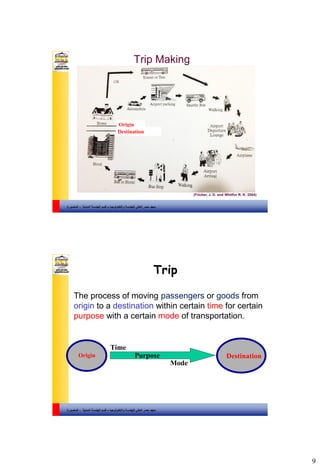
This document appears to be lecture slides for a transportation and traffic engineering course. It includes definitions of transportation engineering and traffic engineering. It outlines the course contents which cover topics like transportation planning, traffic flow characteristics, highway geometric design, and traffic control devices. It also defines key concepts like trips, transportation systems, land use and its relationship to transportation, and highway functional classification. The overall aim of the course is to introduce students to the fundamentals and principles of transportation and traffic engineering.