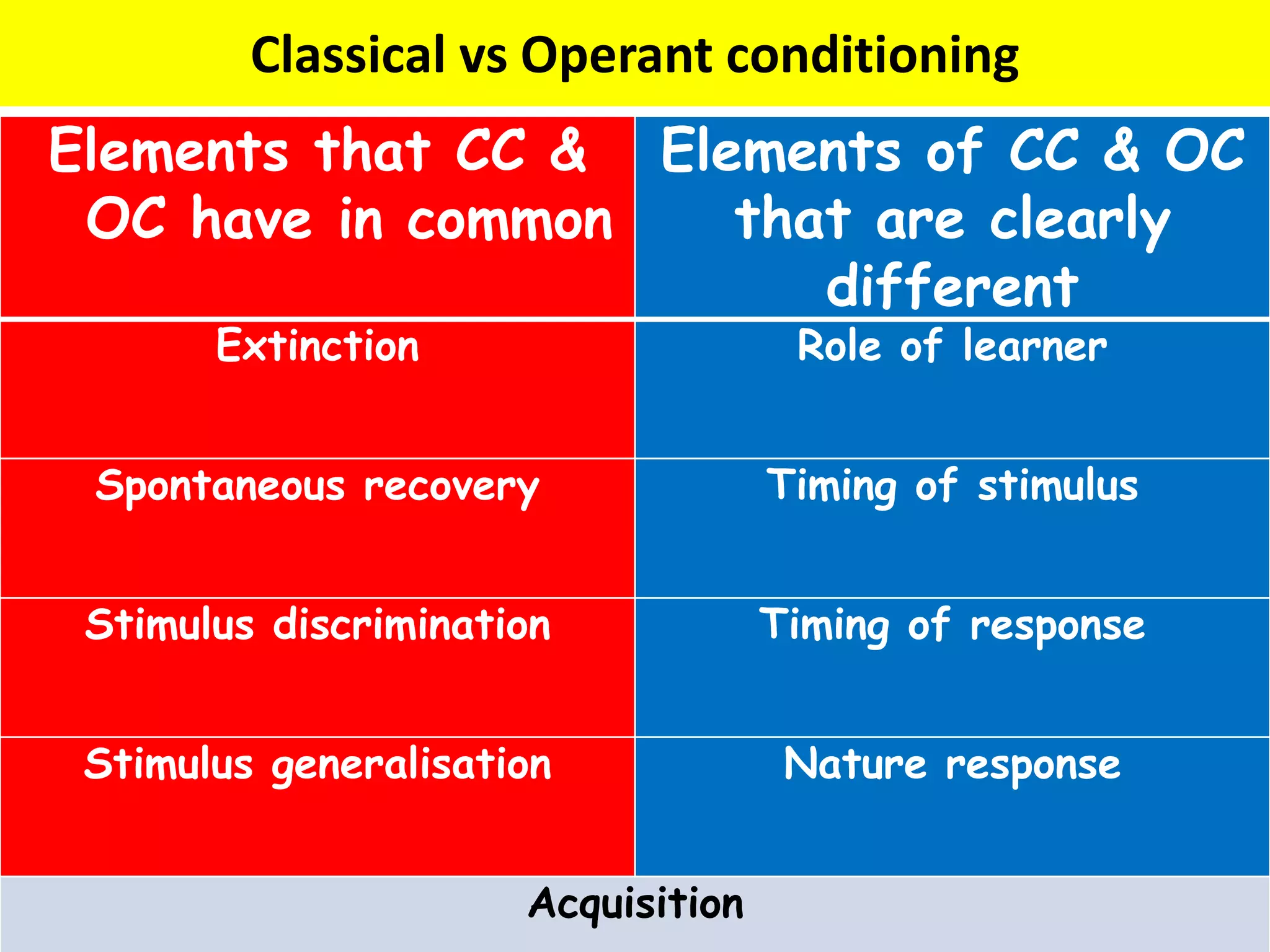
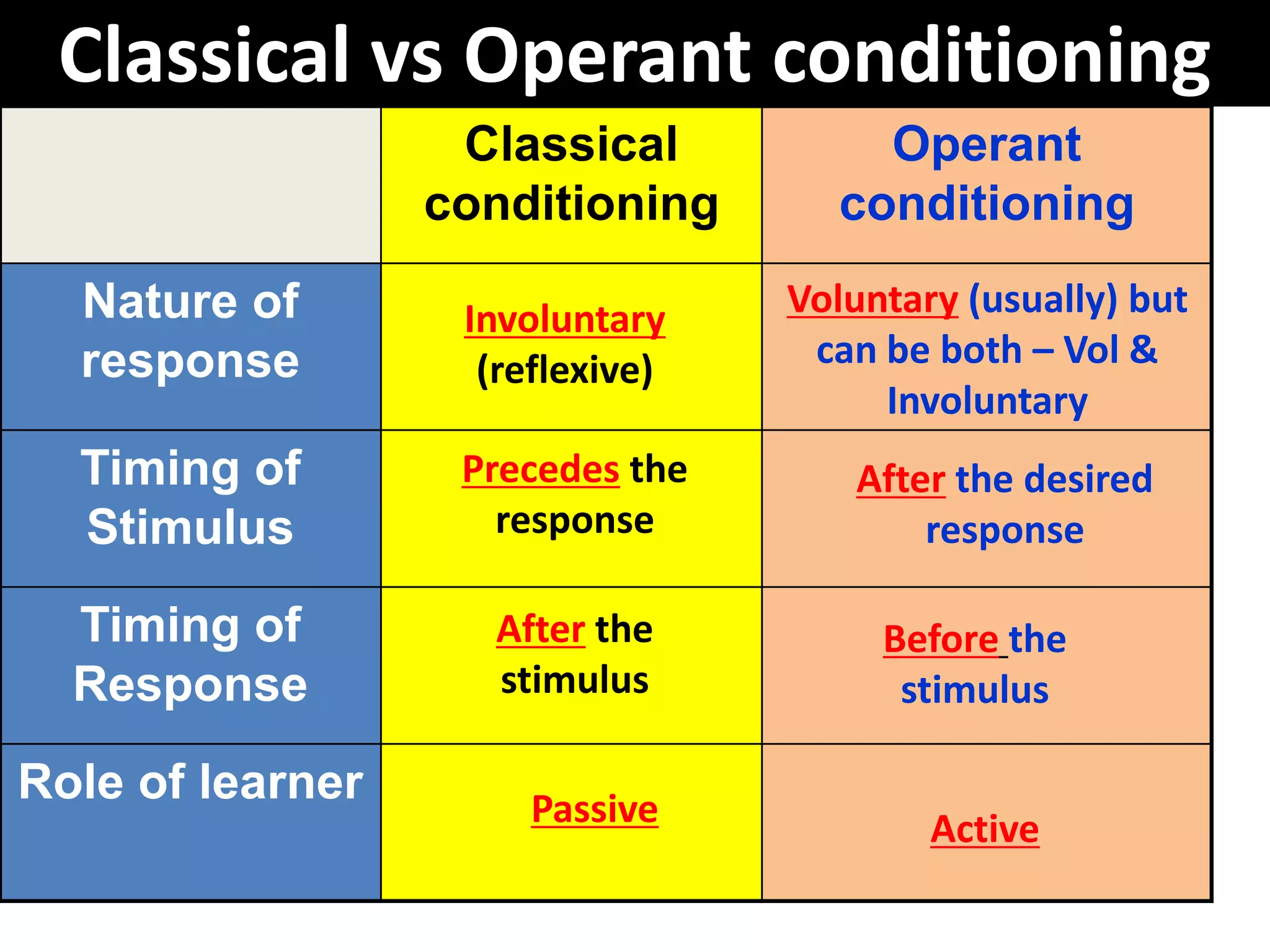
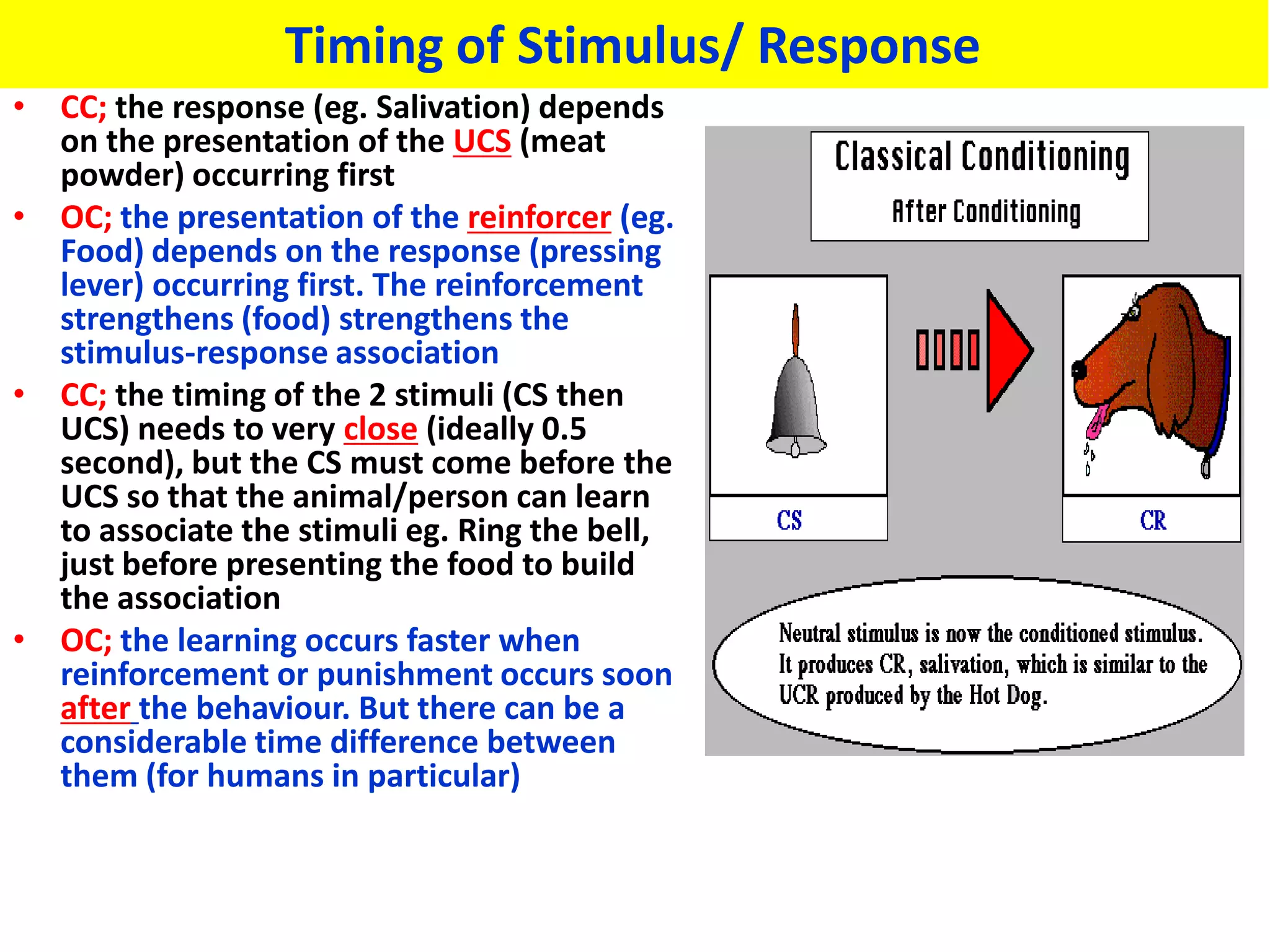
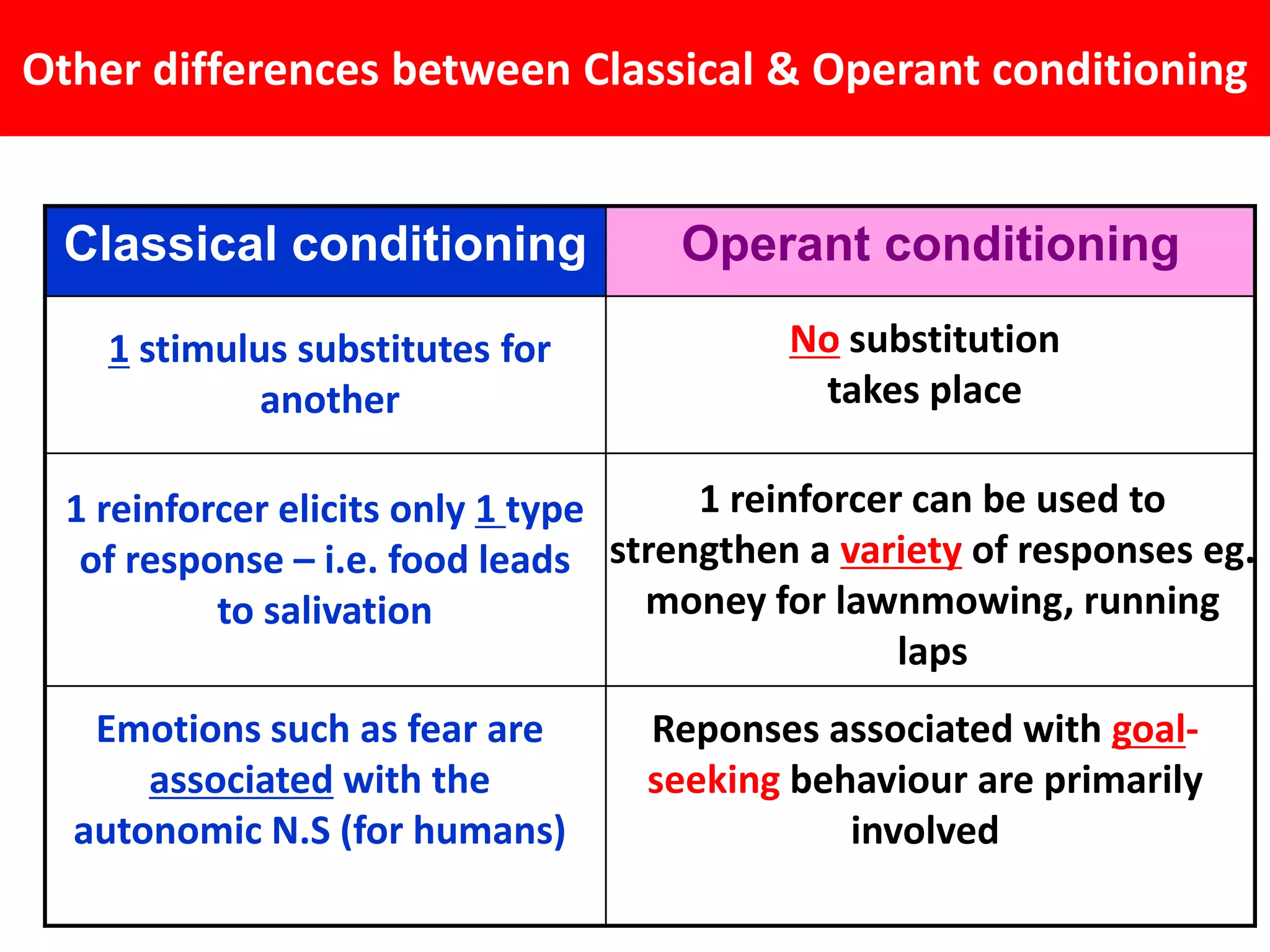
Classical conditioning (CC) and operant conditioning (OC) both involve learning through associations between stimuli and responses. However, they differ in key ways:
1. In CC, the response is involuntary and precedes the stimulus, while in OC the response is voluntary and occurs after reinforcement.
2. CC involves passive learning as the response is automatic, while OC requires an active learner who operates on the environment to obtain reinforcement.
3. The timing of the stimulus and response differ between the two: in CC the stimulus precedes the response, while in OC the response precedes reinforcement.