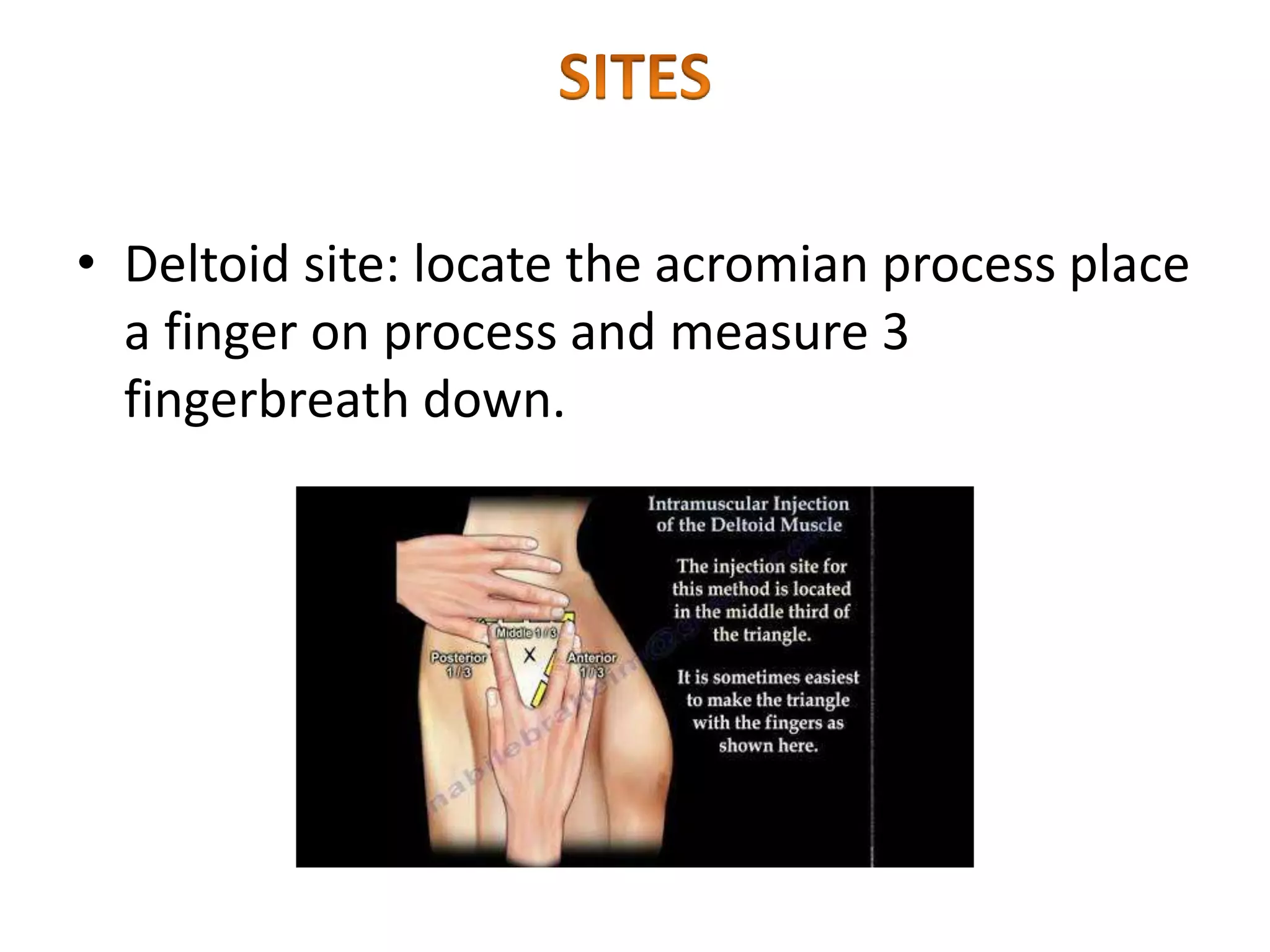
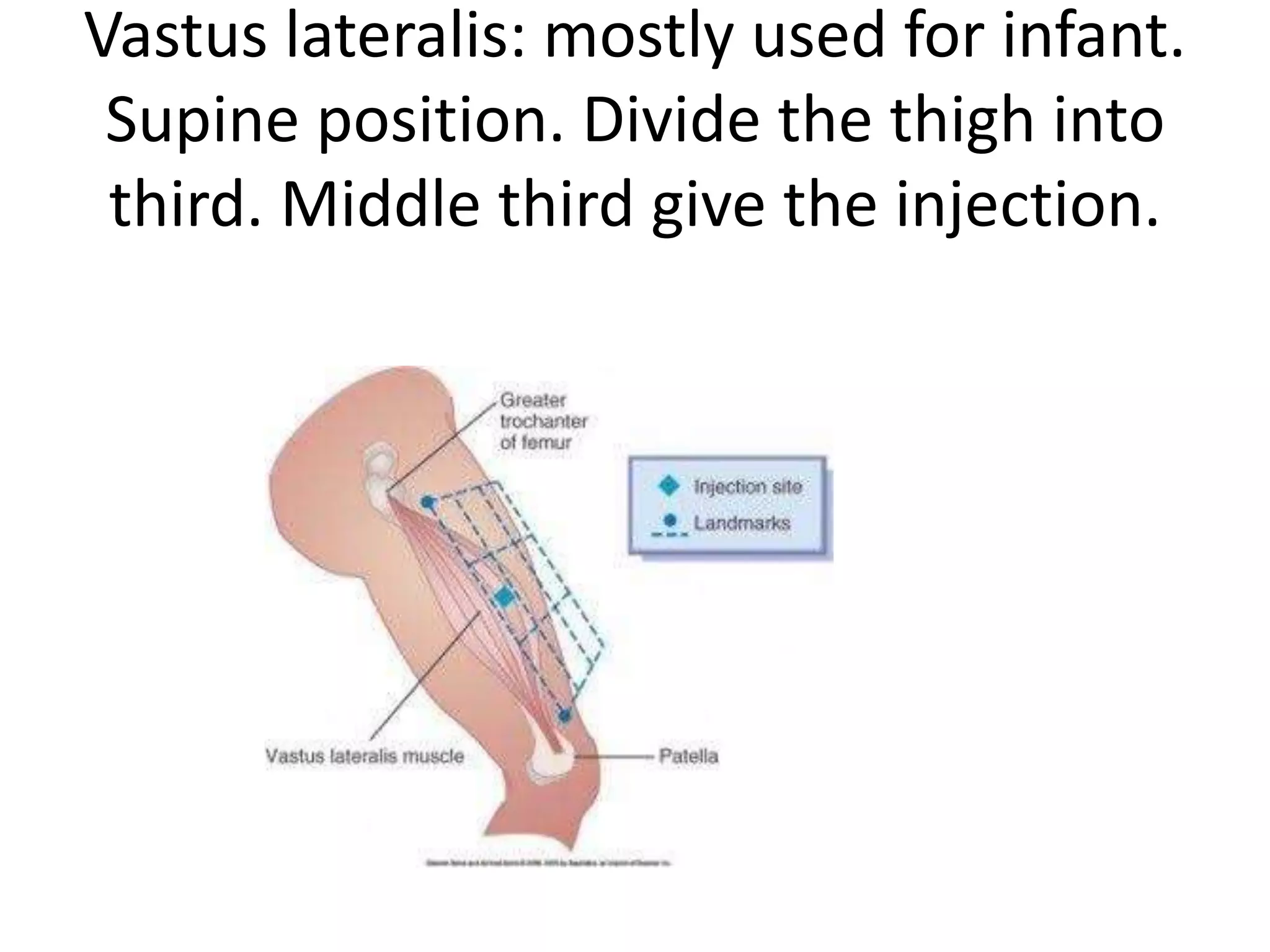
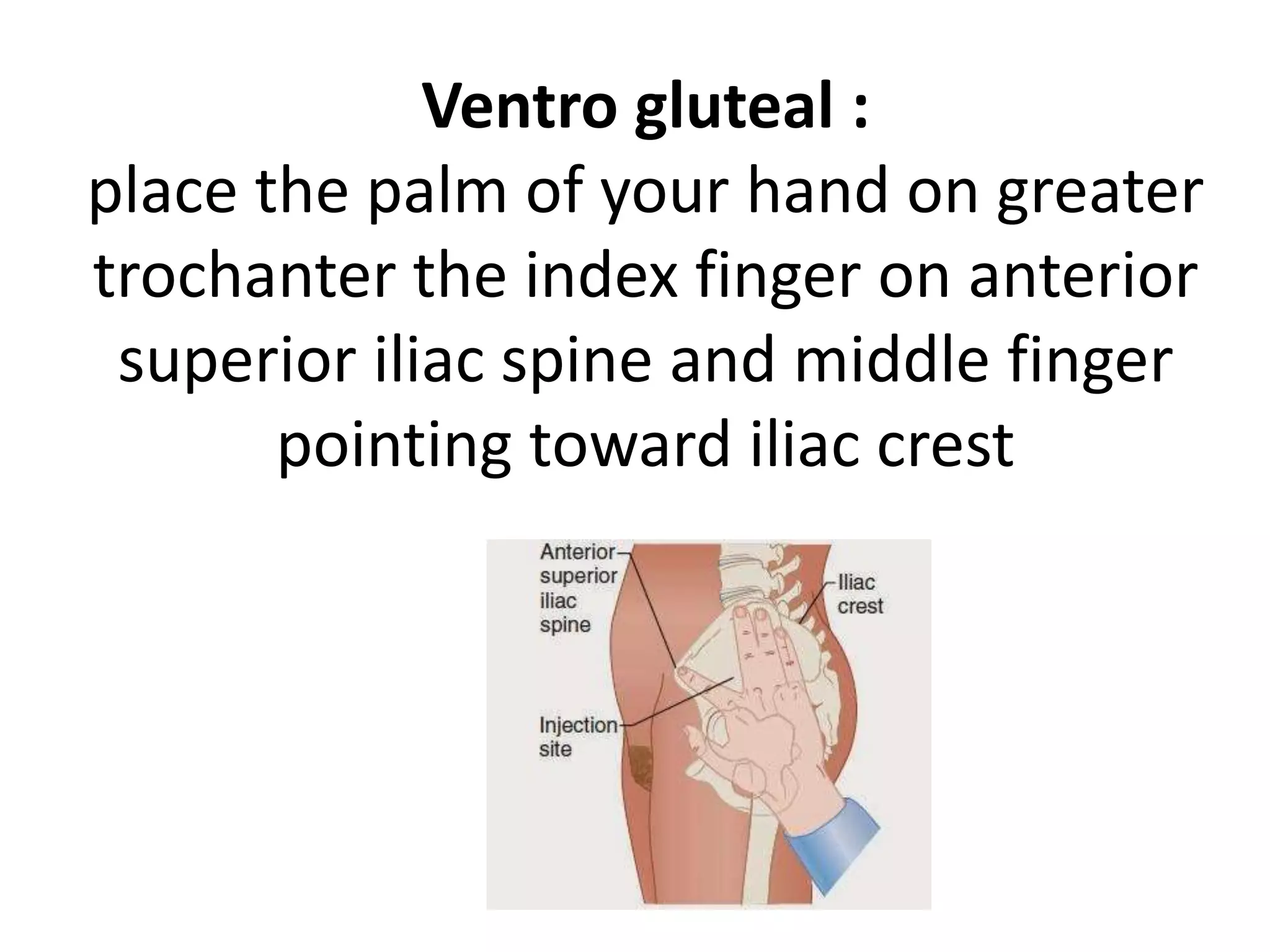
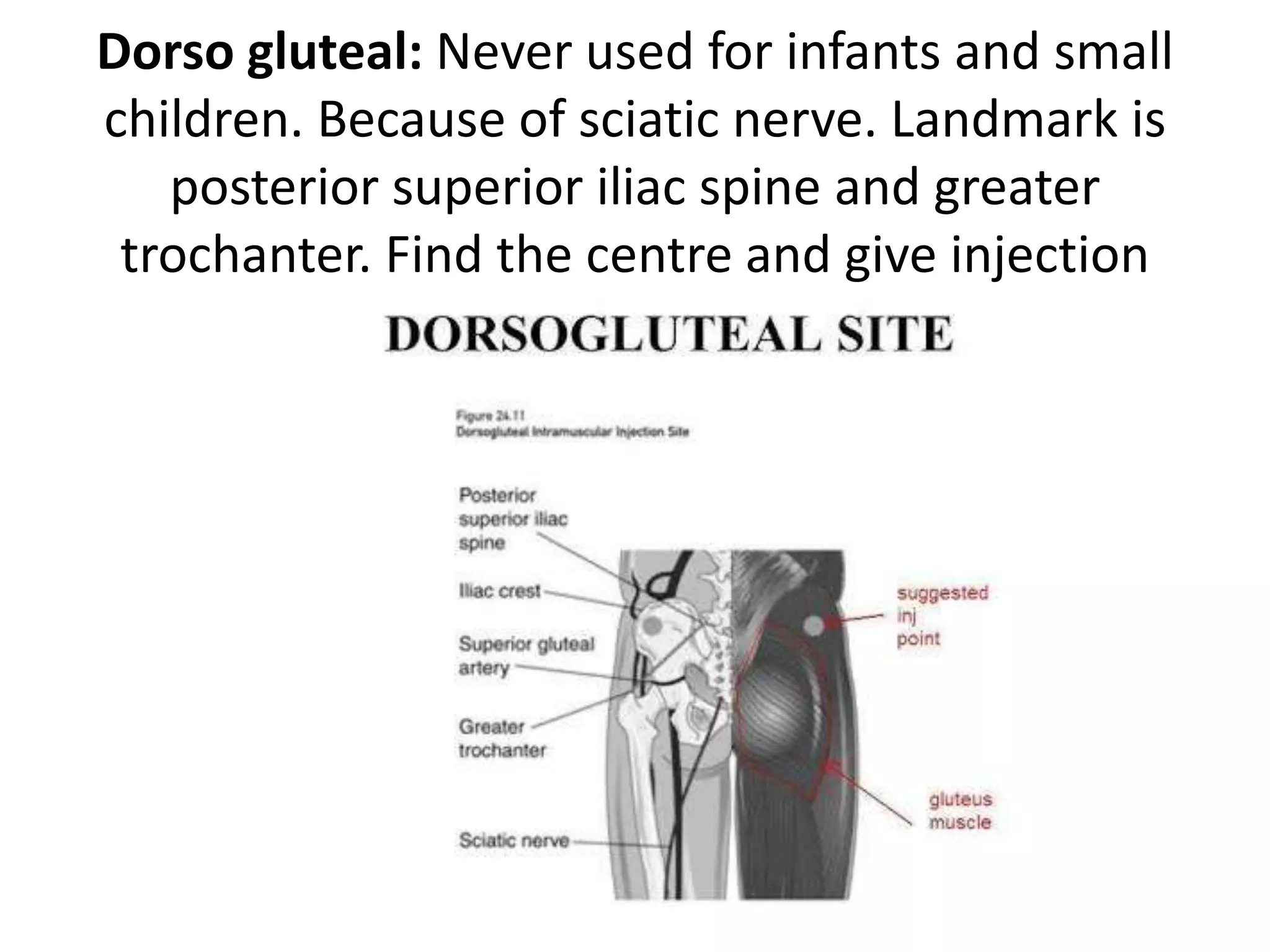
This document provides instructions for administering intramuscular injections including the advantages and disadvantages, recommended injection sites, necessary equipment, and procedures. It discusses delivering injections into the deltoid, vastus lateralis, ventrogluteal, and dorsogluteal regions. The procedures outline preparing the medication, identifying the client, explaining the process, selecting an injection site, administering the injection, and documenting properly. Complications that can arise include abscesses, tissue damage, granulomas, hematomas, and nerve injuries.