Here is a draft paragraph you could write as a cell:
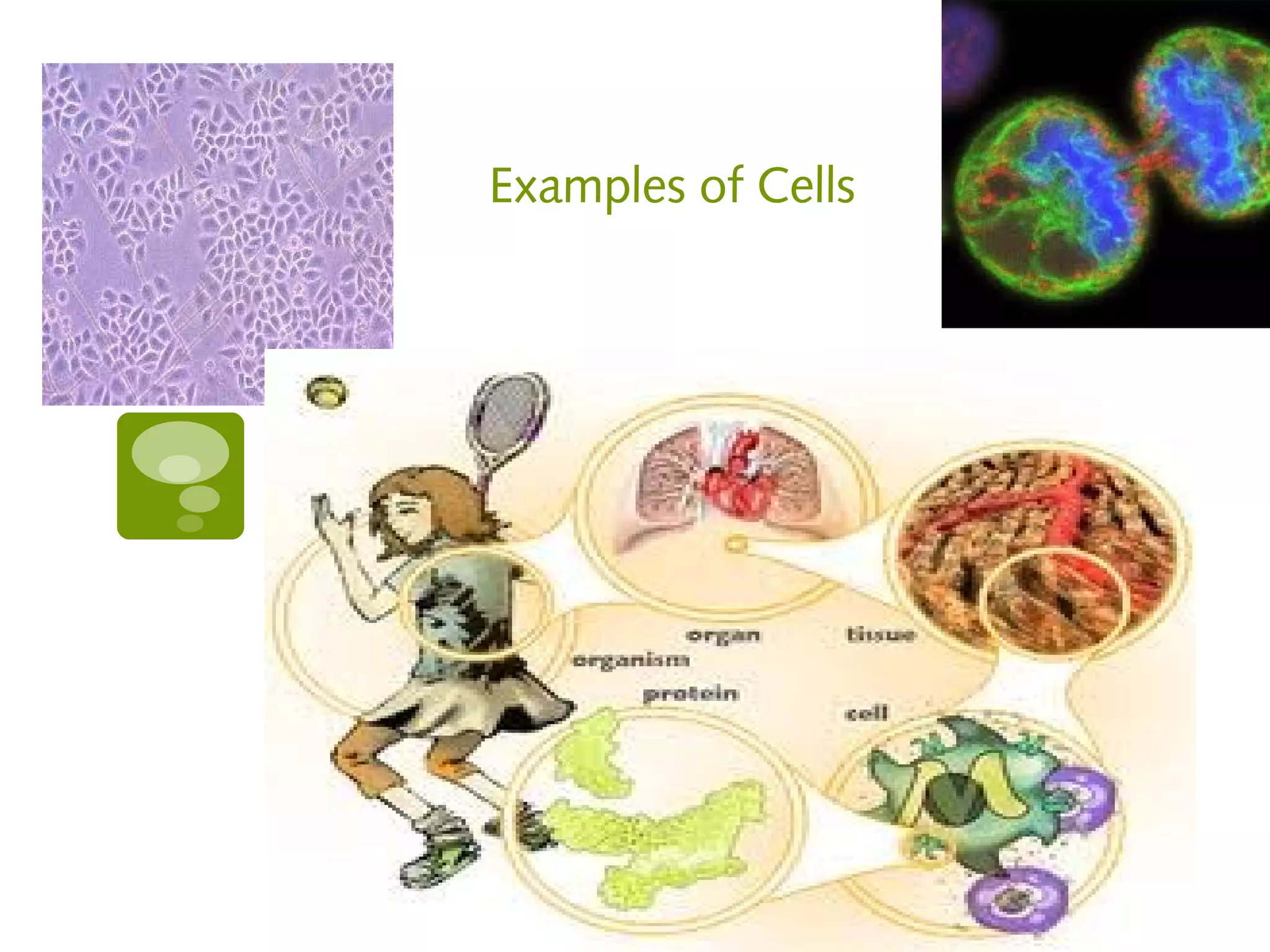
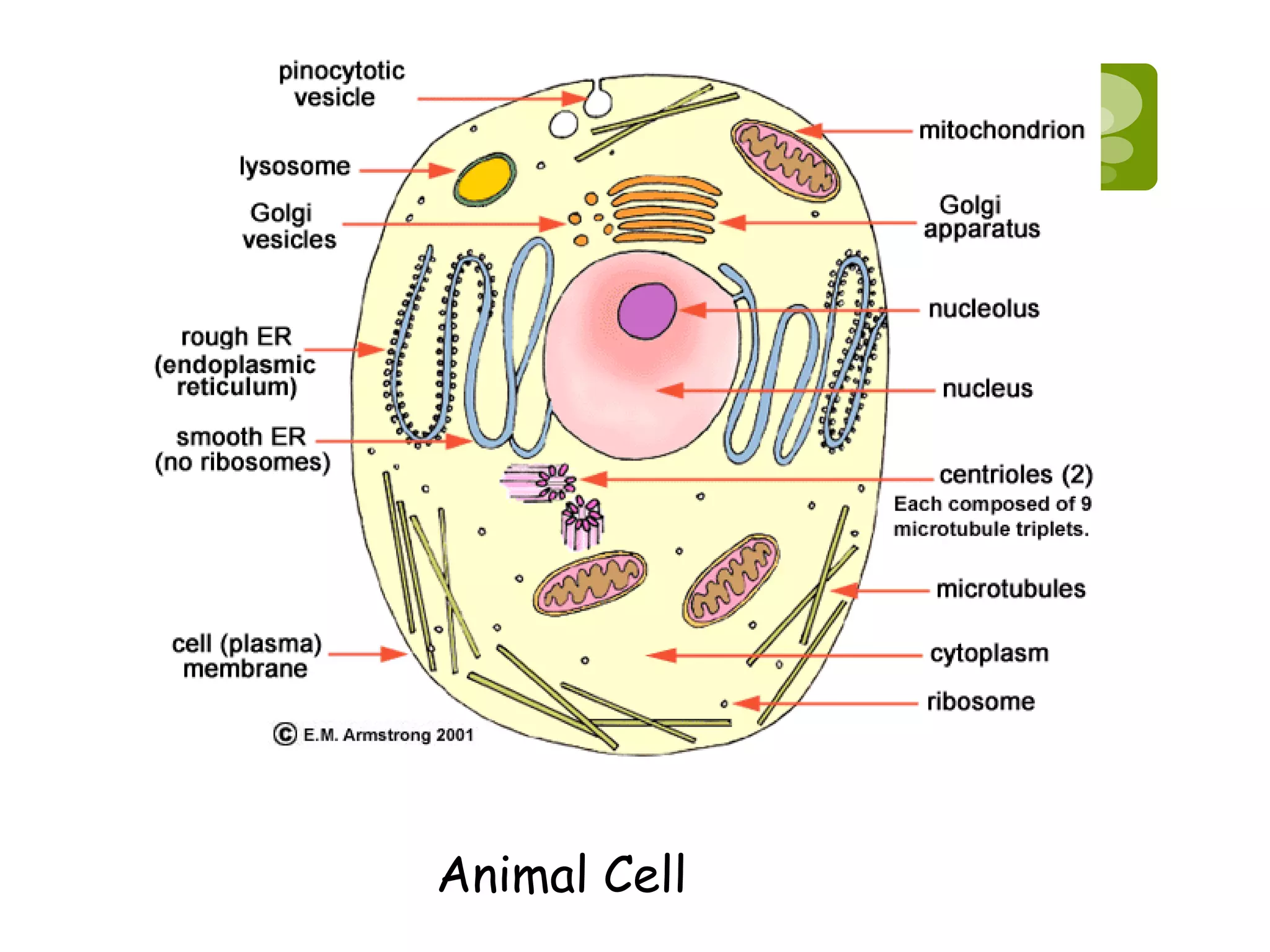
As a cell, I am the basic unit of structure and function that makes up complex organisms. Cells come together to form tissues, which then make up organs. Groups of organs working together are called organ systems. There are two main types of organisms - unicellular organisms that are single cells, and multicellular organisms made of many cells like humans. I am produced through cell division, where my parent cell divides into two new daughter cells. My main structures include a cell membrane that encloses my cytoplasm, a nucleus that controls my functions, mitochondria that provide me energy, and a vacuole for storage. Together with other cells, I form the basic tissues, organs