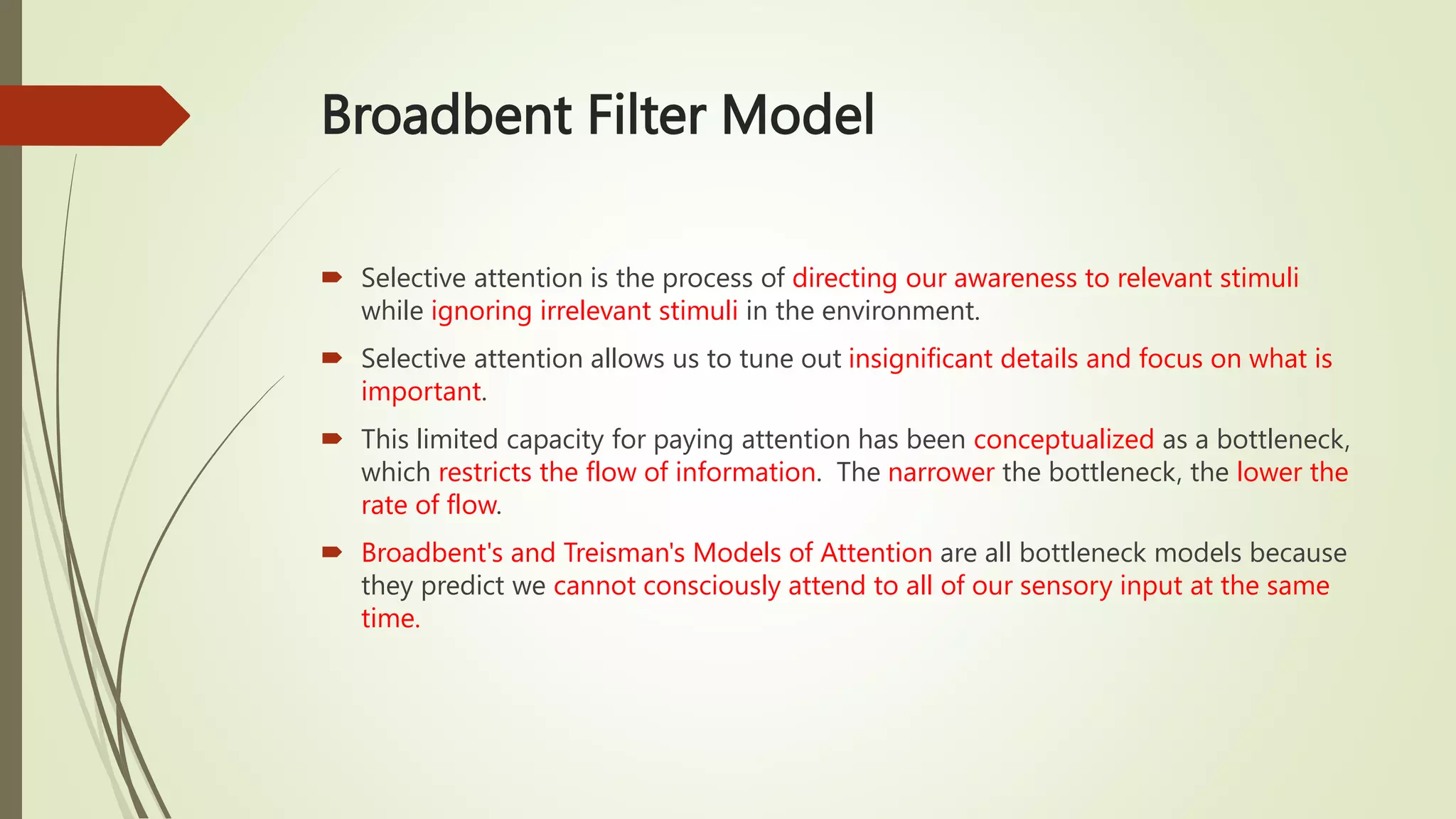
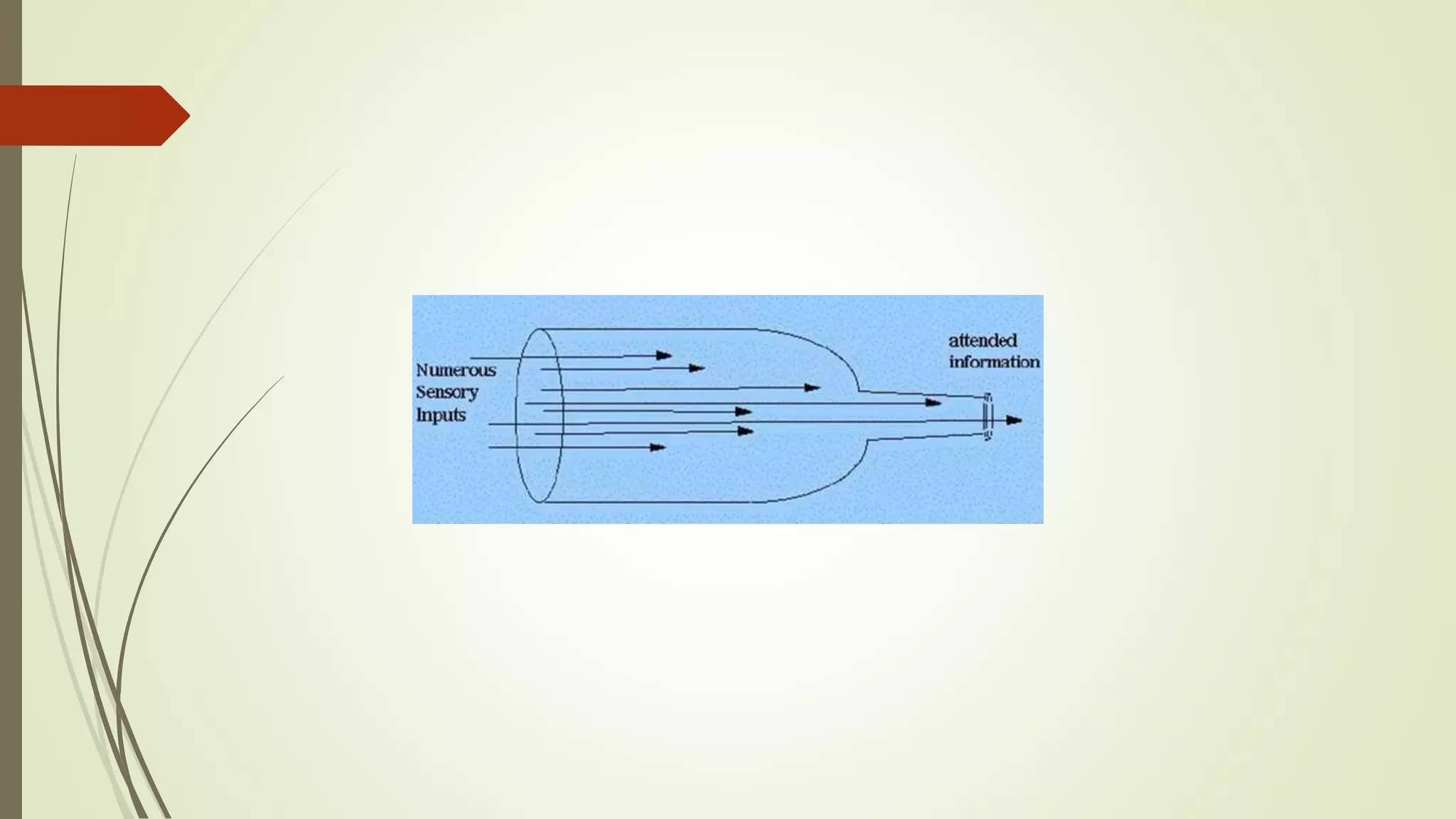
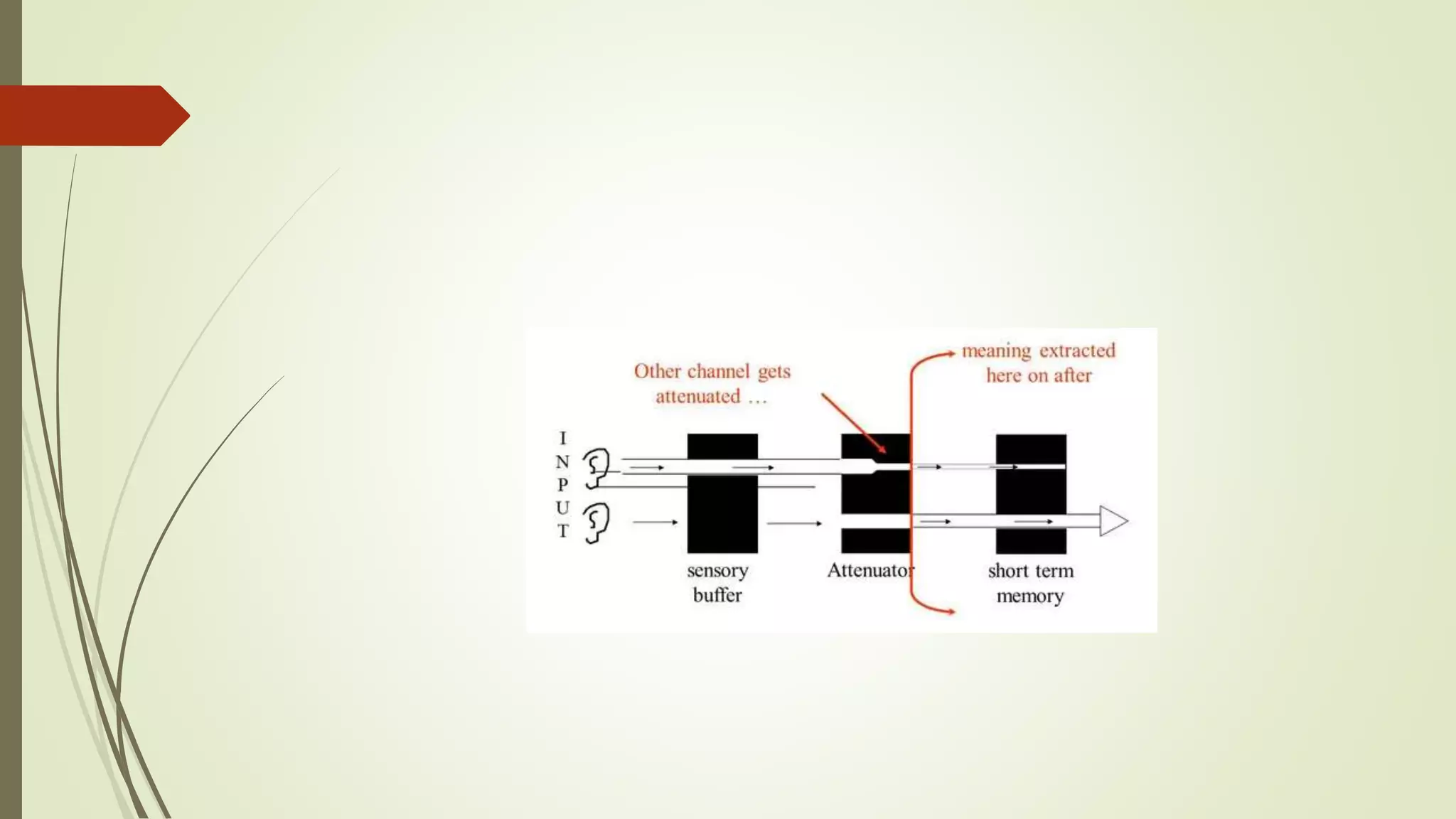
This document discusses selective attention and models of attention. It defines selective attention as focusing on relevant stimuli while ignoring irrelevant stimuli. Two types of selective attention are visual and auditory attention. Models of selective attention discussed include the spotlight model, zoom-lens model, Broadbent's filter model, and Treisman's attenuation model. Broadbent's model proposed stimuli are filtered based on physical characteristics, while Treisman's model proposed unattended stimuli are attenuated, not eliminated. Experiments using dichotic listening tasks provided evidence unattended messages can still be processed for meaning.