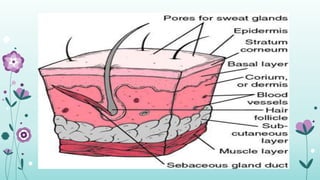
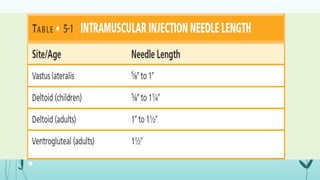
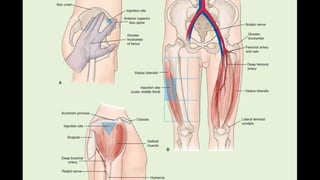
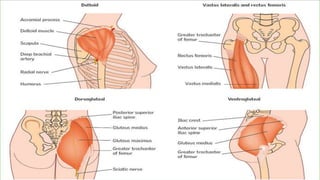
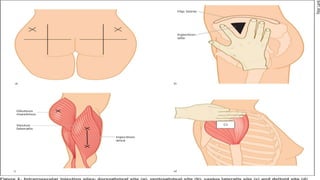
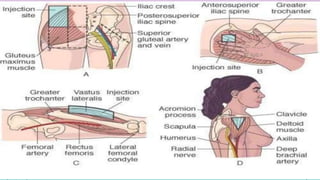
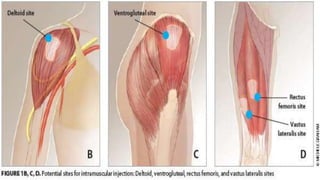
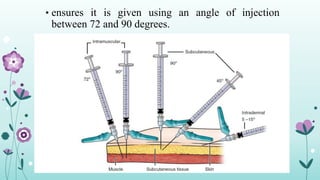
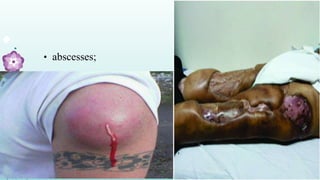
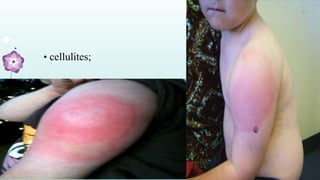
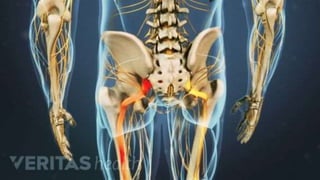
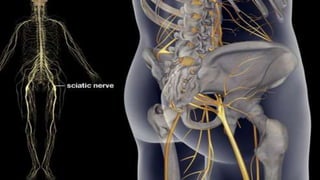
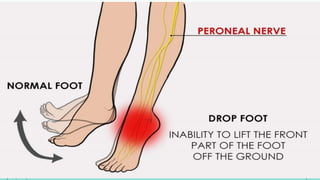
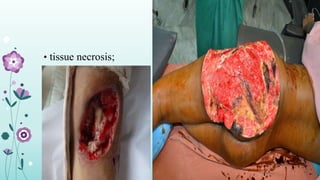
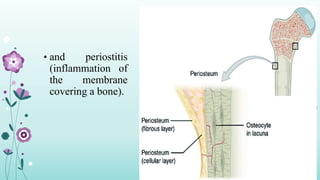
Intramuscular injections deliver medication into muscles through the skin and subcutaneous tissue. They allow for faster drug absorption than subcutaneous injections due to muscles having more blood vessels. The correct technique involves using a 23G needle at a 72-90 degree angle and rotating injection sites. Potential complications include abscesses, cellulitis, and nerve damage.