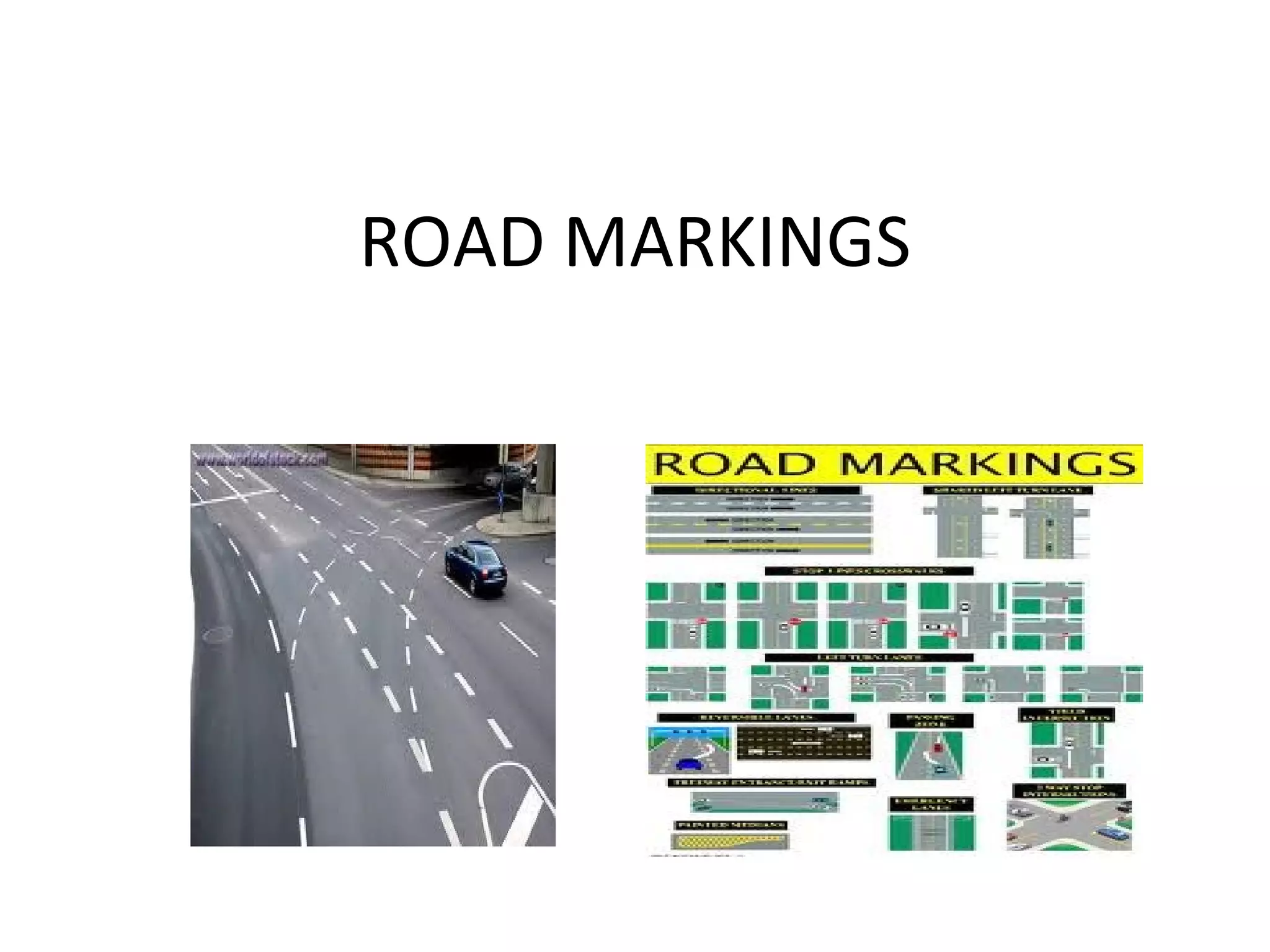
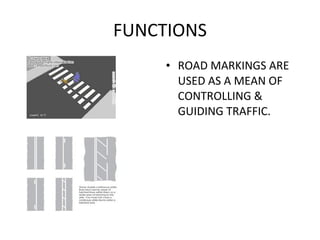
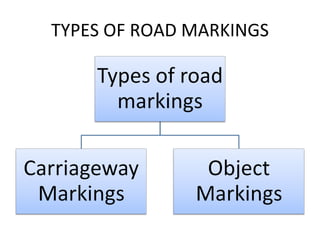
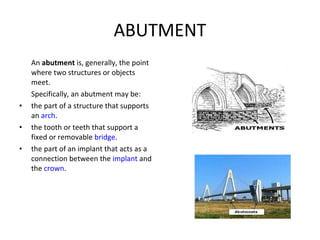
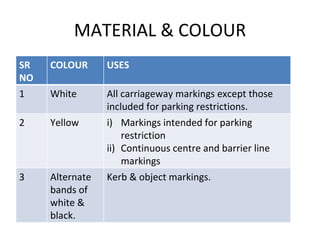
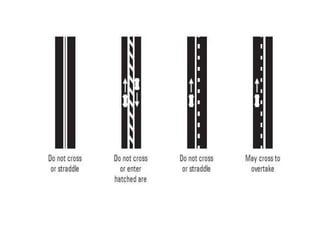
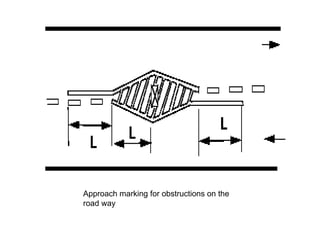
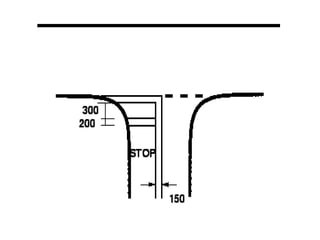
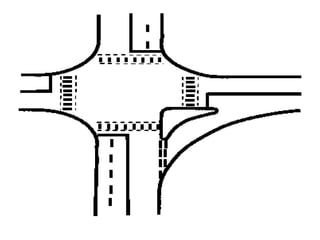
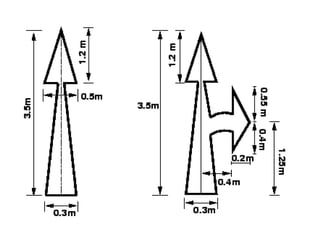
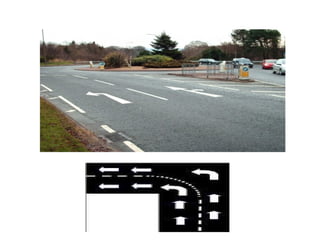
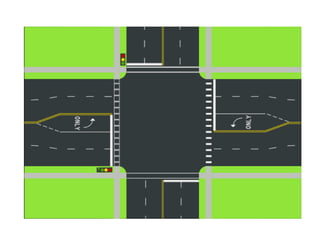
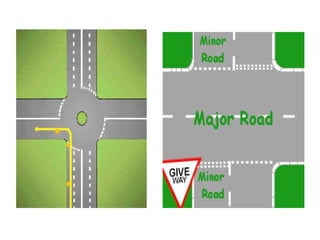
Road markings function to control and guide traffic. There are different types of road markings including carriageway markings, object markings, and kerbs. Carriageway markings are applied to roadways while object markings are used to mark features like traffic islands, culverts, piers, and abutments. Kerbs define the edge of roads and pathways.