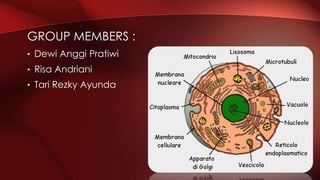
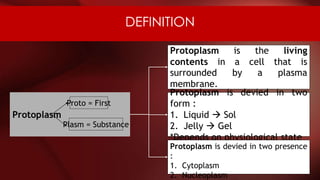
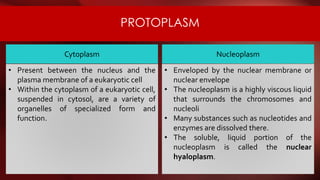
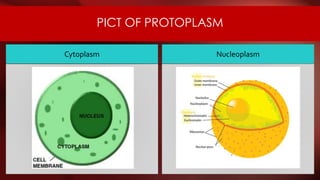
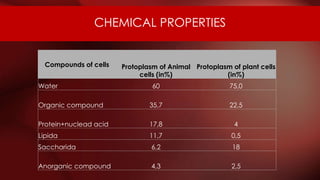
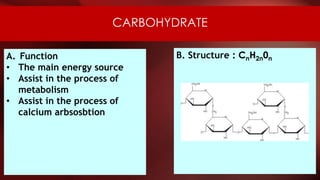
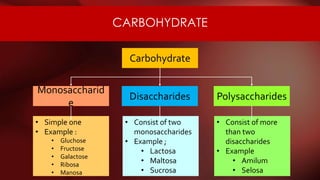
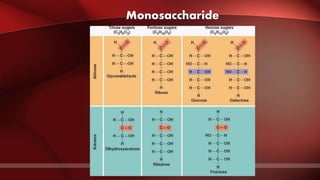
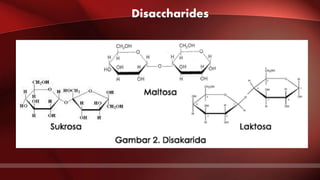
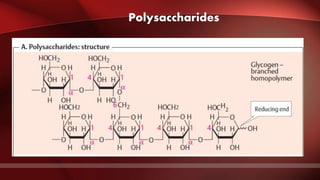
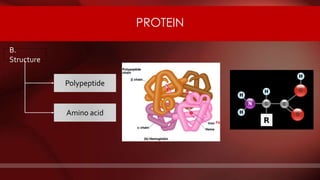
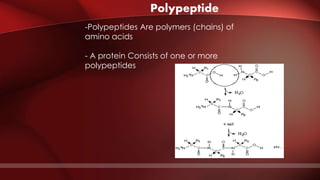
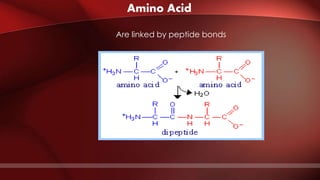
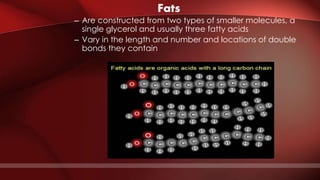
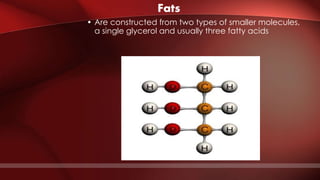
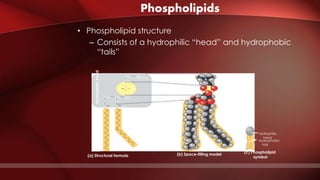
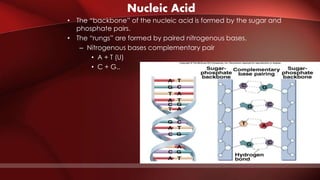
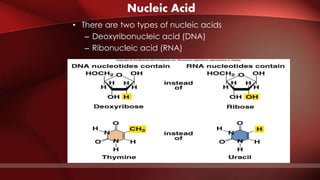
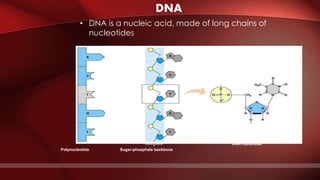
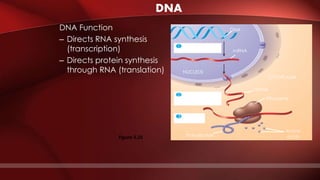
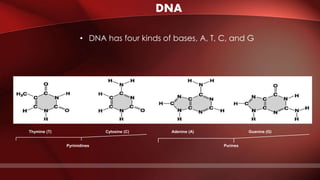
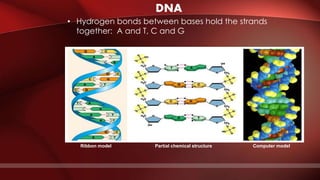
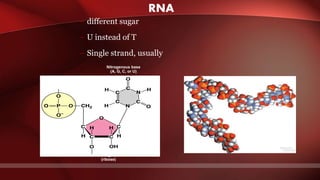
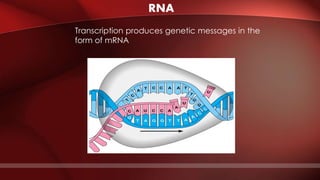
The document defines protoplasm as the living contents of a cell surrounded by a plasma membrane. It is present in both the cytoplasm and nucleoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Protoplasm consists of water, organic compounds like carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, as well as inorganic compounds. It exhibits physical properties like Brownian motion, the Tyndall effect, and ameboid movement due to its colloidal nature. Protoplasm allows cells to carry out life functions and maintains the shape of cells.