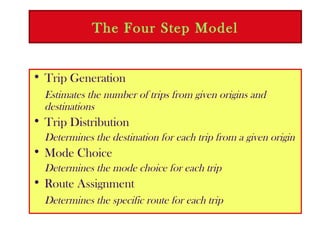
Transportation forecasting uses a four step model to estimate future travel demand:
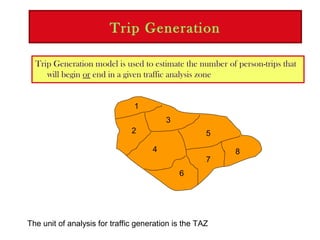
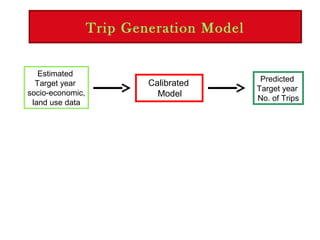
1) Trip generation estimates the number of trips originating and ending in each traffic analysis zone based on socioeconomic and land use data.
2) Trip distribution determines trip destinations from origins.
3) Mode choice identifies the transportation mode for each trip.
4) Route assignment specifies the routes for each trip.
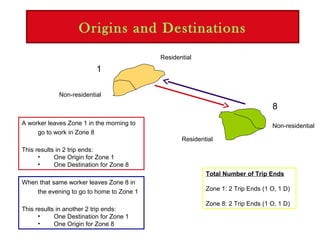
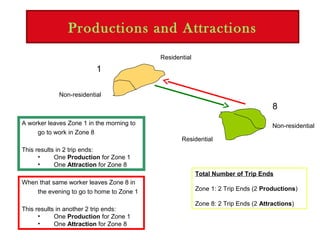
Trip generation models predict trip "ends" as either origins and destinations, with origins at residential zones and destinations at non-residential zones, or as productions at residential zones and attractions at non-residential zones.