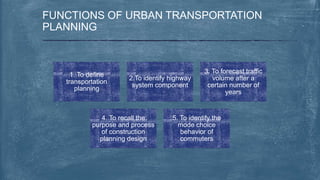
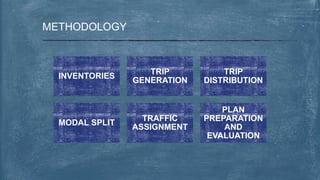
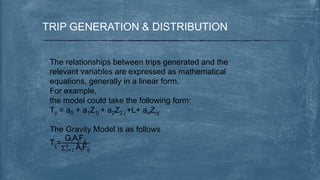
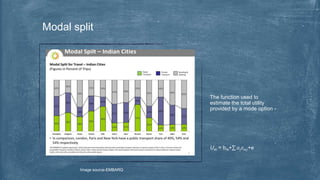
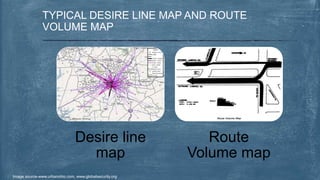
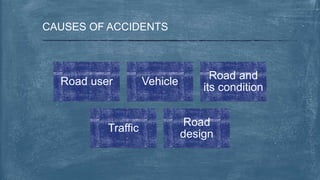
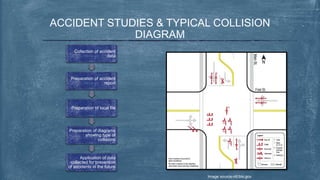
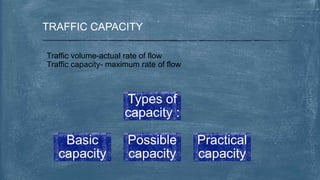
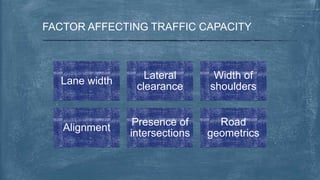
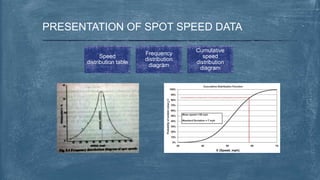
This document discusses various topics related to transportation planning. It includes sections on traffic flow characteristics, accident studies, traffic volume studies, speed studies, frequently asked questions, functions, methodology, origin-destination studies, and parking studies. The methodology section outlines the process of transportation planning which includes inventories, trip generation, trip distribution, modal split, traffic assignment, and plan preparation and evaluation. Other topics covered in detail include trip generation and distribution models, origin-destination studies methods, causes of accidents, factors affecting traffic capacity, and types of speed studies.