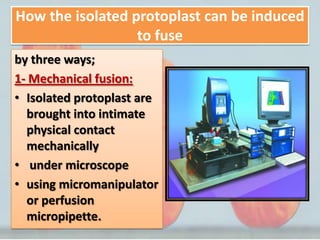
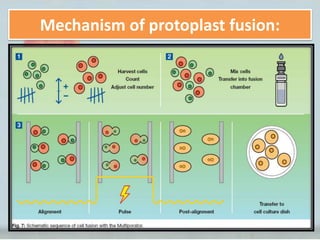
Protoplast fusion technology involves removing the cell walls from cells, leaving only the cell membrane. This allows the fusion of the cell membranes and cytoplasm of two different cell types, transferring genes. There are three main methods of inducing protoplast fusion - mechanical fusion using microtools, chemical fusion using substances like polyethylene glycol, and electrofusion using electric fields. Enzymes like cellulase and pectinase are used to break down plant cell walls, while lysozyme degrades bacterial cell walls. Protoplast fusion has applications in strain improvement for industrial purposes by creating cells with desired properties.