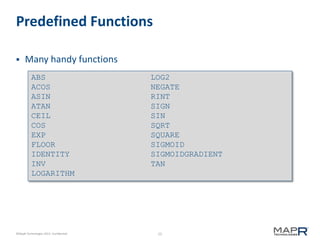
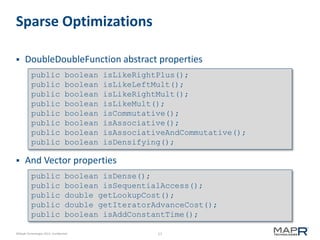
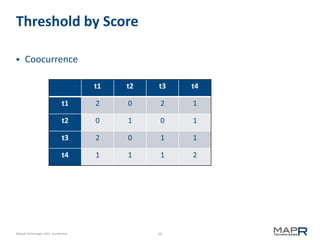
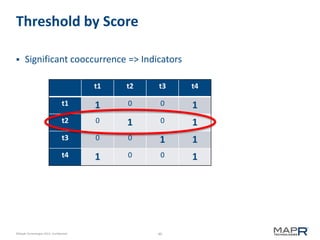
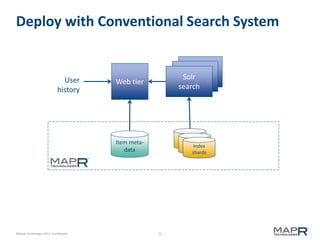
This document provides an introduction to Mahout, an Apache project for scalable machine learning. It discusses Mahout's math library capabilities including matrices, vectors, functions and sampling. It also covers Mahout's clustering, classification and recommendation algorithms. The document focuses on recommendation systems, describing basic collaborative filtering approaches and how to address problems like cold starts and leverage multiple data types. It introduces the idea of cross-recommendation to predict items from different behavior streams.









![12©MapR Technologies 2013- Confidential
Assign
Matrices
Vectors
Matrix assign(double value);
Matrix assign(double[][] values);
Matrix assign(Matrix other);
Matrix assign(DoubleFunction f);
Matrix assign(Matrix other, DoubleDoubleFunction f);
Vector assign(double value);
Vector assign(double[] values);
Vector assign(Vector other);
Vector assign(DoubleFunction f);
Vector assign(Vector other, DoubleDoubleFunction f);
Vector assign(DoubleDoubleFunction f, double y);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/minn-mahout-introduction-130805130917-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-Mahout-12-320.jpg)
![13©MapR Technologies 2013- Confidential
Views
Matrices
Vectors
Matrix viewPart(int[] offset, int[] size);
Matrix viewPart(int row, int rlen, int col, int clen);
Vector viewRow(int row);
Vector viewColumn(int column);
Vector viewDiagonal();
Vector viewPart(int offset, int length);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/minn-mahout-introduction-130805130917-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-Mahout-13-320.jpg)