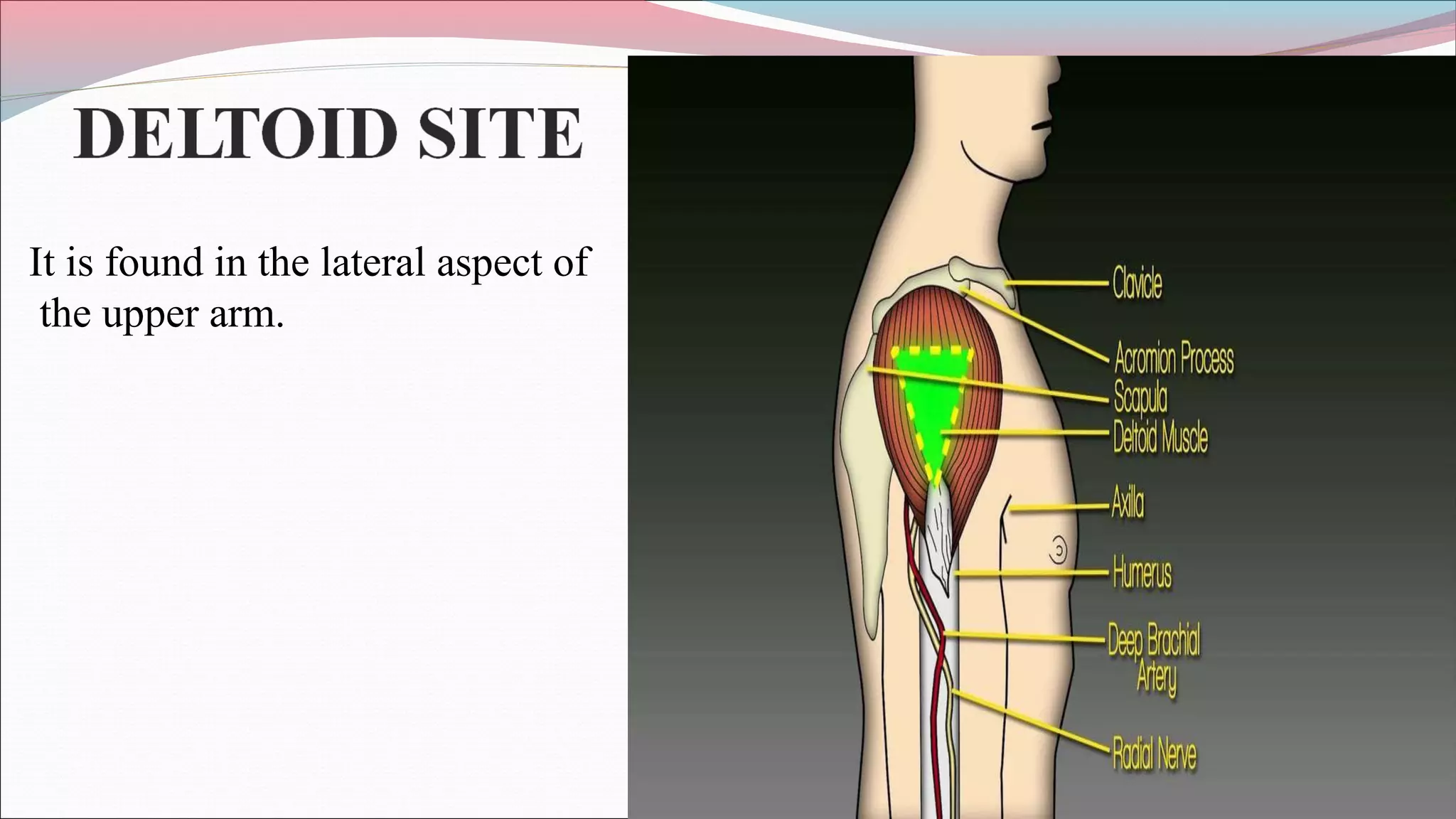
The document discusses intramuscular injections including defining intramuscular injections as introducing medication into muscle tissue, describing their purpose to ensure systemic absorption of drugs that cannot be given orally or intravenously, and outlining best practices for administering intramuscular injections including using proper technique and sites like the ventrogluteal, dorsogluteal, vastus lateralis, deltoid, and rectus femoris muscles.