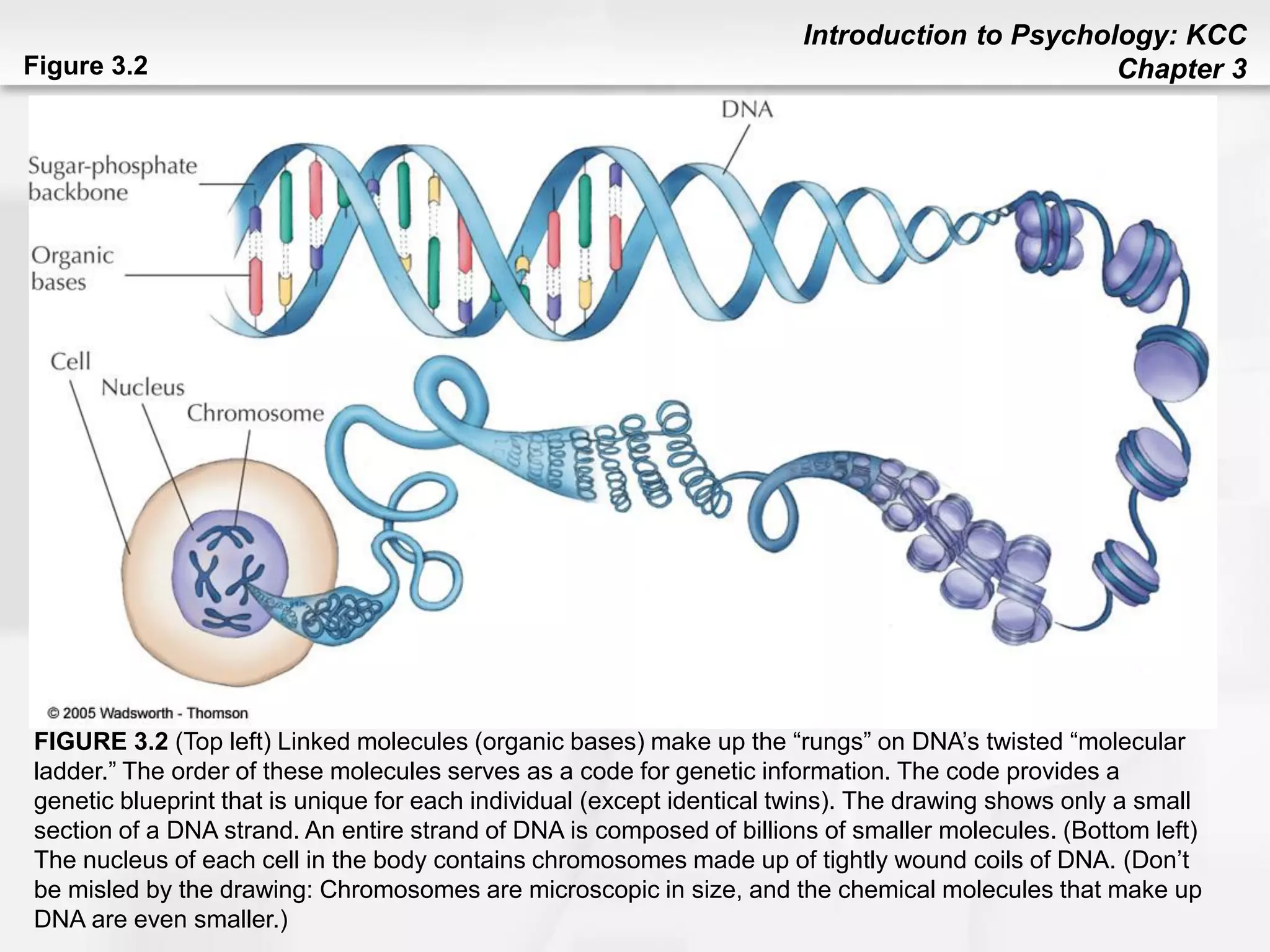
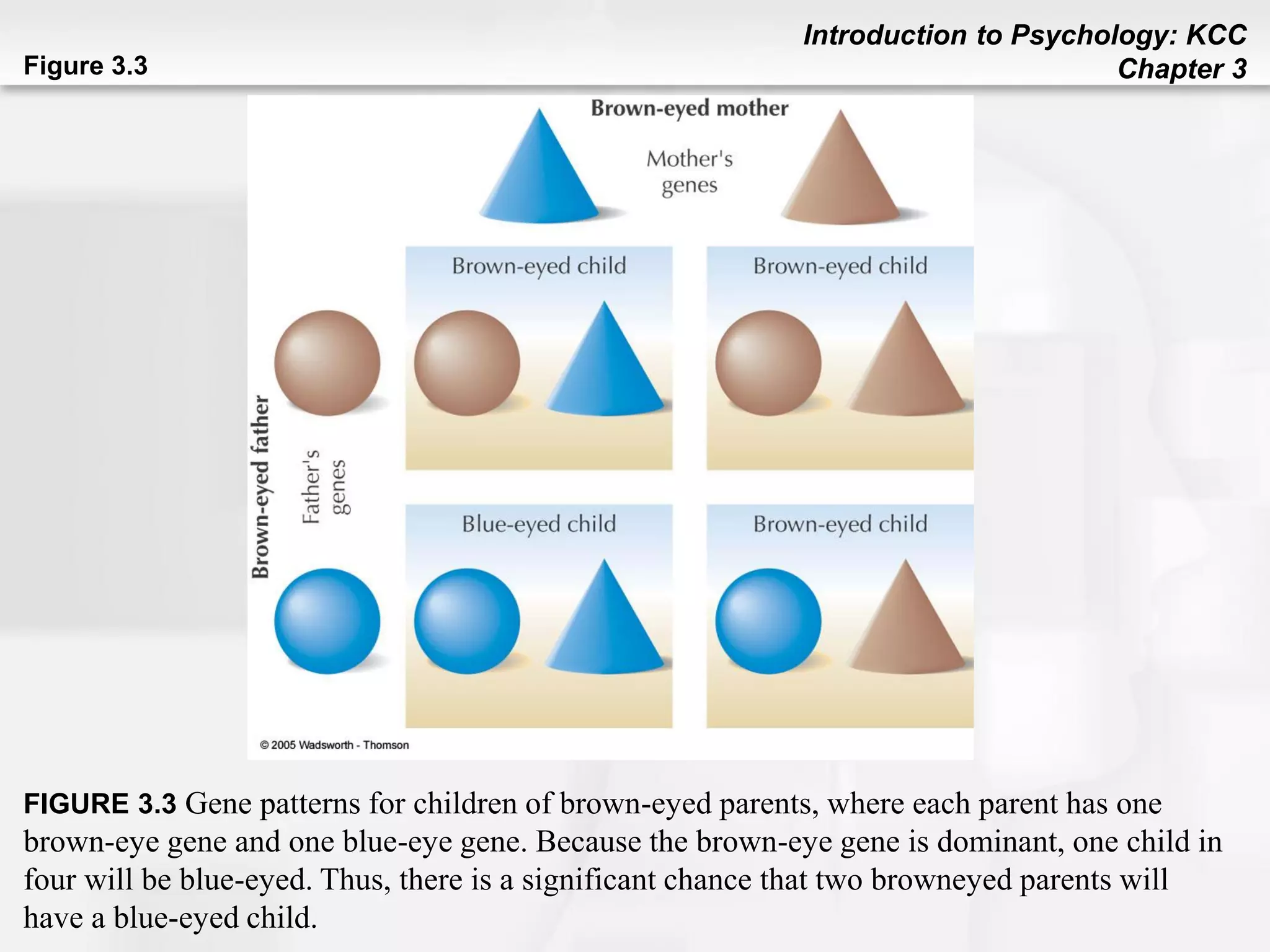
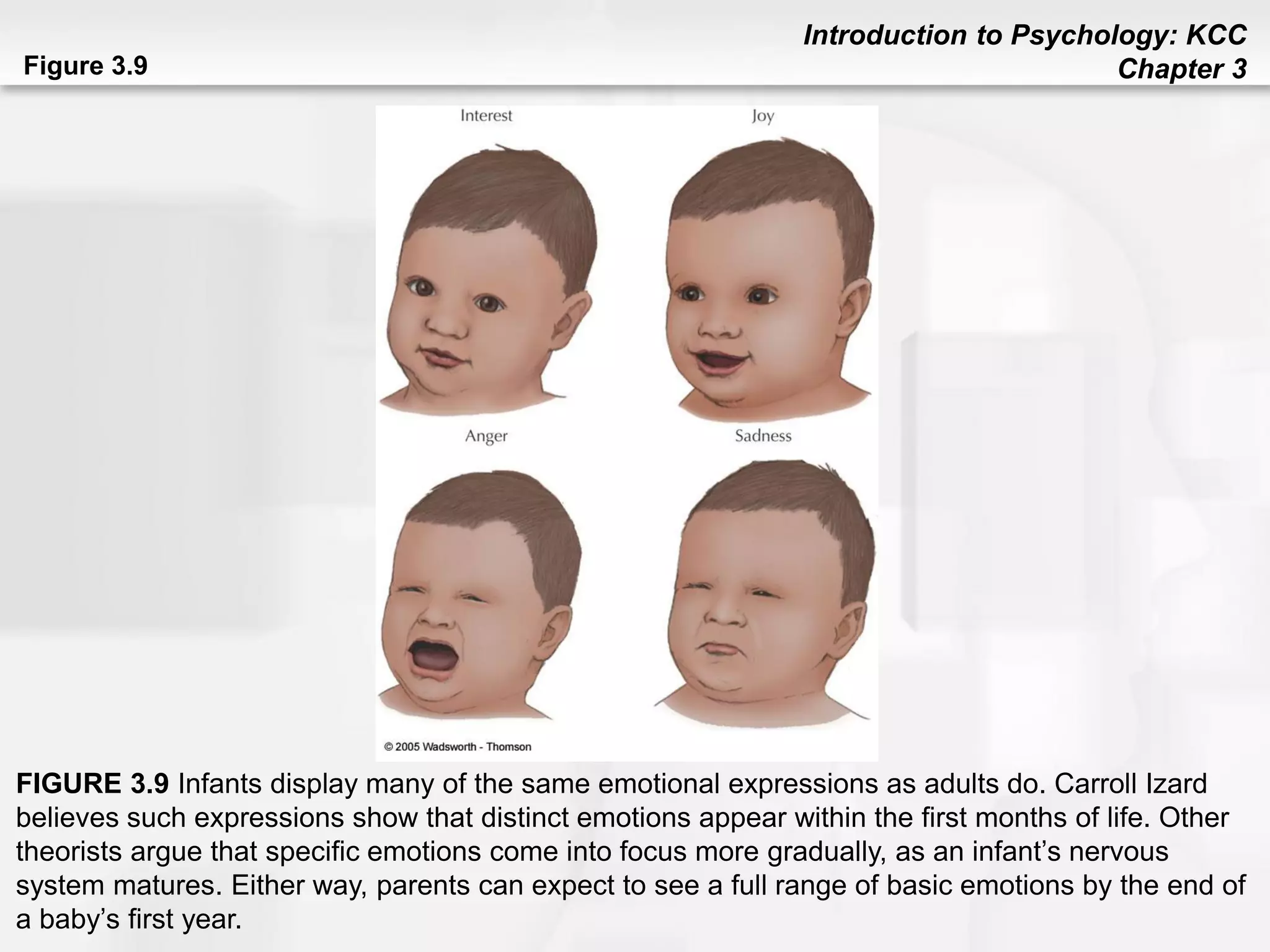
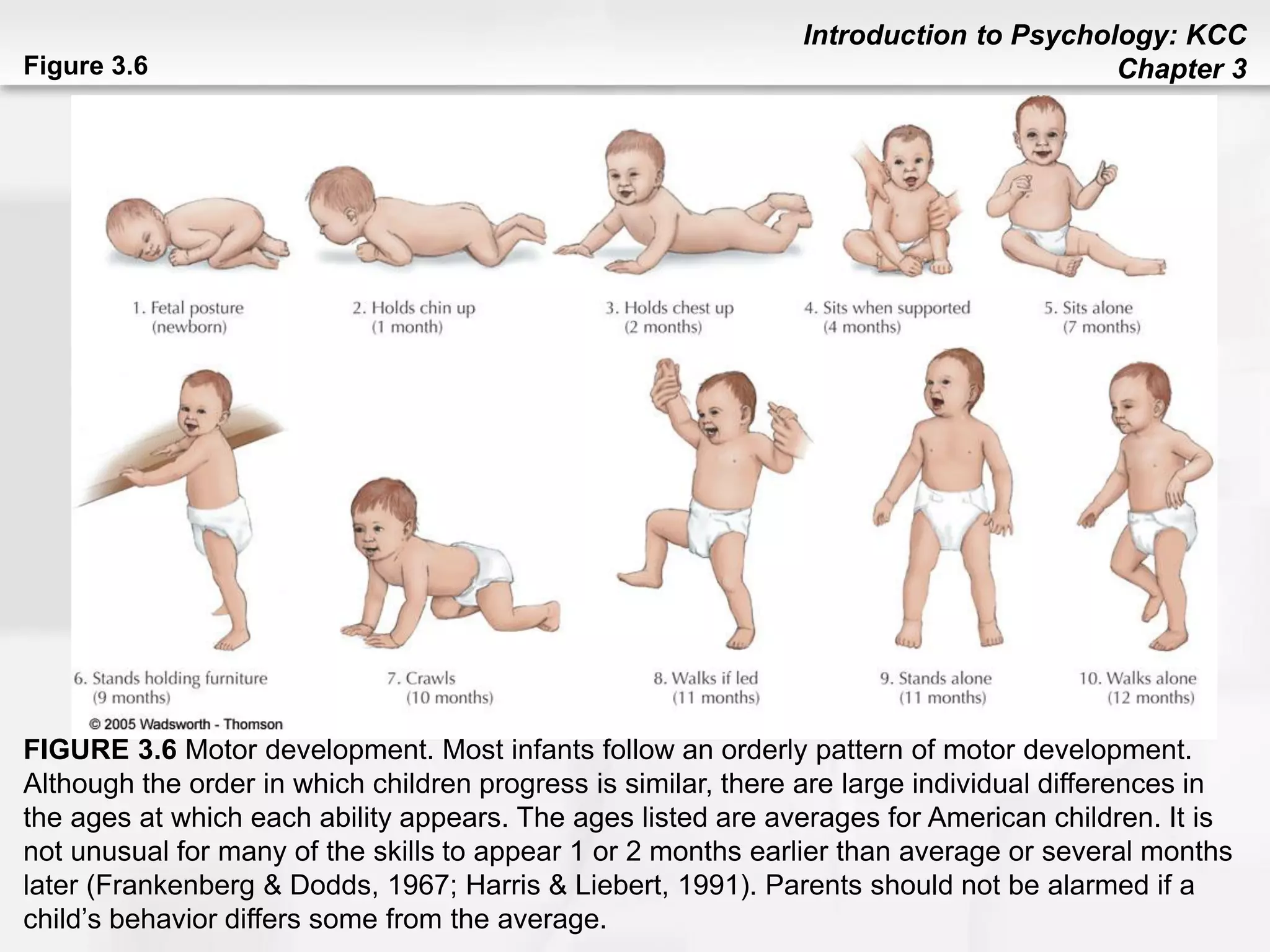
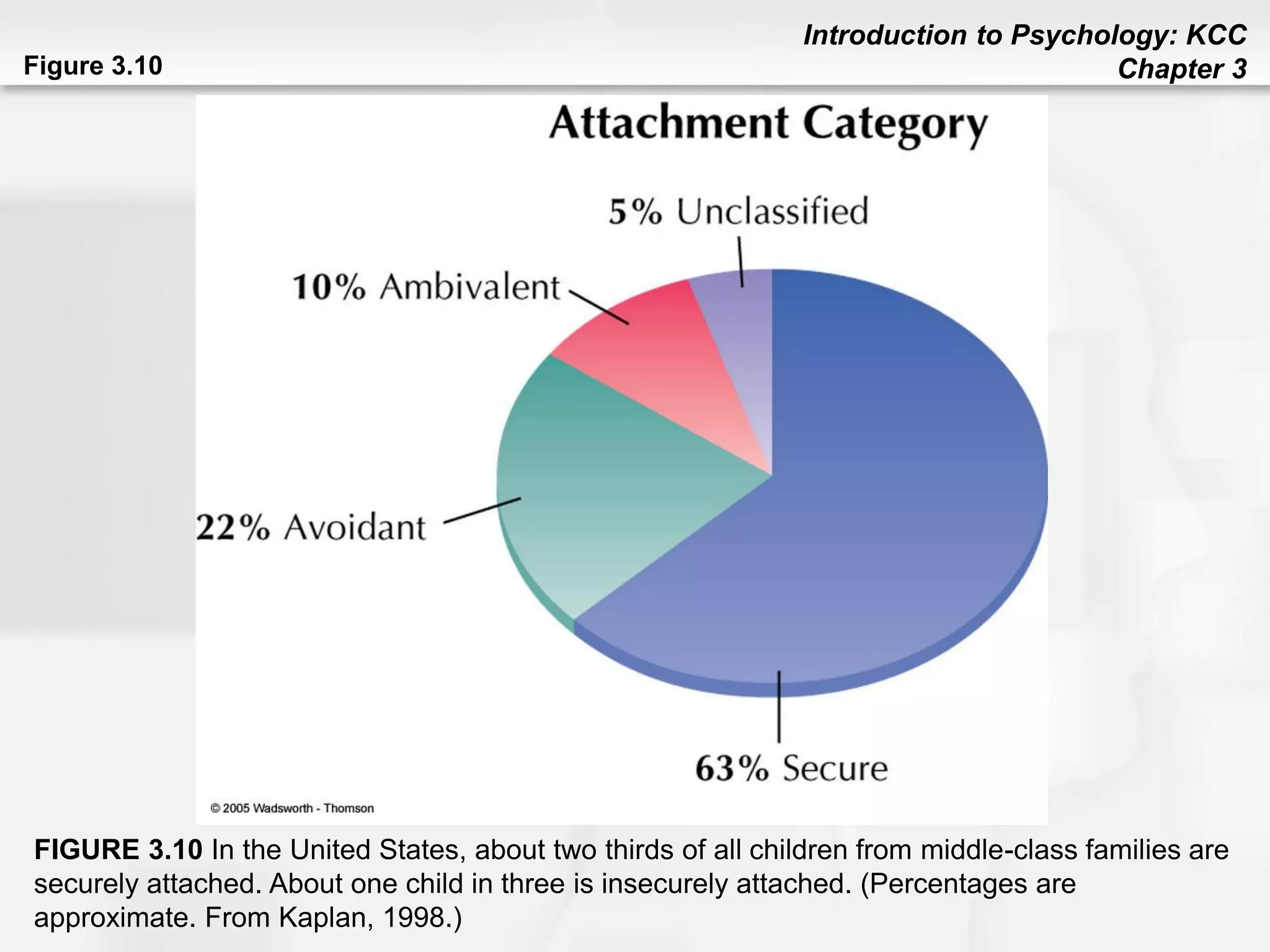
This chapter discusses human development from conception through death. It covers heredity and genes, noting that traits are transmitted from parents to children through DNA located on chromosomes. Prenatal development and factors affecting it like temperament, environment, and teratogens are addressed. Stages of child development are outlined, including physical, cognitive, language, social/emotional, and moral development. Theories of development from theorists like Piaget, Erikson, Kohlberg, Chomsky, and Ainsworth are summarized. The chapter concludes with topics like aging, cognitive changes, and end of life processes.