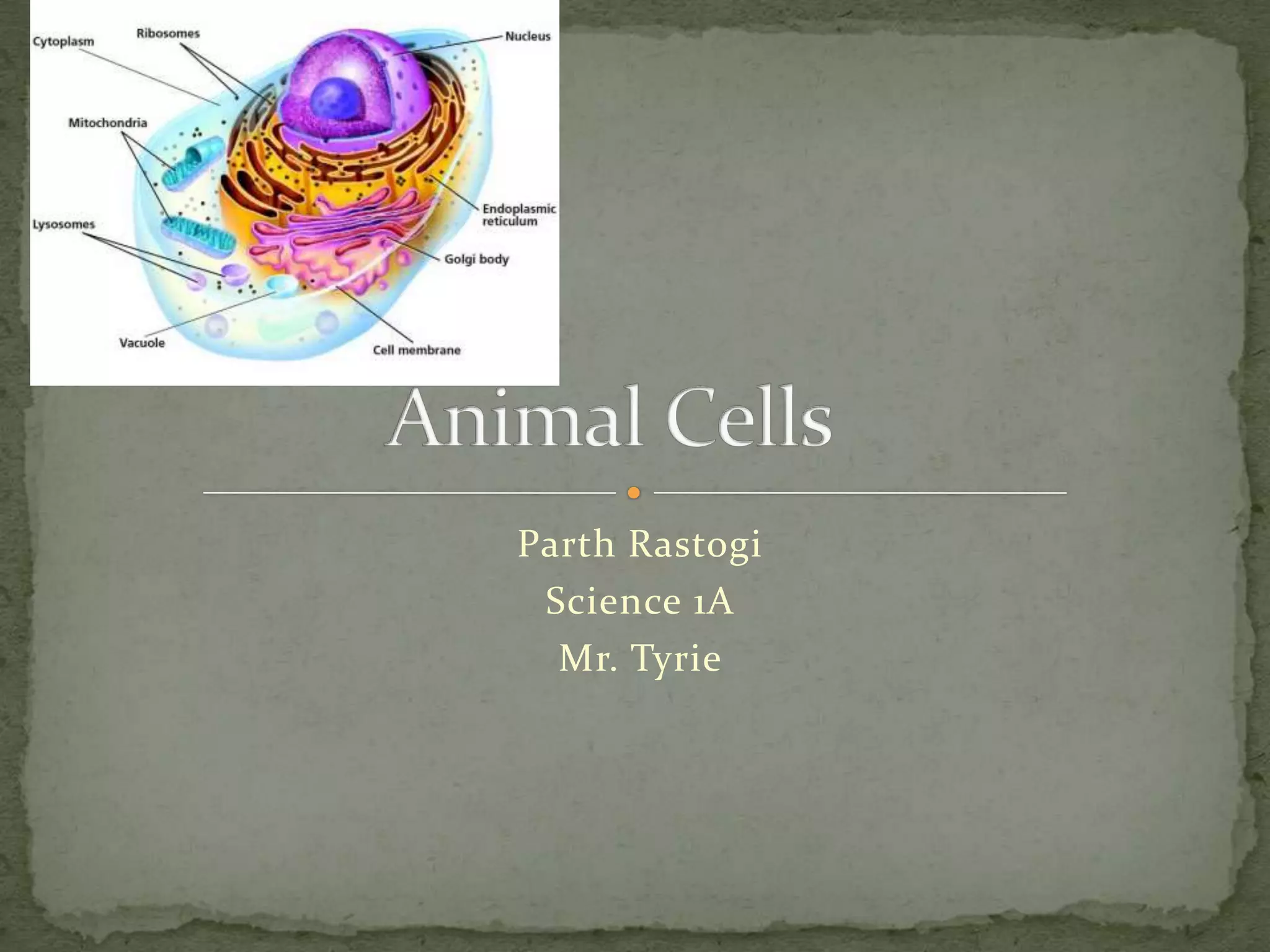
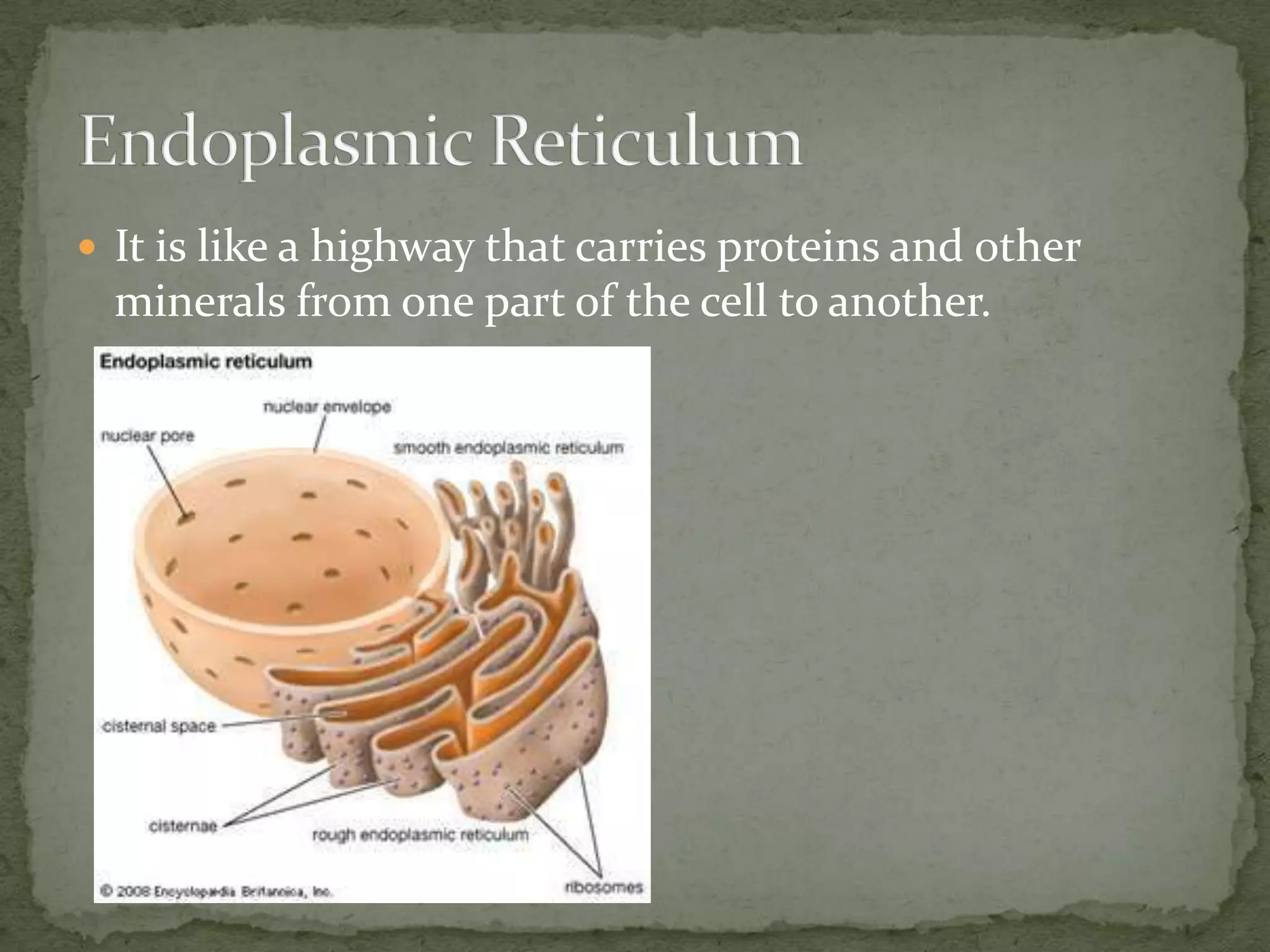
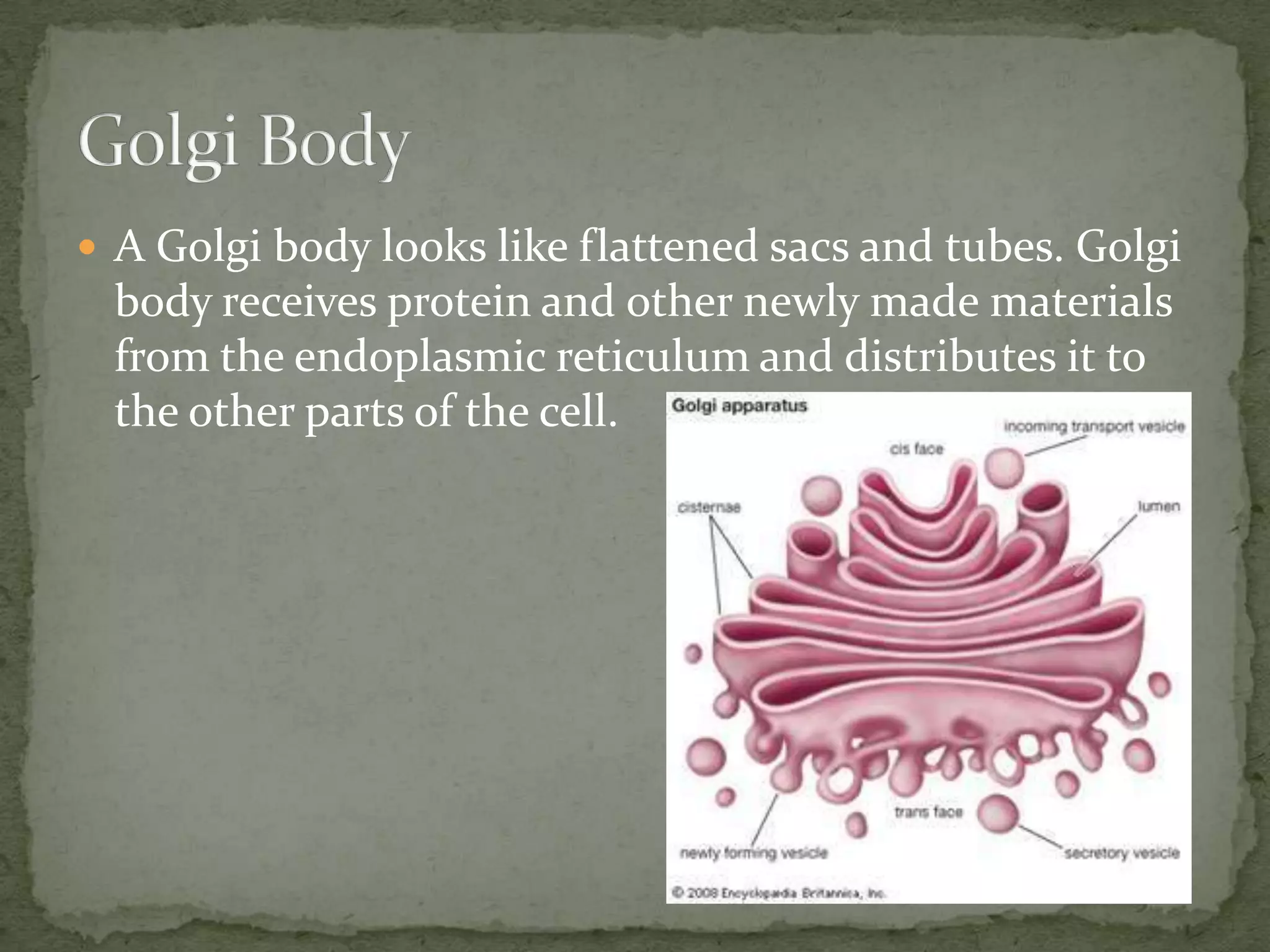
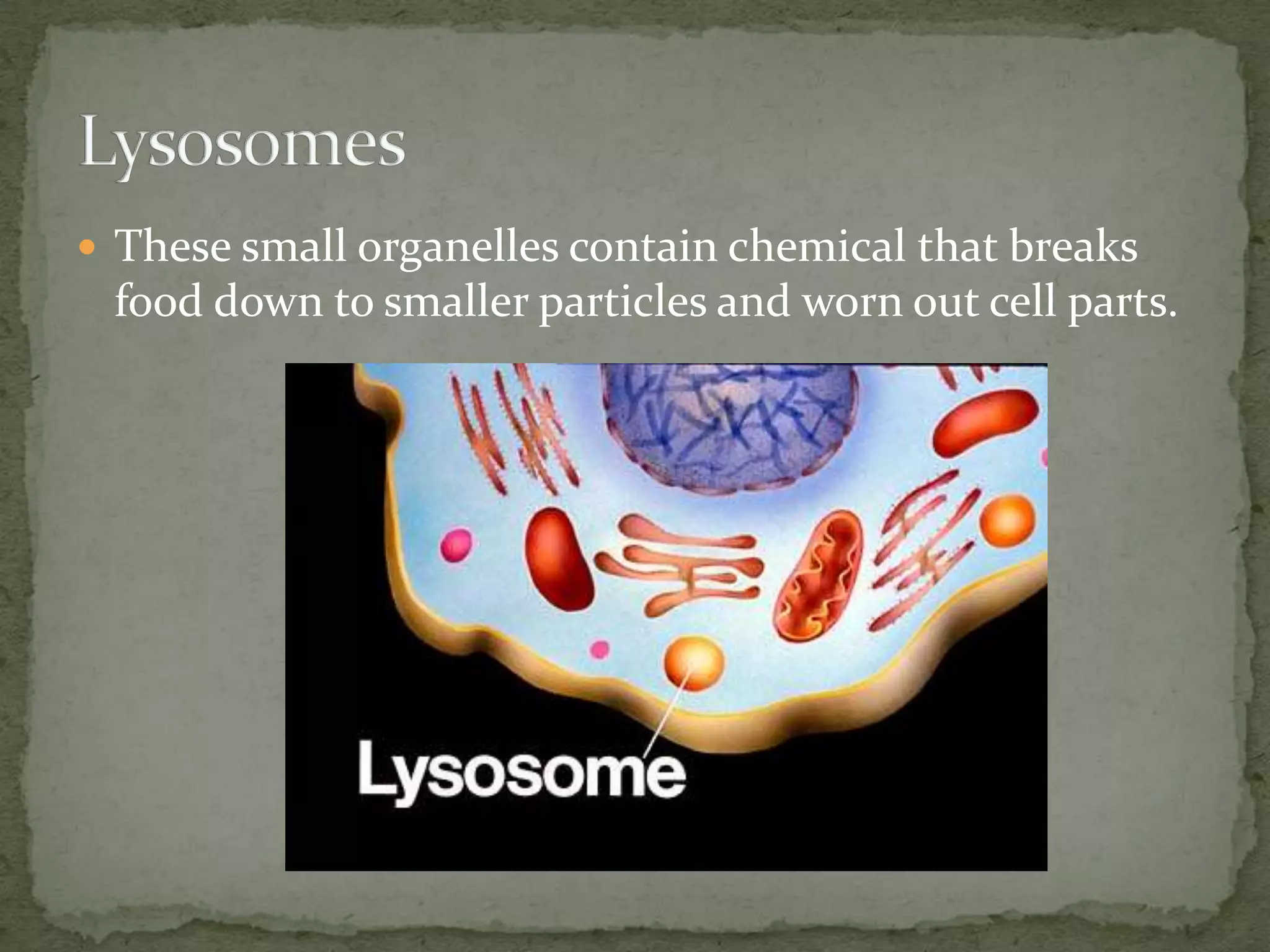
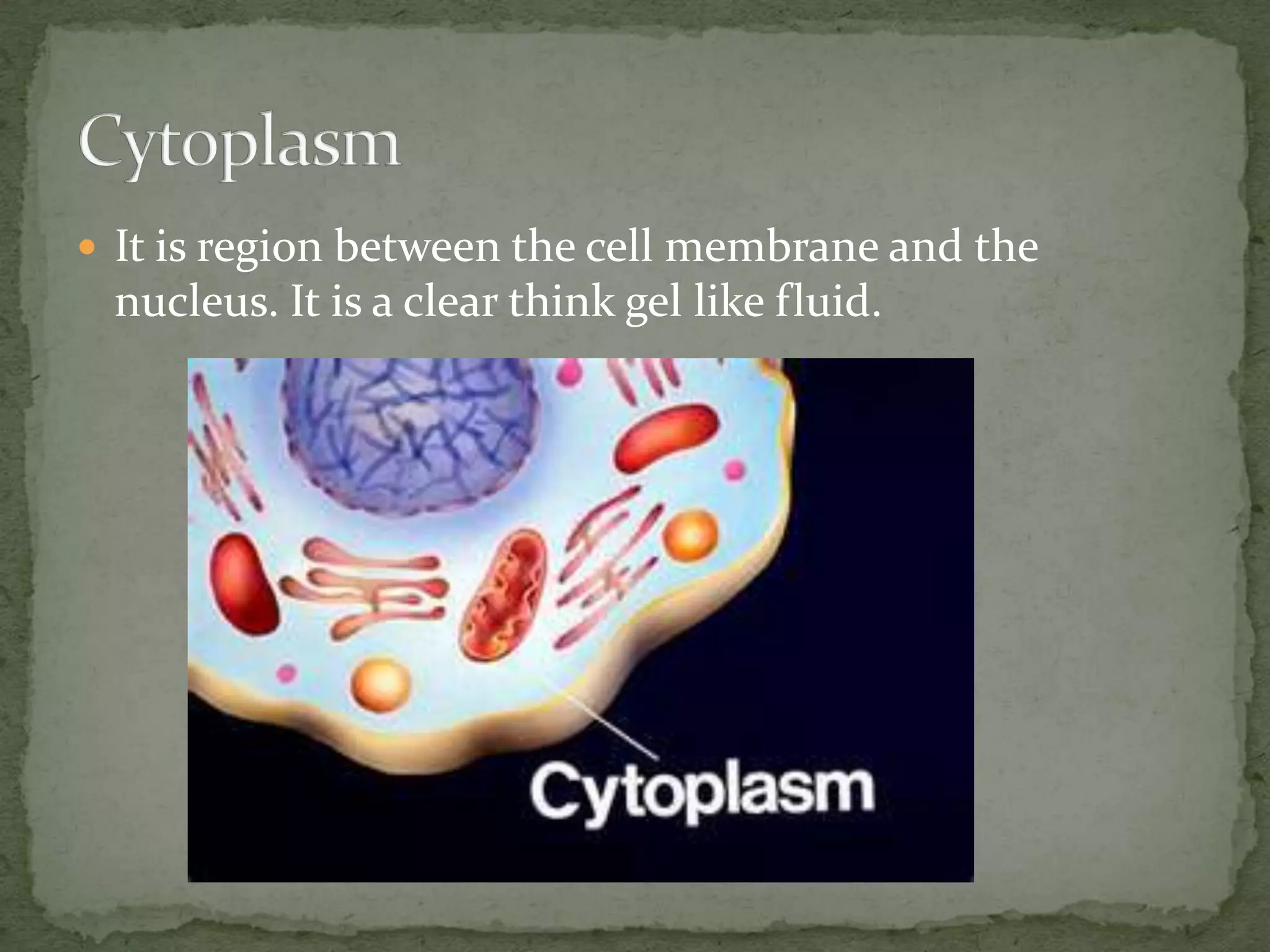
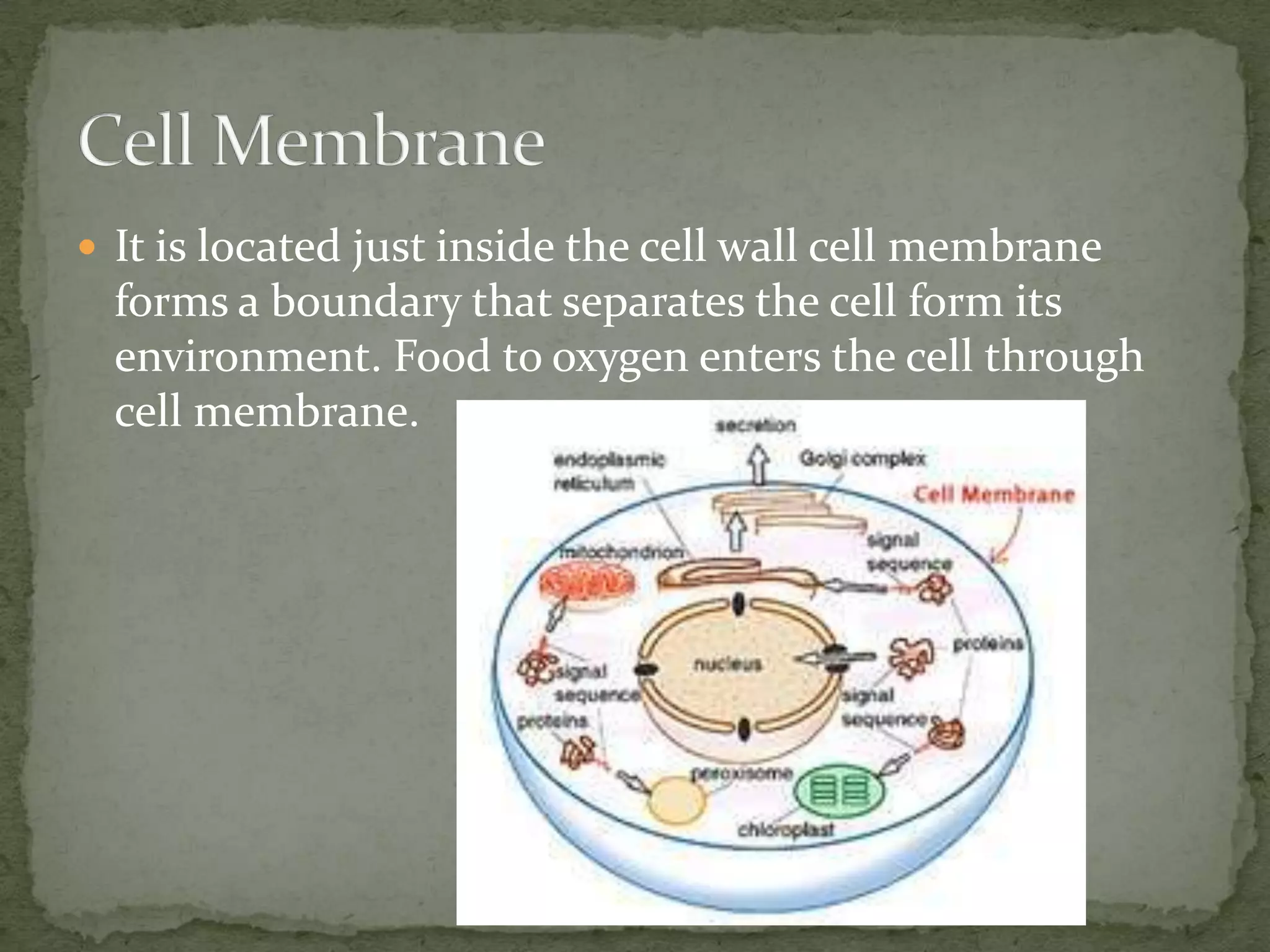
The document discusses the key organelles of an animal cell including the nucleus, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi body, vacuole, lysosomes, cytoplasm, mitochondria, and cell membrane. The nucleus controls all cellular activity and contains chromatin, nucleolus, and a nuclear envelope. Ribosomes produce proteins and are located on the endoplasmic reticulum, which transports proteins and minerals within the cell. The Golgi body receives and distributes proteins and materials. The vacuole stores materials, and lysosomes break down food and cell parts. The cytoplasm and mitochondria provide structure and energy to the cell, while the cell membrane regulates what enters and exits.