Recommended
PPTX
Introduction to Transportation Engineering.pptx
PPT
Transport engineering copy
PPT
introduction to Transportation
PPT
0-introduction to elements of transportation
PPT
0-introduction how you are find them.ppt
PPT
giio shsgjgsh shghsgh hgshgsh gshgshghgshgs ggh
PPTX
Introduction_to_Transportation_Engineeri.pptx
PPT
PDF
PPTX
PPTX
Introduction to the Infra Projects in India
PPTX
Introduction to Transportation Engineering
PDF
kupdf.net_transportation-engineering-lrkadiyali.pdf
PPTX
Introduction Transportation
PPT
Highway And traffic Engineering
PPTX
Transportation Lecture 1.pptx
PDF
INTRODUCTION_TO_TRANSPORTATION_ENGINEERI.pdf
PDF
Transportation Engineering I
PDF
PPTX
transportation engineering introduction.pptx
PPTX
GROUP-1-CHAPTER-PRESENTATION-TRANSPORTATION
PPT
Introduction to Transportation Engineering_1.ppt
PDF
TRANSPORTATION_ENGINEERING_M1.pdf
PDF
Transportation Planning & Management
PPTX
Introduction to transport engg (3)
PPTX
PPT
Transportation Industry. What is Transportation?
PPTX
Transportation Engineering- Modes of Transport, Types of roads, Components of...
PPTX
FROM MEASUREMENT TO MEANING : Metrology-Driven Battery Testing for Reliable ...
PDF
God series - Physics video office crossed
More Related Content
PPTX
Introduction to Transportation Engineering.pptx
PPT
Transport engineering copy
PPT
introduction to Transportation
PPT
0-introduction to elements of transportation
PPT
0-introduction how you are find them.ppt
PPT
giio shsgjgsh shghsgh hgshgsh gshgshghgshgs ggh
PPTX
Introduction_to_Transportation_Engineeri.pptx
PPT
Similar to Transportation_Engineering_Planning_Designed (1).pptx
PDF
PPTX
PPTX
Introduction to the Infra Projects in India
PPTX
Introduction to Transportation Engineering
PDF
kupdf.net_transportation-engineering-lrkadiyali.pdf
PPTX
Introduction Transportation
PPT
Highway And traffic Engineering
PPTX
Transportation Lecture 1.pptx
PDF
INTRODUCTION_TO_TRANSPORTATION_ENGINEERI.pdf
PDF
Transportation Engineering I
PDF
PPTX
transportation engineering introduction.pptx
PPTX
GROUP-1-CHAPTER-PRESENTATION-TRANSPORTATION
PPT
Introduction to Transportation Engineering_1.ppt
PDF
TRANSPORTATION_ENGINEERING_M1.pdf
PDF
Transportation Planning & Management
PPTX
Introduction to transport engg (3)
PPTX
PPT
Transportation Industry. What is Transportation?
PPTX
Transportation Engineering- Modes of Transport, Types of roads, Components of...
Recently uploaded
PPTX
FROM MEASUREMENT TO MEANING : Metrology-Driven Battery Testing for Reliable ...
PDF
God series - Physics video office crossed
PPTX
Applications of cloud computing in education
PDF
A Newbie’s Journey: Hidden MySQL Pain Points That Vitess Quietly Solves
PPTX
Unit-2: Network Models--OSI Reference Model, TCP/IP Reference Model
PDF
5.5 Inch 4K TFT LCD Display 3840×2160 UHD Panel – LS055D1SX05(G)
PDF
EDIH TRAINING AI FOR COMPANIES: MODULE 4
PDF
Chip Designer's Code - Linux Terminal Part 6 - Text Viewers
PPTX
CHAPTER 13 - NUCLEI - CLASS XII PHYSICS 2025-26
PPTX
Tips for Designing Flex Circuits for Medical Applications
PDF
Mahabir - Structural Steel Brochure - 2025
PDF
FPGA Fabric and Synthesis All Parts Combined
PDF
JVM in the Age of AI: 2026 Edition - Deep Dive
PPTX
Explore how AI-powered maintenance checklists transform asset reliability and...
PDF
Chip Designer's Code - Linux Terminal Part 7.1 - Text Processing
PDF
TechRush Hackathon 2026: A Platform for Innovation, Learning, and Real-World ...
PDF
PROBLEM SLOVING AND PYTHON PROGRAMMING UNIT 2.pdf
PPTX
Filtration-slow sand filtration and rapid sand filtration.pptx
PPT
psoc_unit_one_for_all_thoery_potion_are_coverd_in_the_this_unit_for_everything
PDF
TRUSTWORTHY AI: BUILDING SAFE AND ETHICAL MACHINE LEARNING SYSTEMS
Transportation_Engineering_Planning_Designed (1).pptx 1. 2. What is Transportation?
• Movement of goods and people from one place to another
• Safe, efficient, reliable, and sustainable movement over time and space
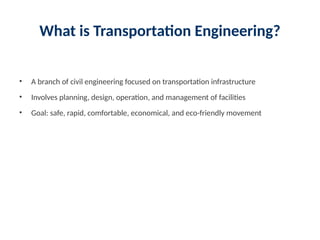
3. What is Transportation Engineering?
• A branch of civil engineering focused on transportation infrastructure
• Involves planning, design, operation, and management of facilities
• Goal: safe, rapid, comfortable, economical, and eco-friendly movement
4. Characteristics of Transportation Systems
• Multi-modal: air, land, sea
• Multi-sector: government, private, public
• Multi-problem: policy, planning, management
• Multi-objective: economic, environmental, social goals
• Multi-disciplinary: engineering, economics, law, social sciences
5. History of Transportation
• From walking to use of animals, wheel, roads
• Development of roads and transport technologies over time
• Role of transportation in urbanization and civilization growth
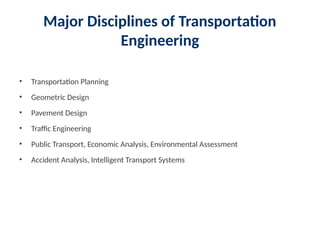
6. Major Disciplines of Transportation
Engineering
• Transportation Planning
• Geometric Design
• Pavement Design
• Traffic Engineering
• Public Transport, Economic Analysis, Environmental Assessment
• Accident Analysis, Intelligent Transport Systems
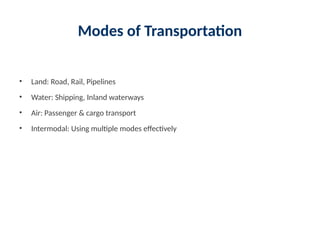
7. Modes of Transportation
• Land: Road, Rail, Pipelines
• Water: Shipping, Inland waterways
• Air: Passenger & cargo transport
• Intermodal: Using multiple modes effectively
8. Transportation System Components
• Fixed facilities: roads, railways, ports, airports
• Flow entities: vehicles, trains, aircraft, ships
• Control systems: traffic lights, ATC, road signs
9. Role of Transportation in Society
• Economic: supports production, distribution, consumption
• Social: connects rural & urban, cultural exchange
• Political: links political units, supports governance
• Environmental: pollution, safety concerns
10. Historical Development of Roads
• Roman Roads: durable, drainage-focused
• Tresaguet Roads: compact stone layers
• Telford Construction: graded stone sizes
• Macadam Roads: interlocked stones
• Modern Roads: asphalt, concrete, advanced tech
11. Transportation Planning
• Short, Medium, Long-term planning
• System approach: analysis, engineering, decision-making
• Consider demand, economic, social, environmental factors
12. Objectives of Road Planning
• Establish integrated road networks
• Fulfill societal needs
• National, urban road network planning
• Patterns: Grid Iron, Radial, Ring Roads
13. Classification of Roads (Nepal)
• Administrative: National Highways, Feeder, District, Urban Roads
• Technical: Based on design speed & traffic volume
• Managed by DoR & DOLIDAR