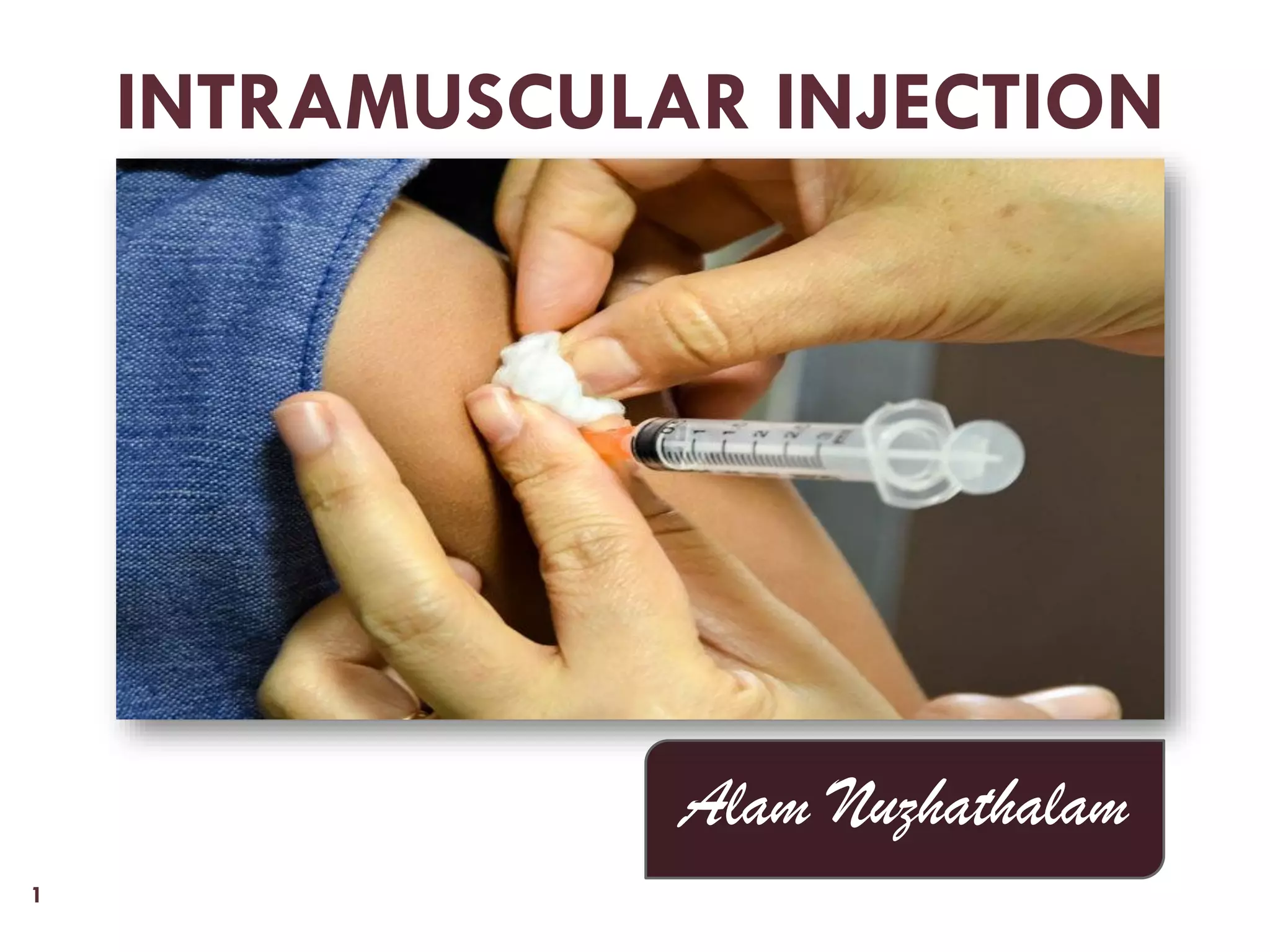
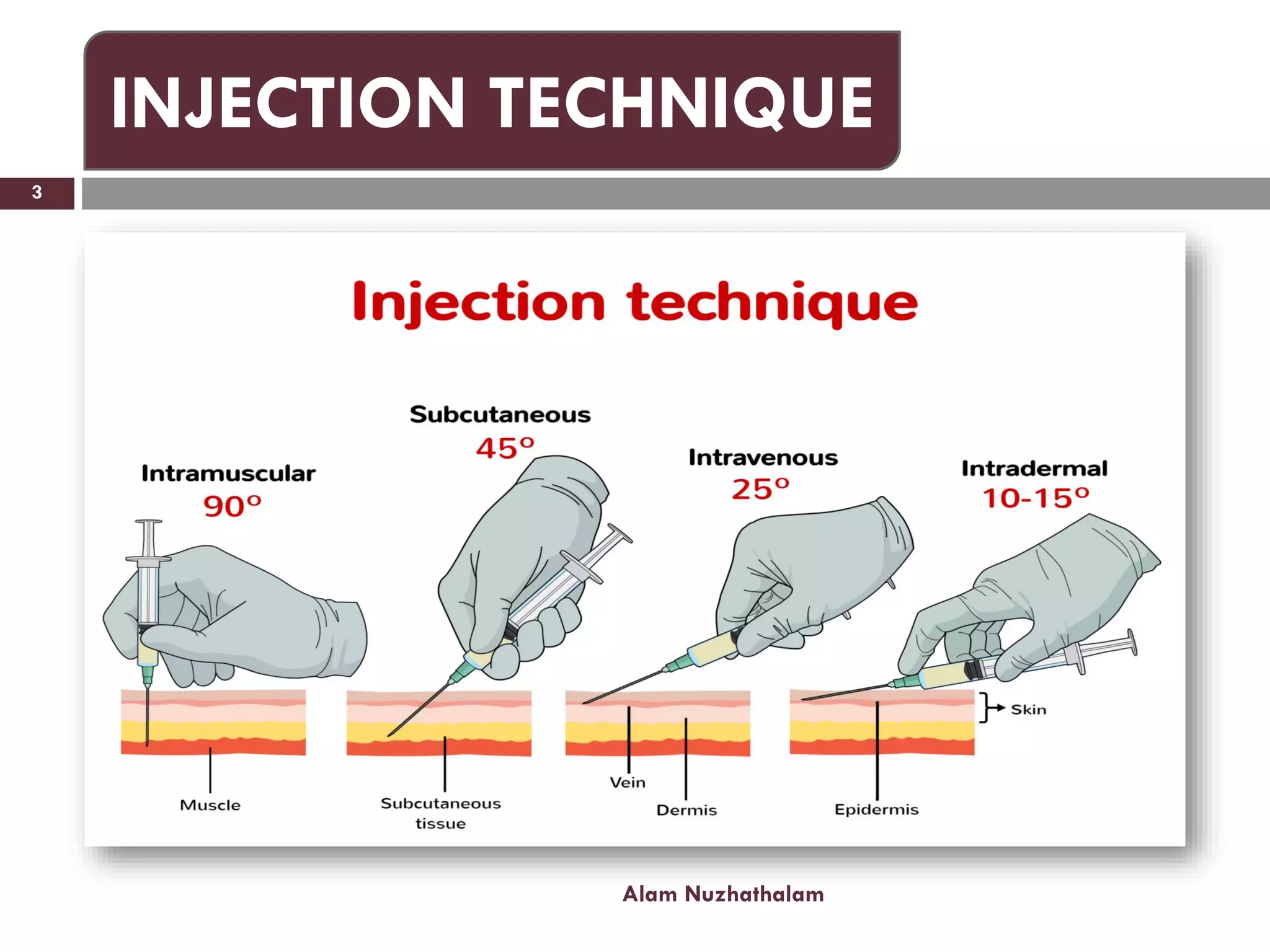
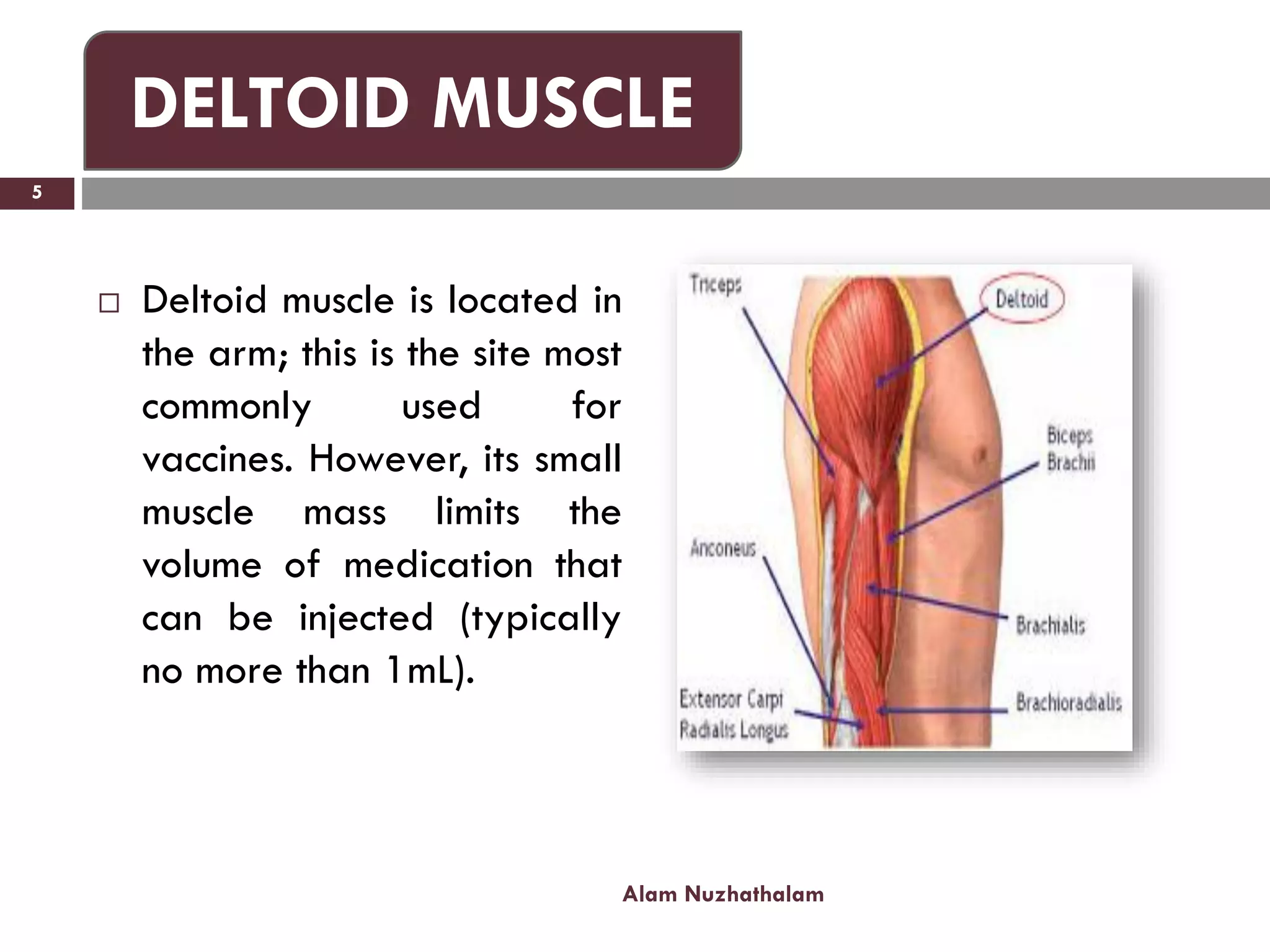
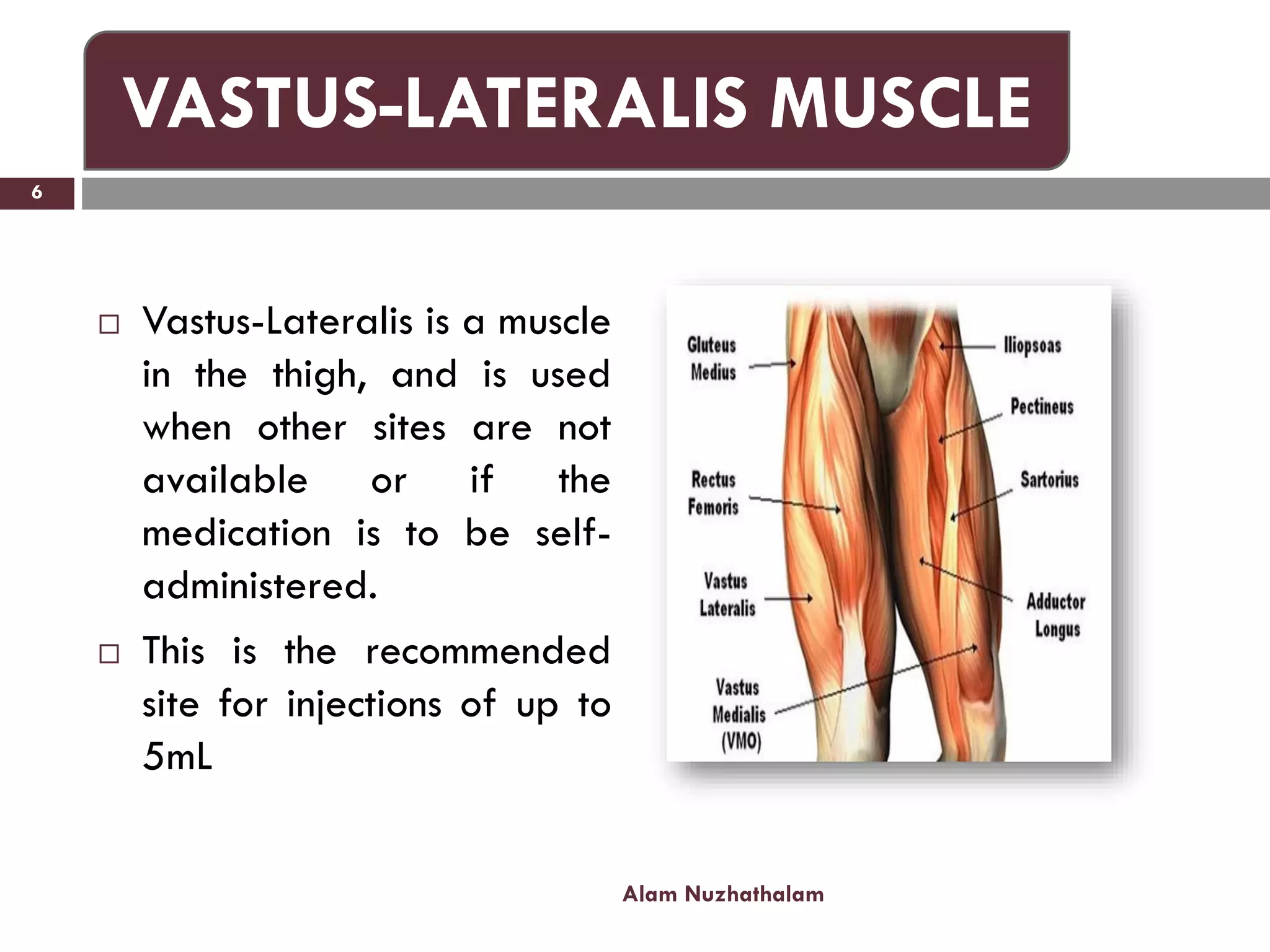
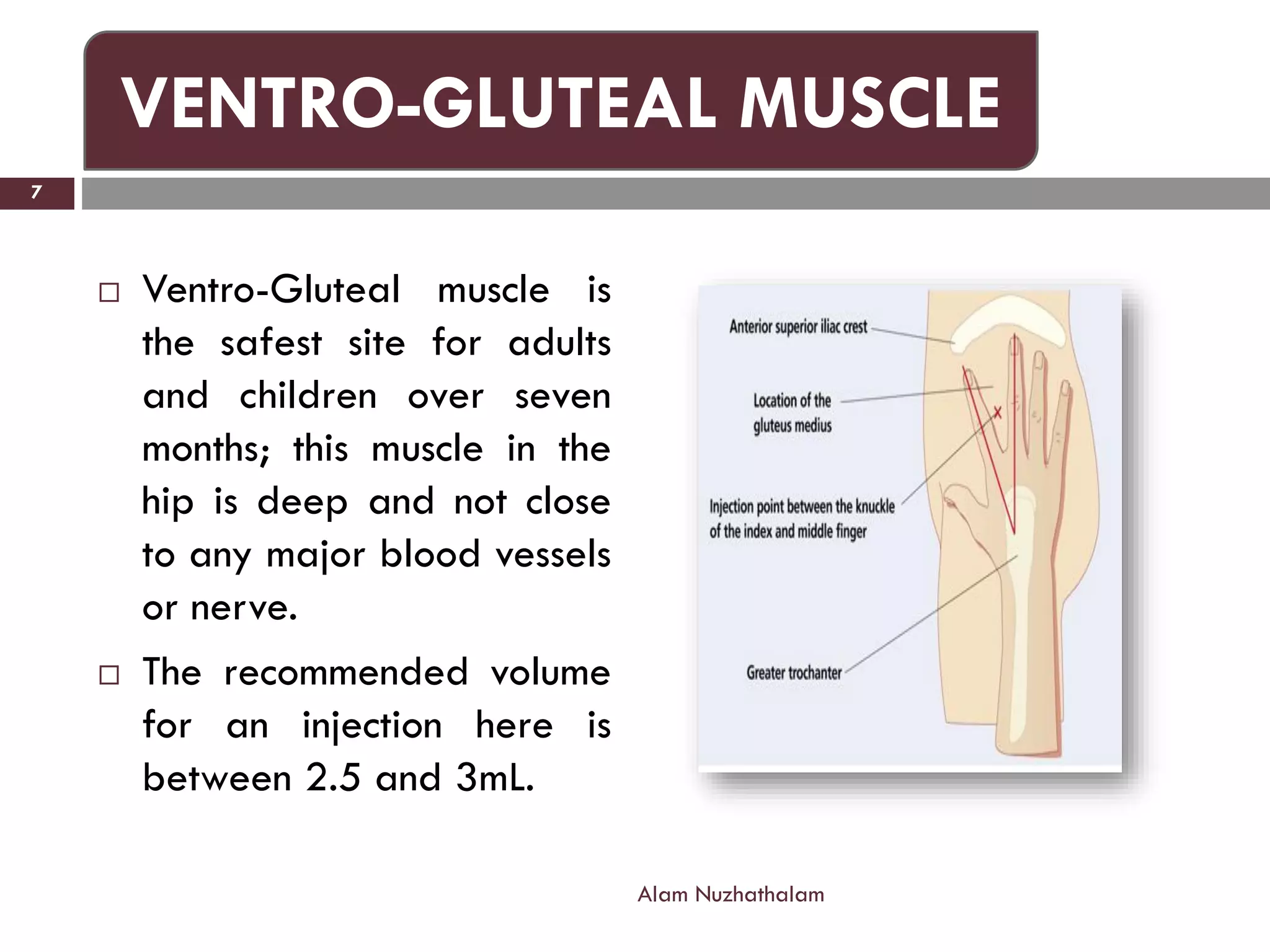
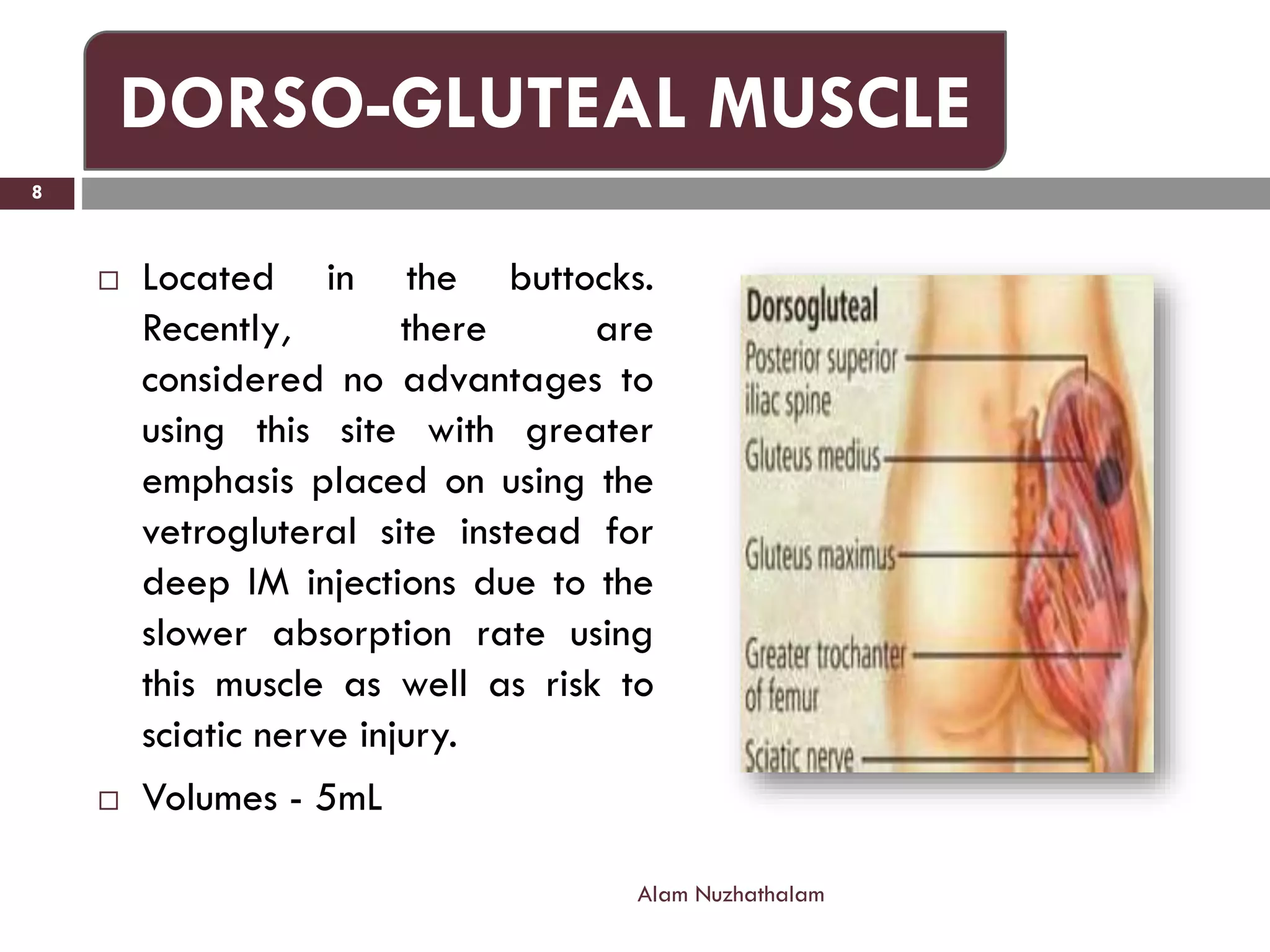
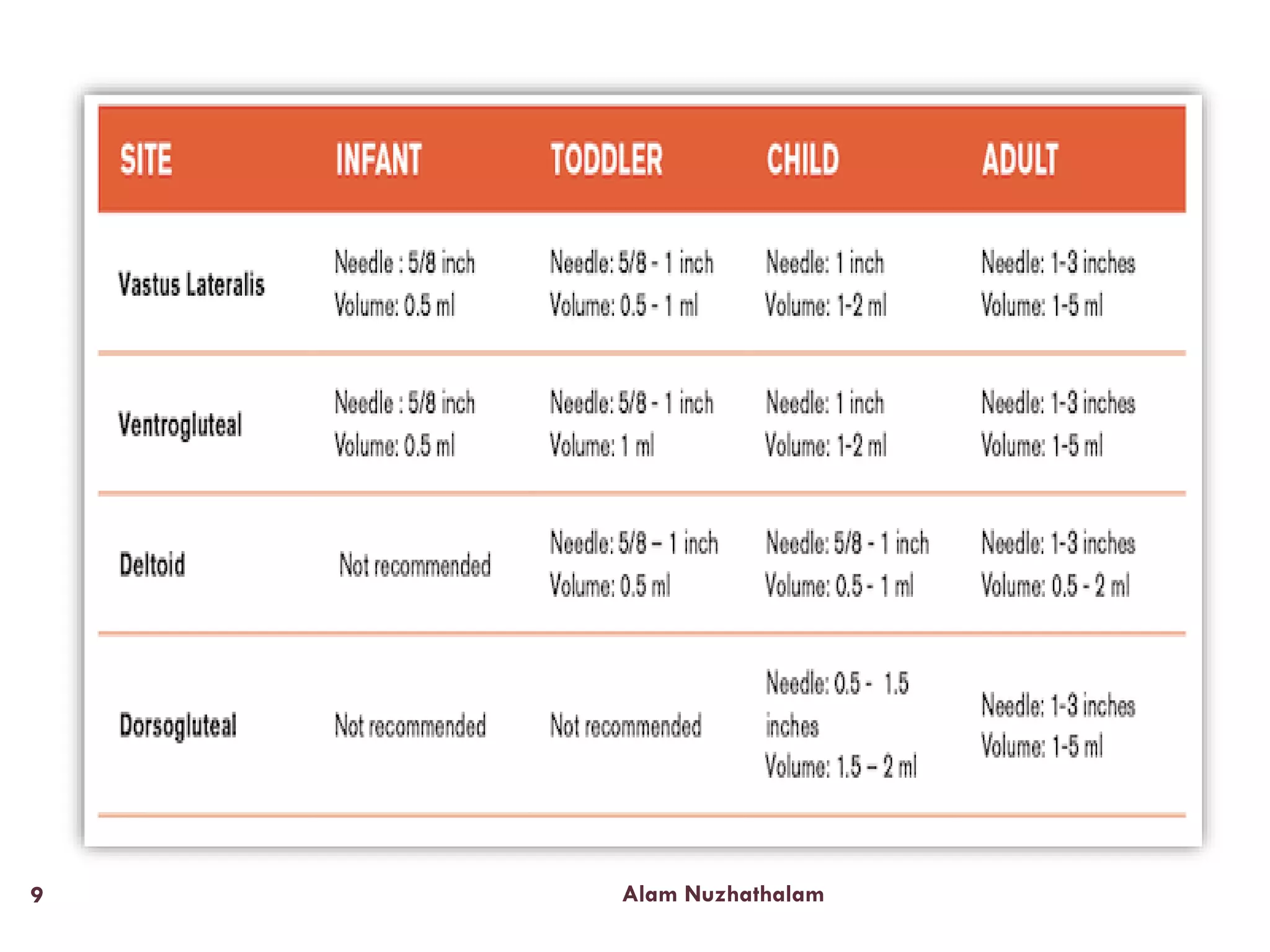
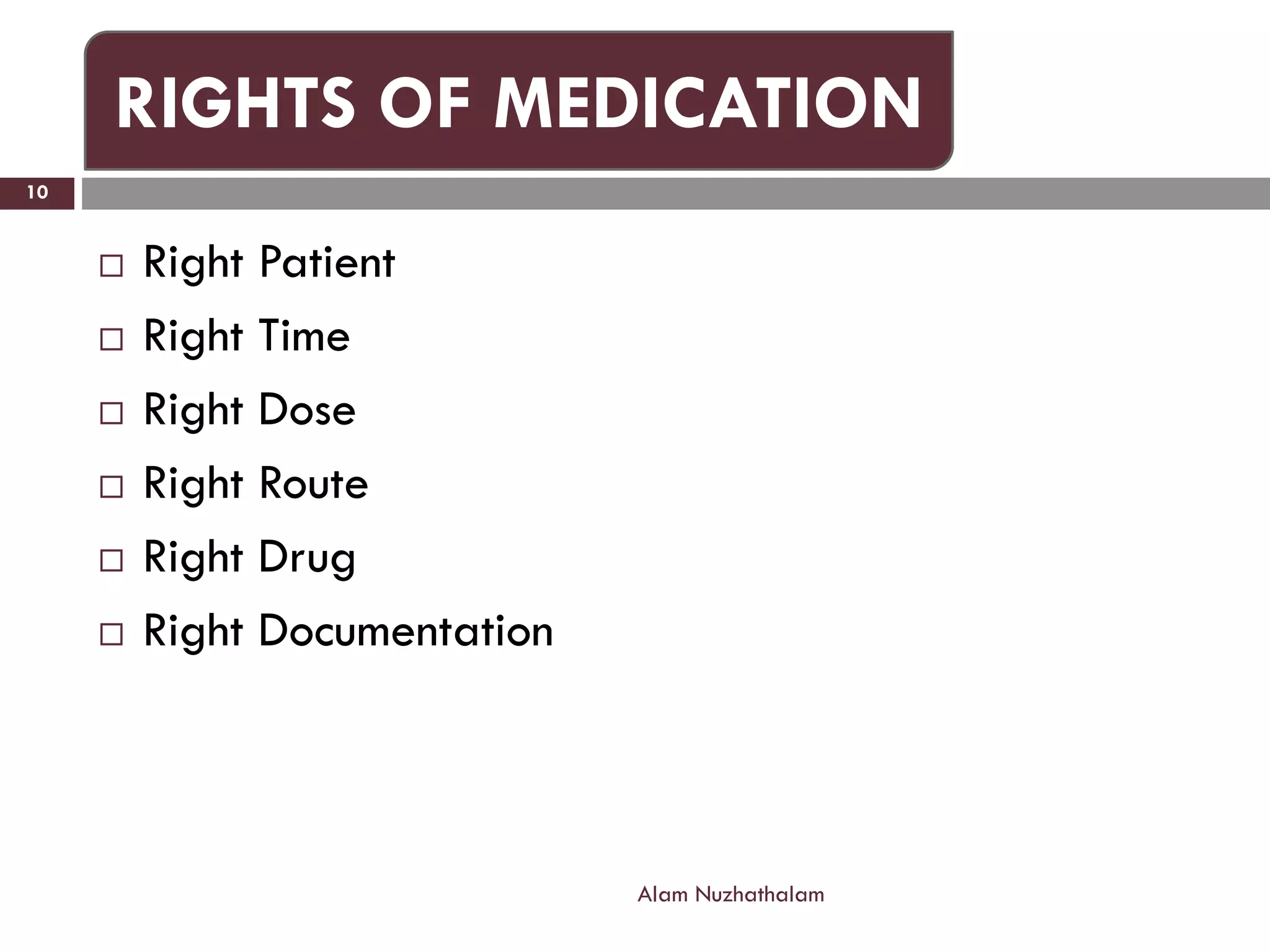
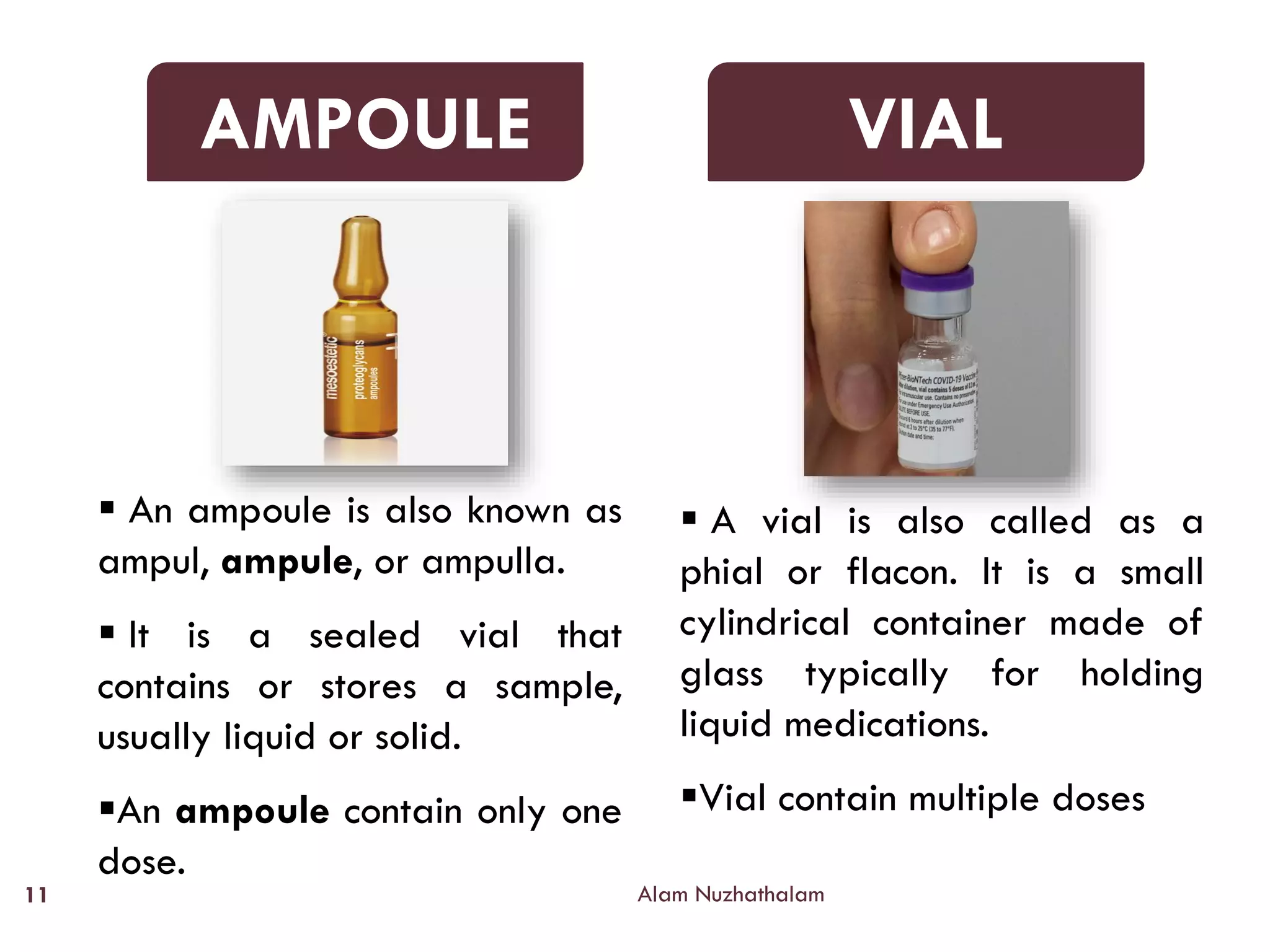
Intramuscular injection involves administering medication directly into the muscle for quick absorption, particularly when intravenous methods are unsuitable. Common injection sites include the deltoid, vastus-lateralis, ventro-gluteal, and dorso-gluteal muscles, with each site offering different volume capacities and safety considerations. Proper technique, patient identification, and post-injection care are crucial components in the execution of intramuscular injections.