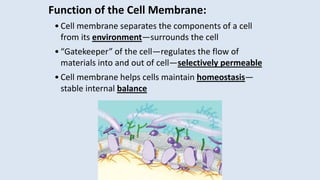
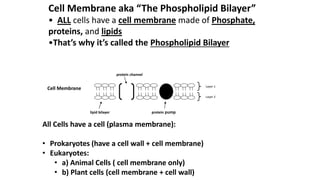
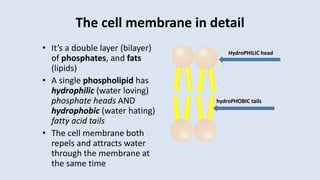
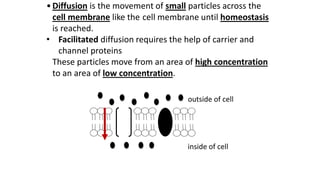
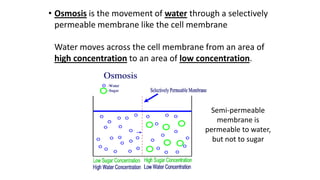
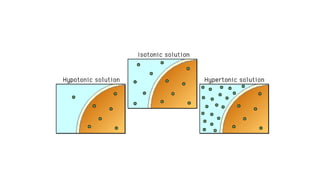
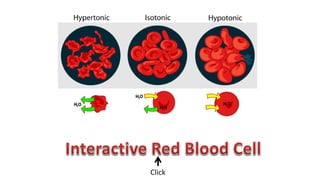
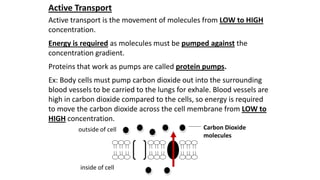
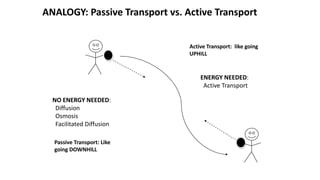
The cell membrane separates a cell from its environment and regulates what passes in and out through selective permeability. It helps maintain homeostasis through balancing pH, temperature, glucose, and water levels using both passive and active transport. Passive transport moves molecules down their concentration gradient without energy, through diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis. Active transport moves molecules against their gradient by using protein pumps and requires energy from ATP.