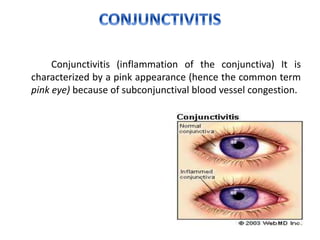
This document discusses different types of conjunctivitis (inflammation of the conjunctiva). It describes the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management of bacterial, viral, allergic, chemical, and vernal conjunctivitis. The most common causes of bacterial conjunctivitis are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Staphylococcus aureus. Viral conjunctivitis is often caused by common cold viruses. Allergic conjunctivitis is a hypersensitivity reaction to allergens like pollen. Chemical conjunctivitis results from exposure to irritants. Vernal conjunctivitis is a chronic condition that occurs mostly in young males during warm weather.