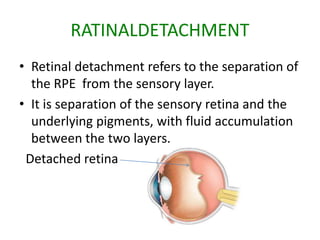
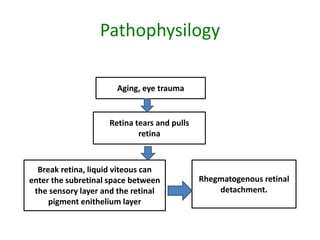
Retinal detachment refers to the separation of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) from the sensory retina. There are four main types: rhegmatogenous, traction, exudative, and a combination. Rhegmatogenous detachment occurs when a hole or tear develops in the sensory retina, allowing fluid to pass through and separate the layers. Risk factors include increasing age, high nearsightedness, eye trauma, and certain eye conditions. Diagnosis involves examination of the eye and sometimes ultrasound imaging. Treatment options are laser photocoagulation to seal retinal breaks, cryotherapy, vitrectomy surgery, or draining subretinal fluids depending on the type and severity of detachment.