Embed presentation
Download to read offline




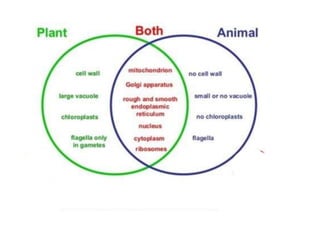




The document discusses the basic components and structures of cells. It defines cells as the fundamental unit of life and outlines several major developments in cell theory over time. The document then describes key cellular structures such as the nucleus, cytoplasm, organelles like mitochondria and lysosomes, and differences in cell size, shape, and components between plant and animal cells. It provides details on the functions of various organelles and cellular components.









