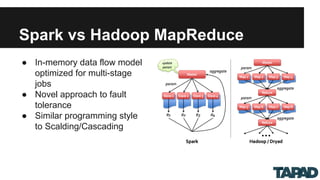
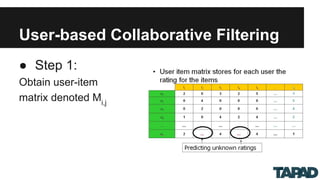
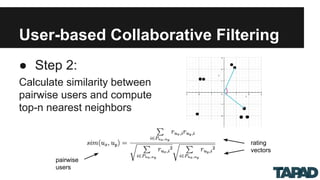
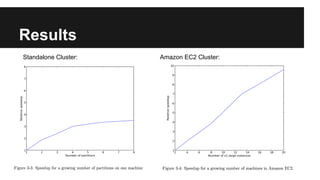
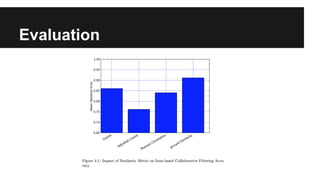
The document discusses scalable collaborative filtering recommendation algorithms using Apache Spark, highlighting its advantages over Hadoop MapReduce in processing large datasets. It explains the functioning of user-based and item-based collaborative filtering, detailing steps for calculating user similarity and effective recommendation scores. Key lessons include optimizing task distribution, using broadcast variables, and accounting for user rating behaviors in large-scale systems.