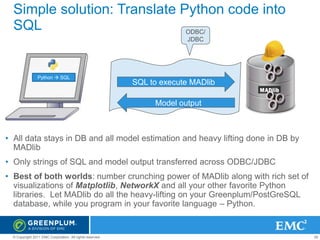
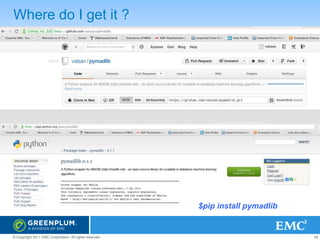
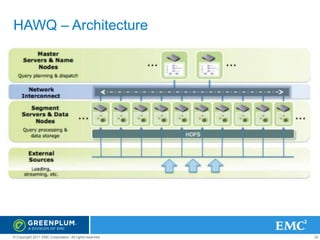
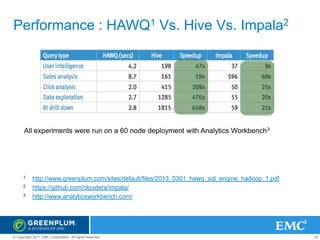
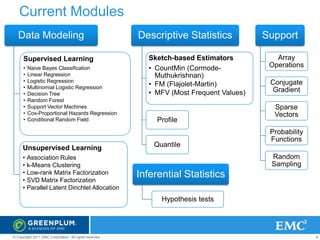
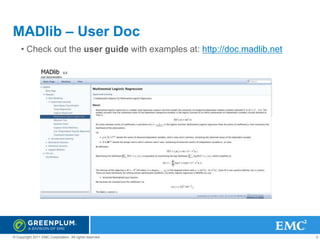
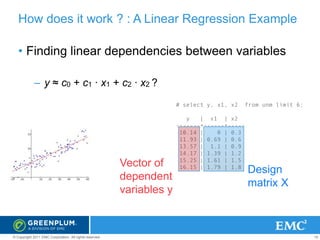
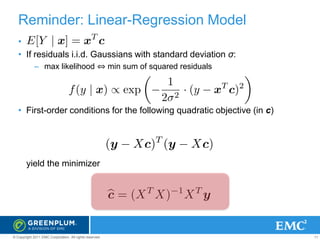
The document provides an overview of Greenplum's Unified Analytics Platform, covering its products like GPDB and GPHG, and introducing Madlib, a project offering machine learning algorithms integrated with databases. It highlights Madlib's architecture, current modules, and performance comparisons with Mahout, as well as introducing pymadlib for Python users. The document also discusses future directions, including HawQ, a parallel SQL engine designed for big data analytics.




![Logistic Regression
• Mahout only has sequential (i.e. single node) IGD implementation
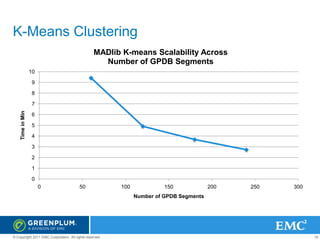
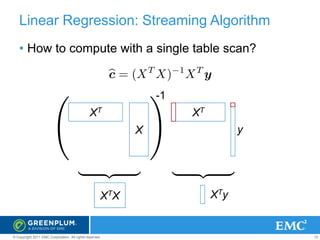
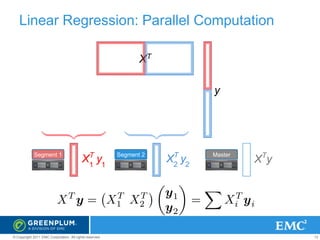
MADlib & Mahout Logistic Regression Scalability Across
Number of Attributes
700
Census data, 48 attributes [Mahout]
600
Time in Minutes
Census data, 48 attributes [MADlib]
500
400
300
200
100
0
1000000
10000000
10000000
1E+09
log(Number of Rows)
© Copyright 2011 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved.
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pymadlib-dataday-texas-131115171856-phpapp02/85/PyMADlib-A-Python-wrapper-for-MADlib-in-database-parallel-machine-learning-library-16-320.jpg)
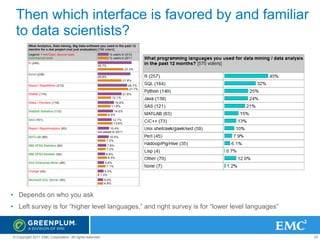
![K-Means Clustering
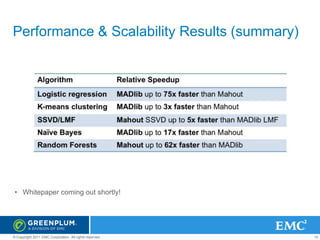
MADlib & Mahout K-means Scalability Across
Number of Rows
350
Census data, 48 attributes [Mahout]
300
Census data, 48 attributes [MADlib]
Time in Min
250
200
150
100
50
0
1000000
10000000
10000000
1E+09
log(Number of Rows)
© Copyright 2011 EMC Corporation. All rights reserved.
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pymadlib-dataday-texas-131115171856-phpapp02/85/PyMADlib-A-Python-wrapper-for-MADlib-in-database-parallel-machine-learning-library-18-320.jpg)