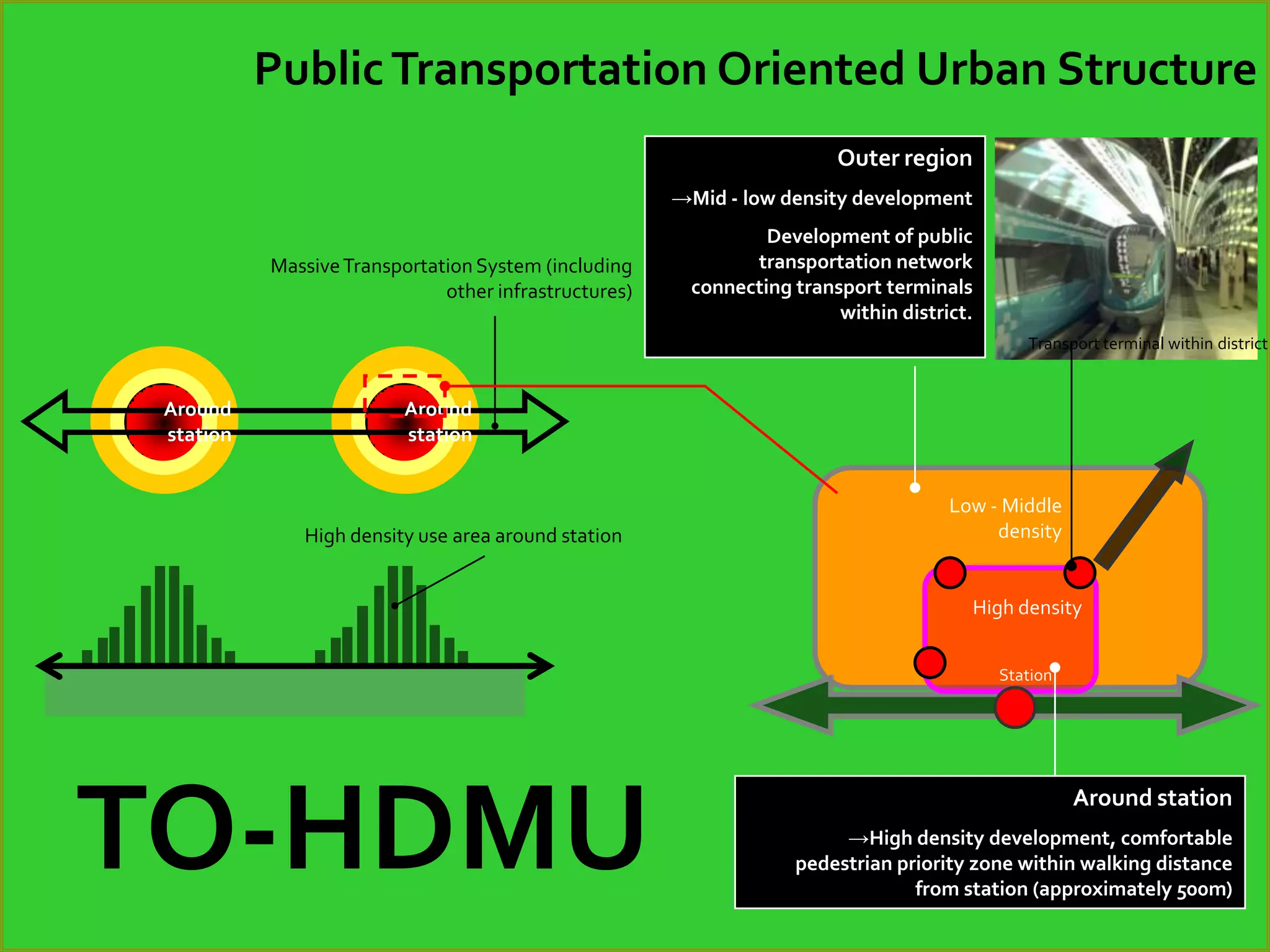
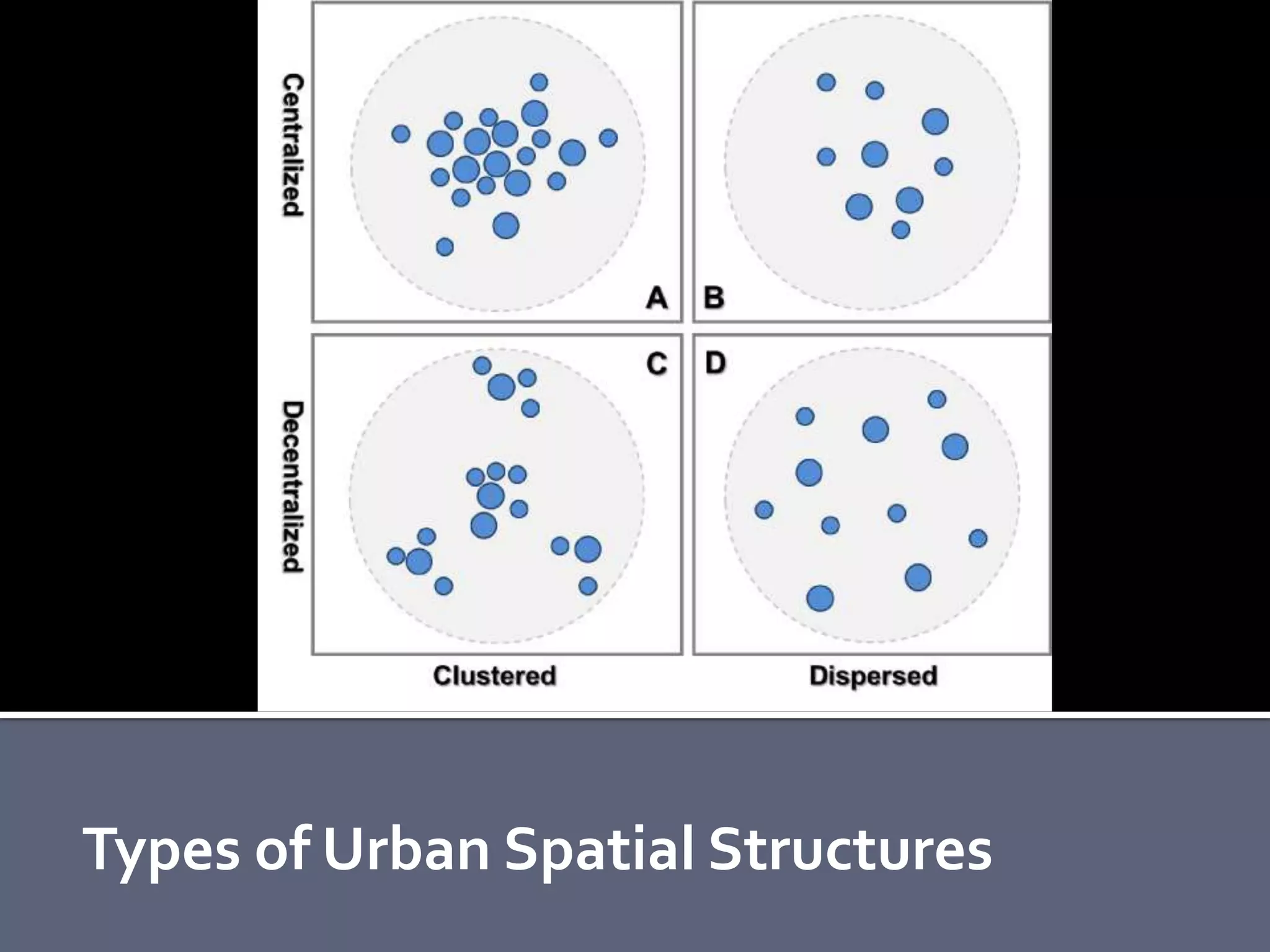
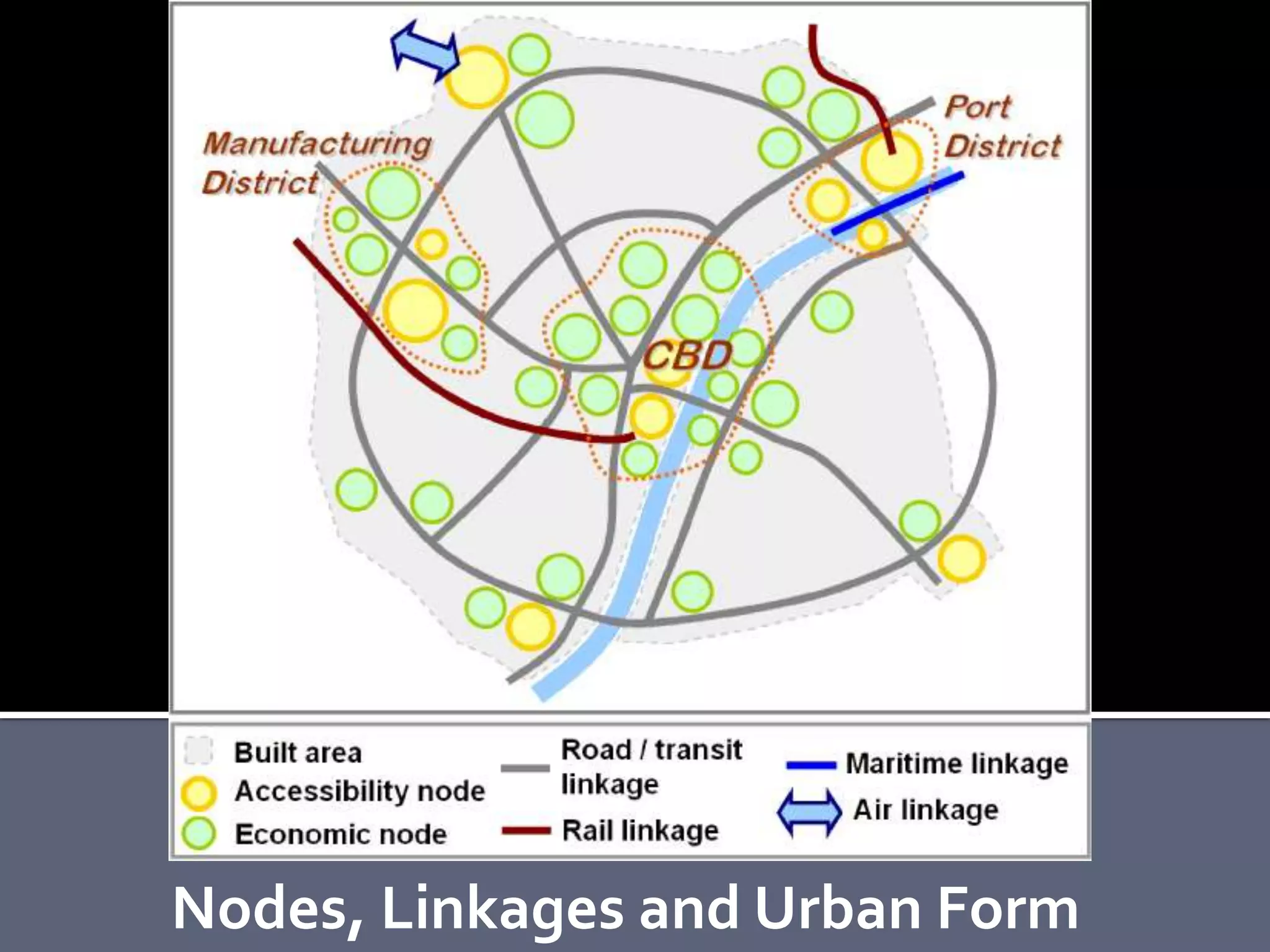
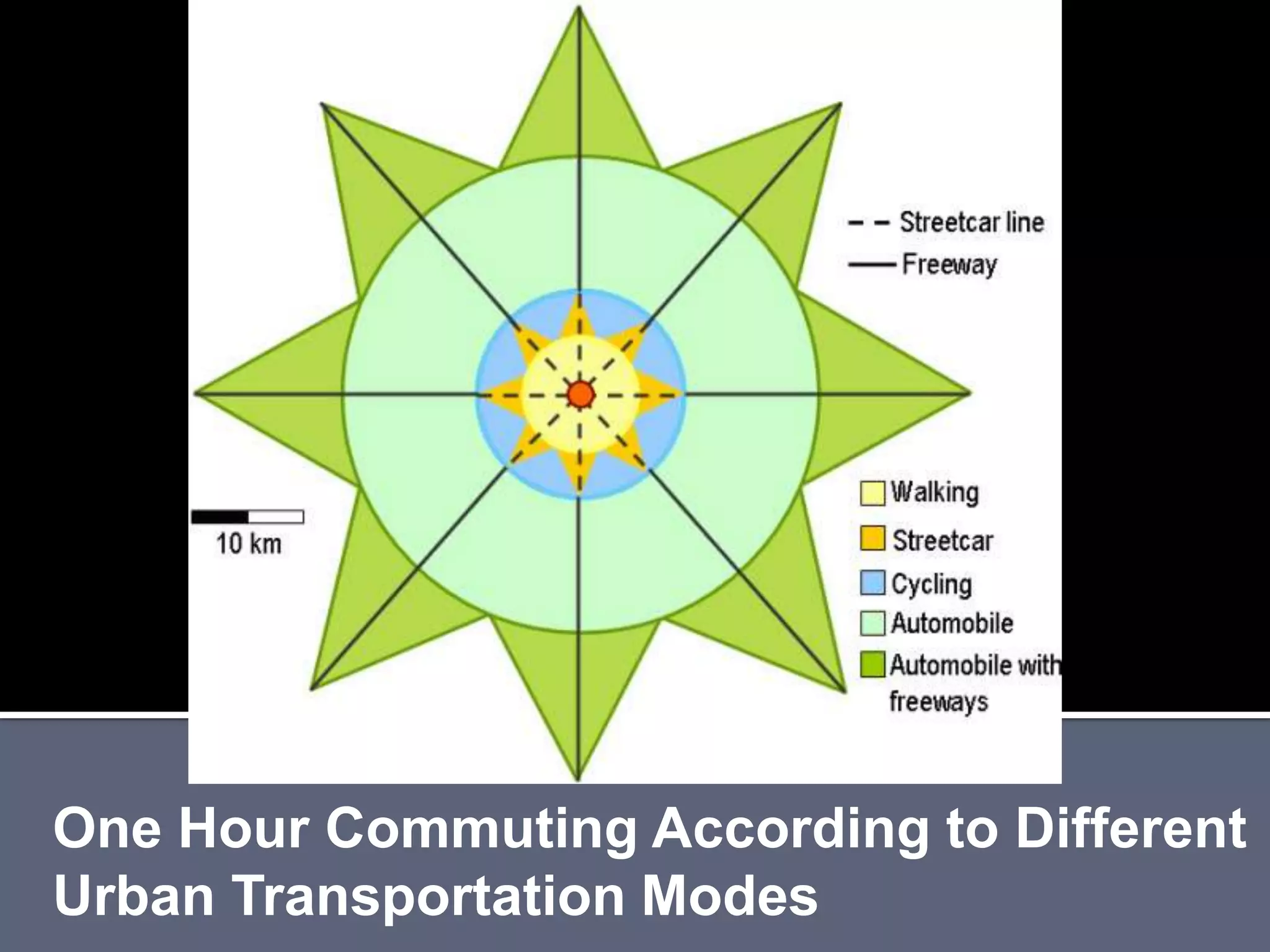
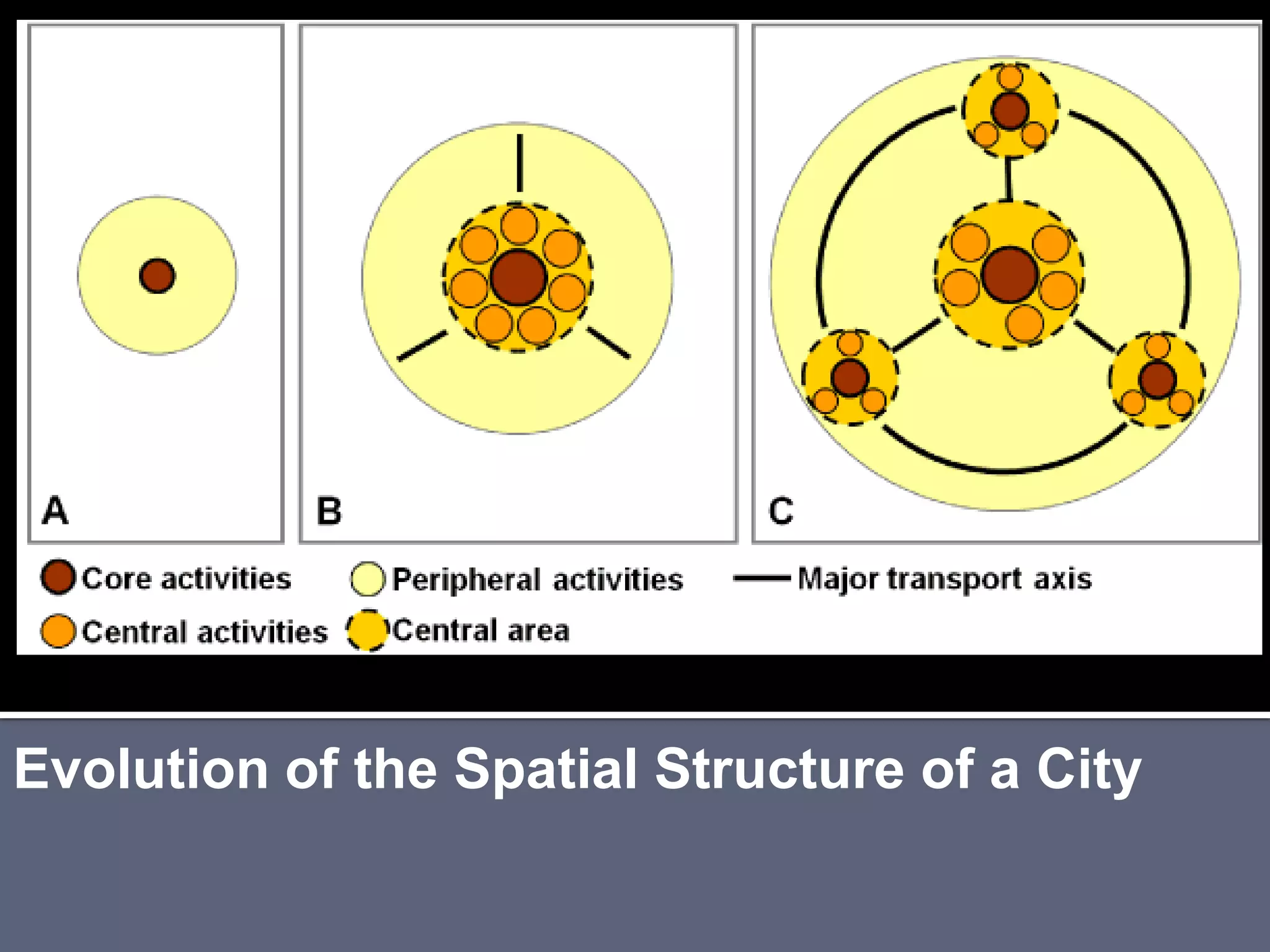
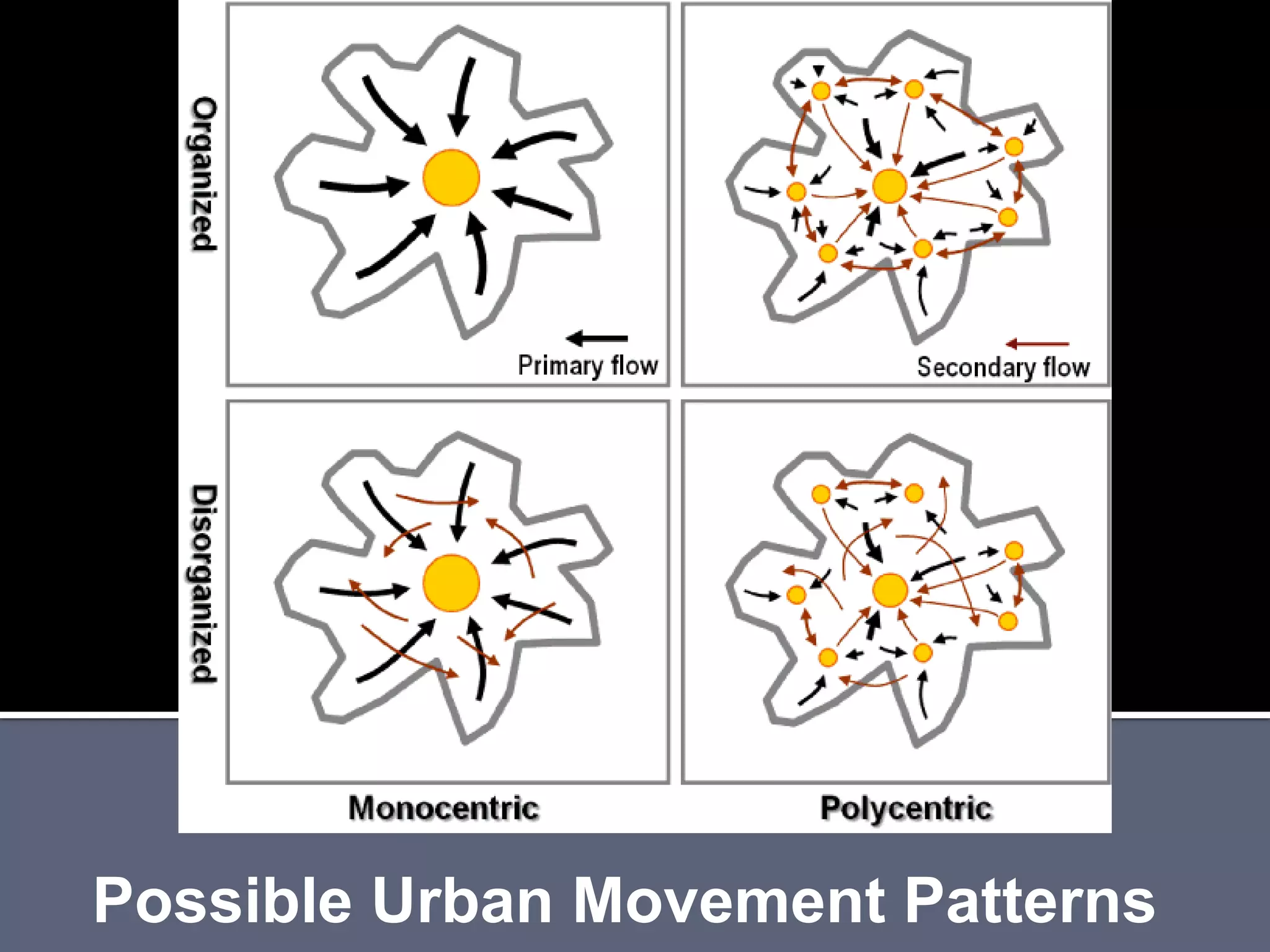
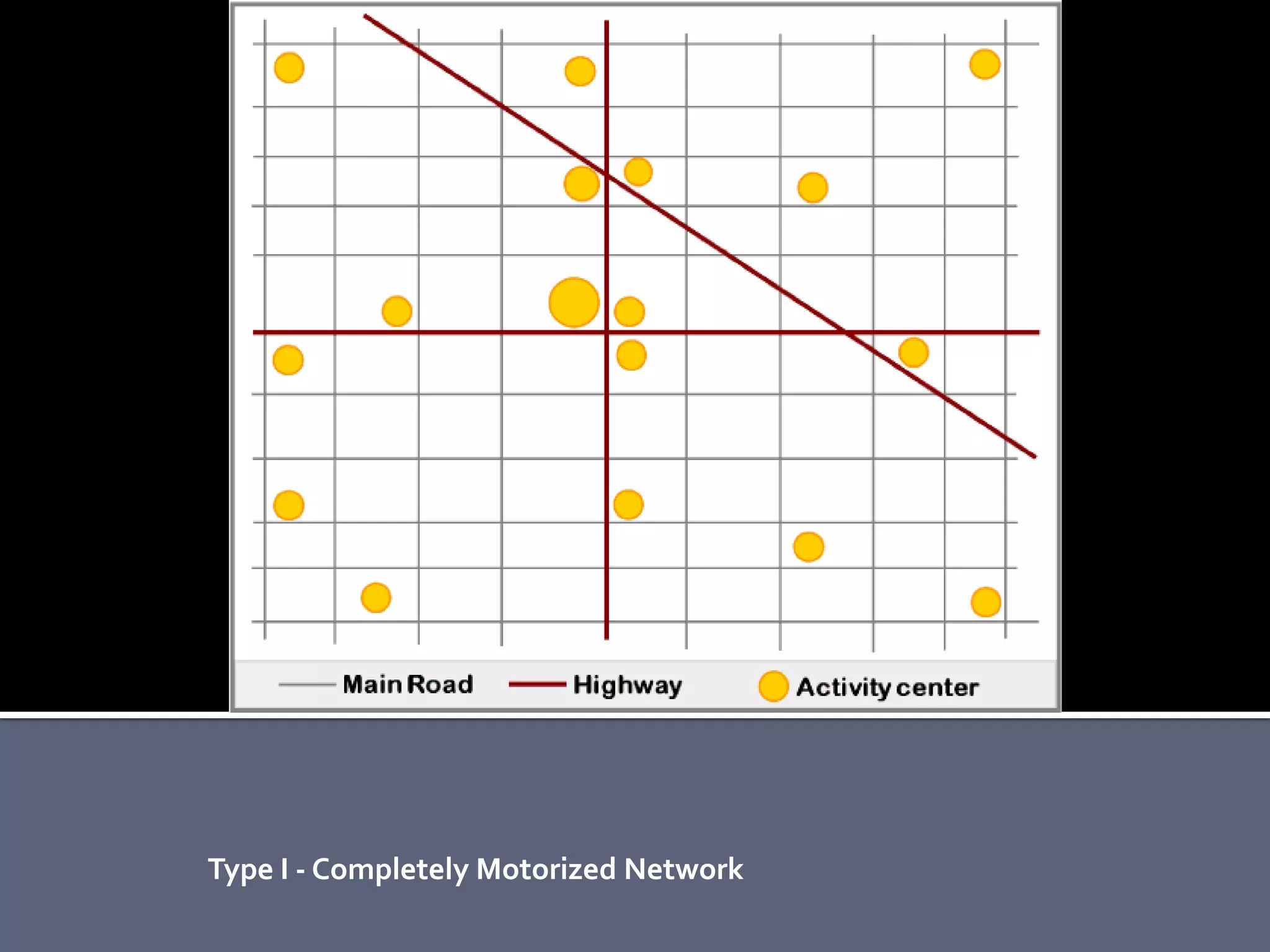
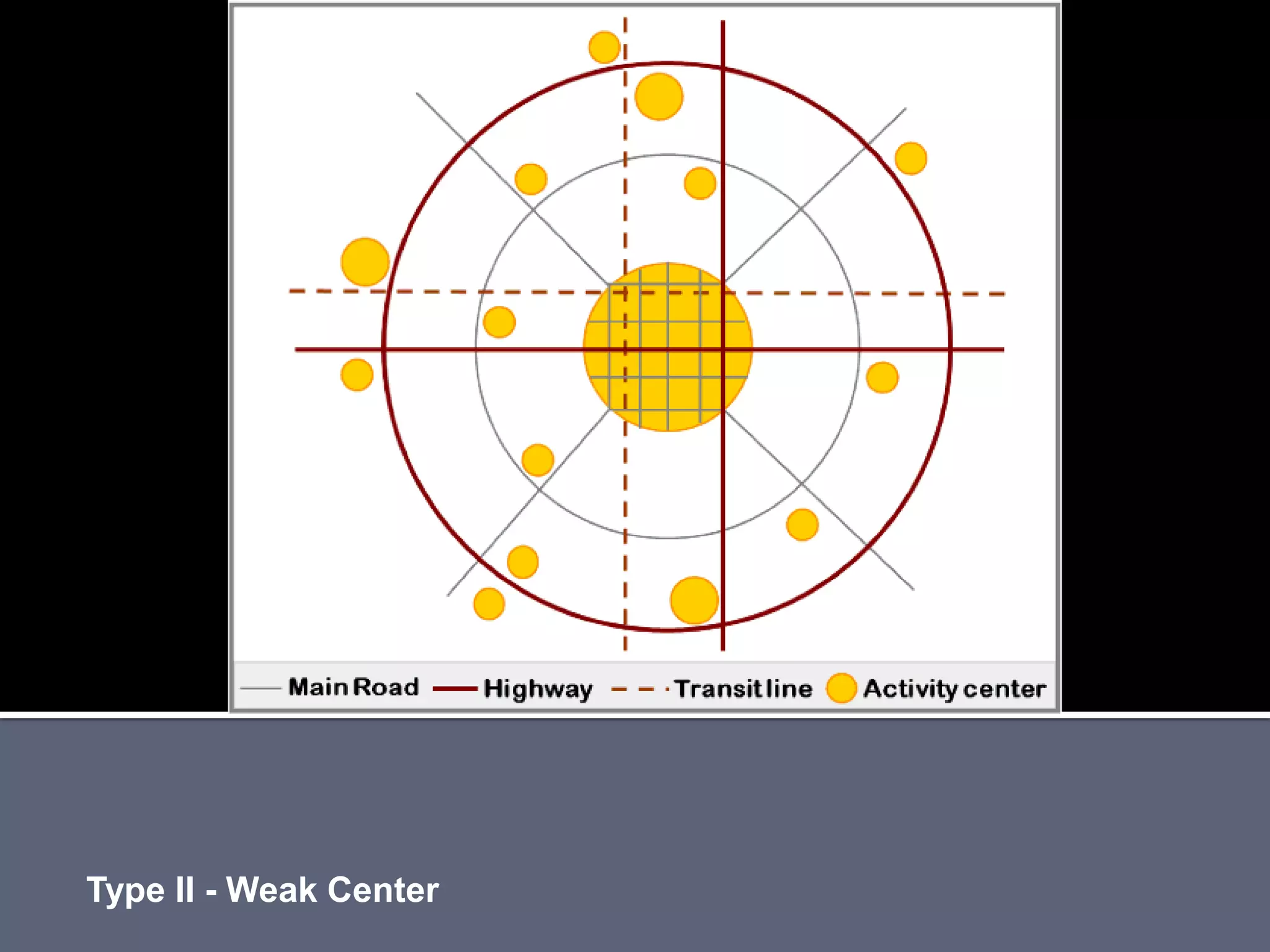
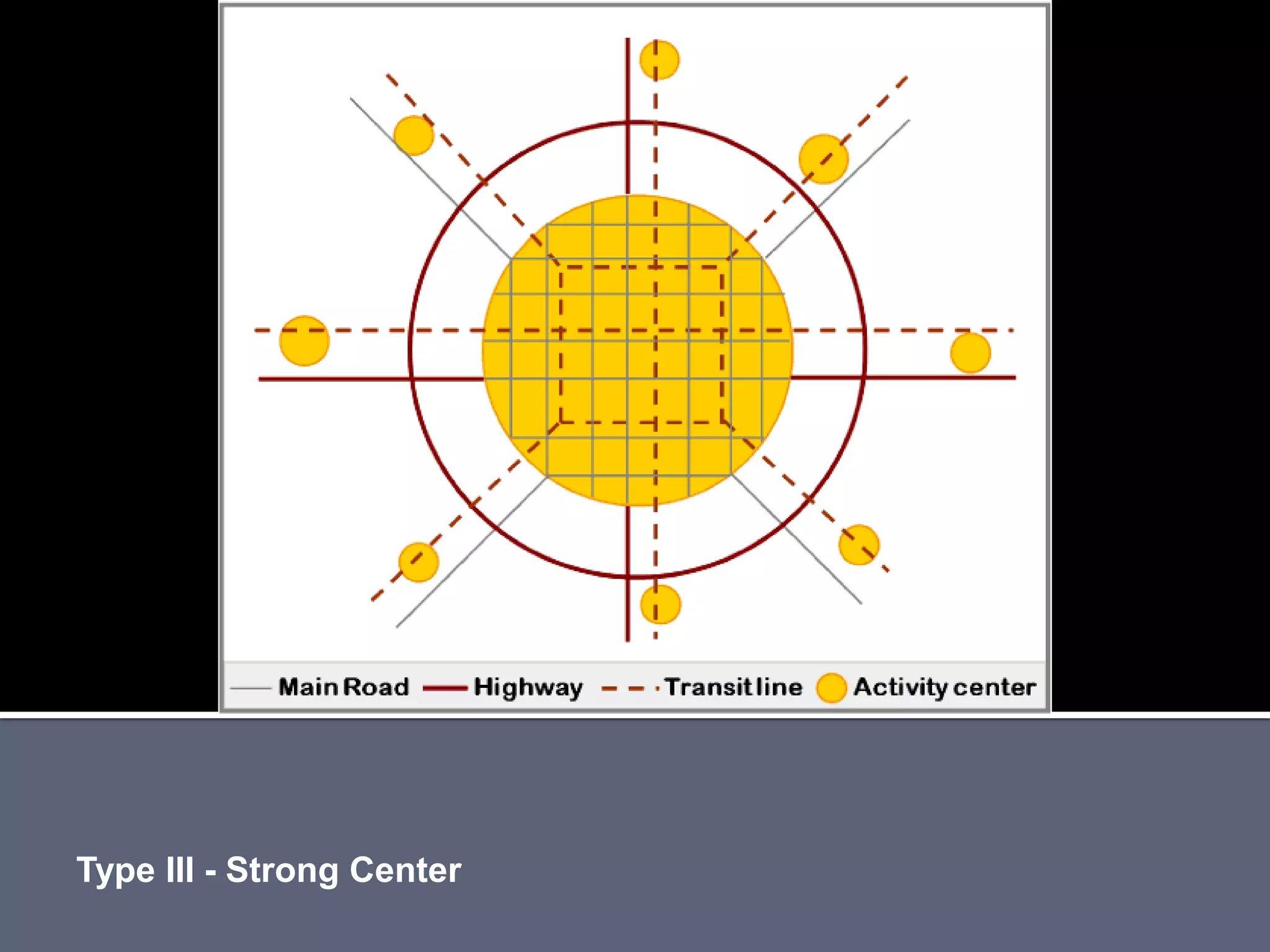
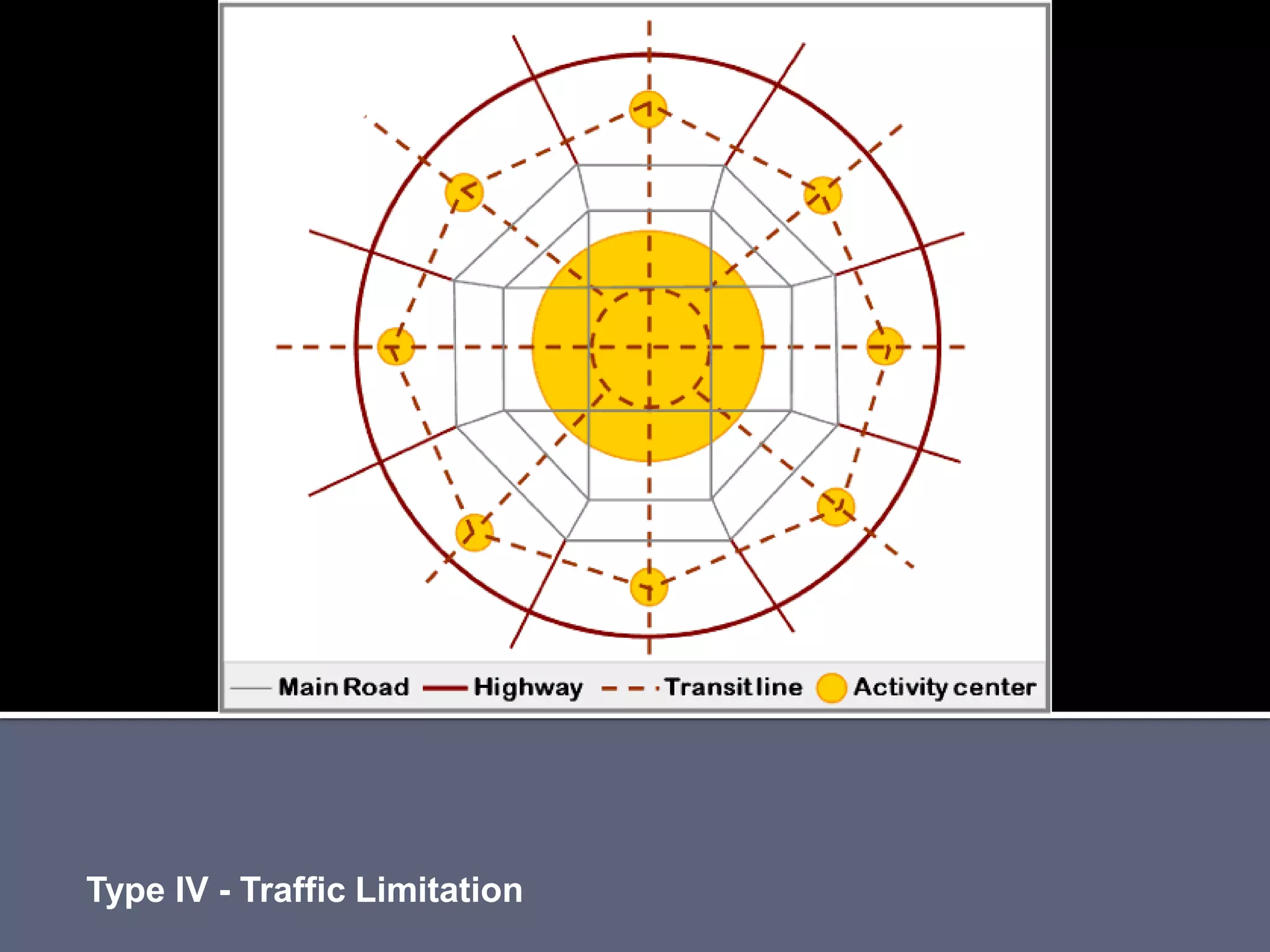
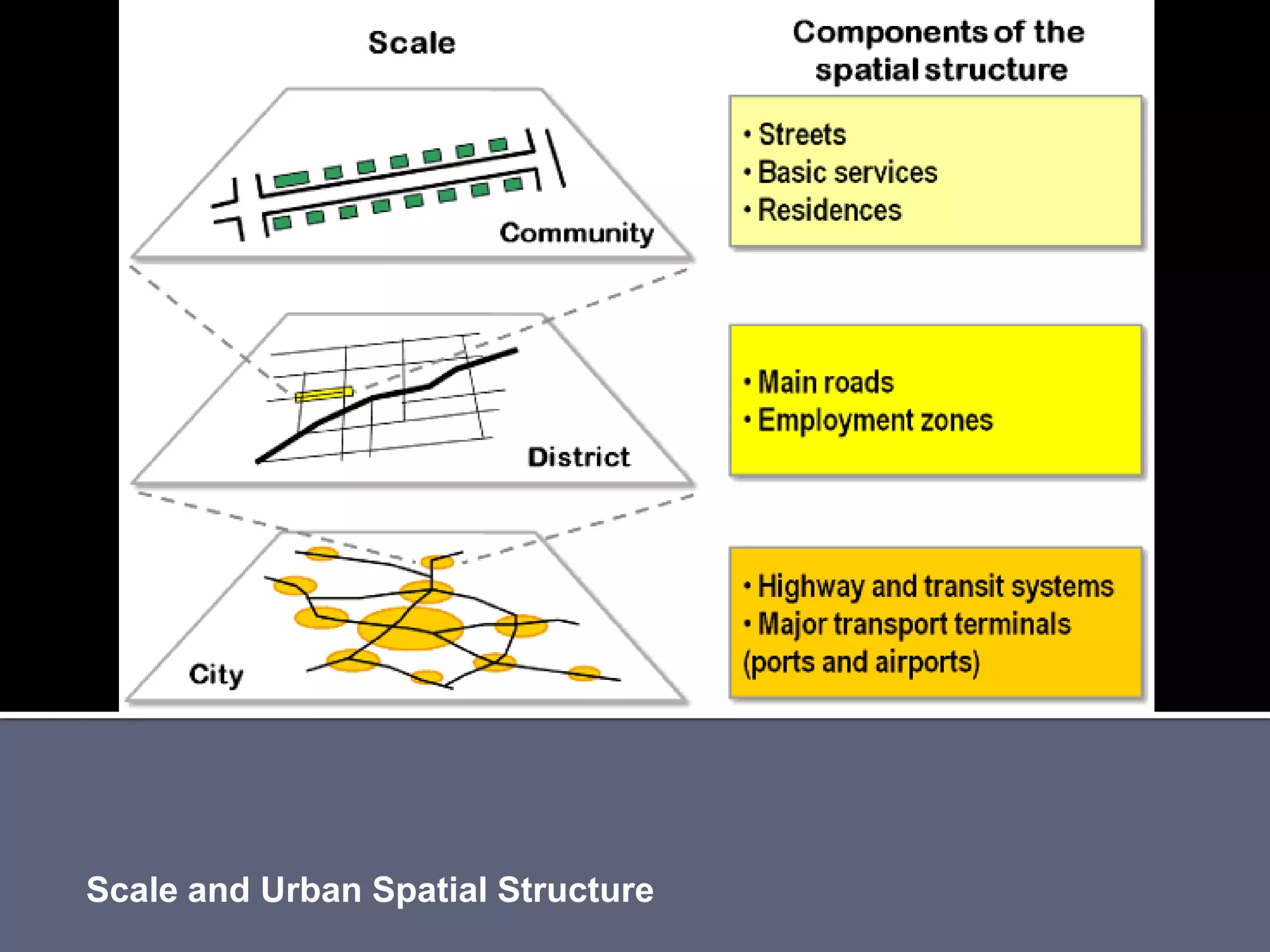
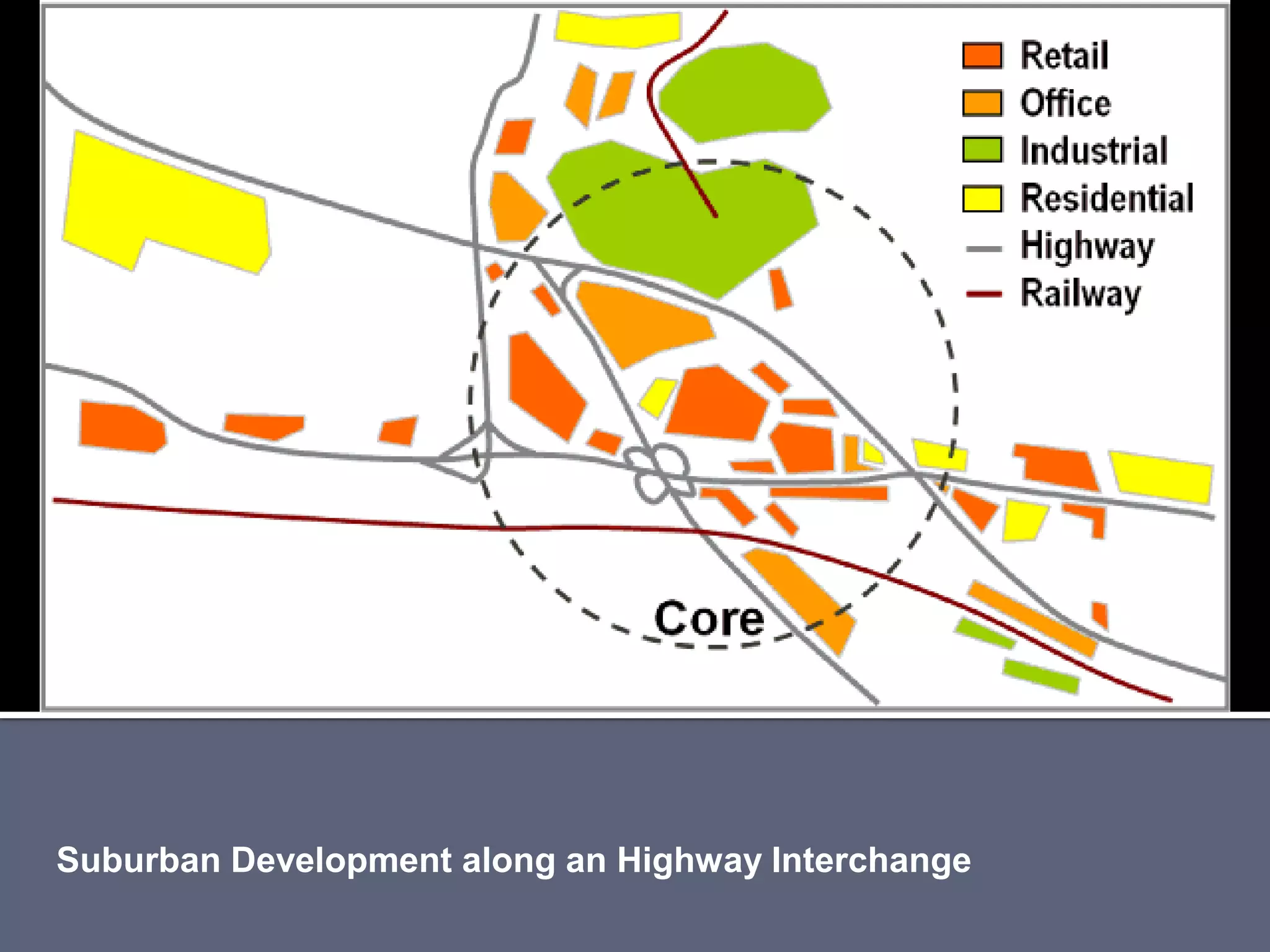
The document discusses energy consumption in the building and construction sector, with buildings accounting for 44% of energy consumption. It also shows graphs of vehicle miles traveled increasing dramatically in the US from 1960-2005 and discusses different models of urban transport and spatial structures like sprawling cities versus multi-polar centralized cities with public transportation as the focus. The document examines concepts like nodes, linkages and different types of urban movement patterns as cities evolve spatially over time.