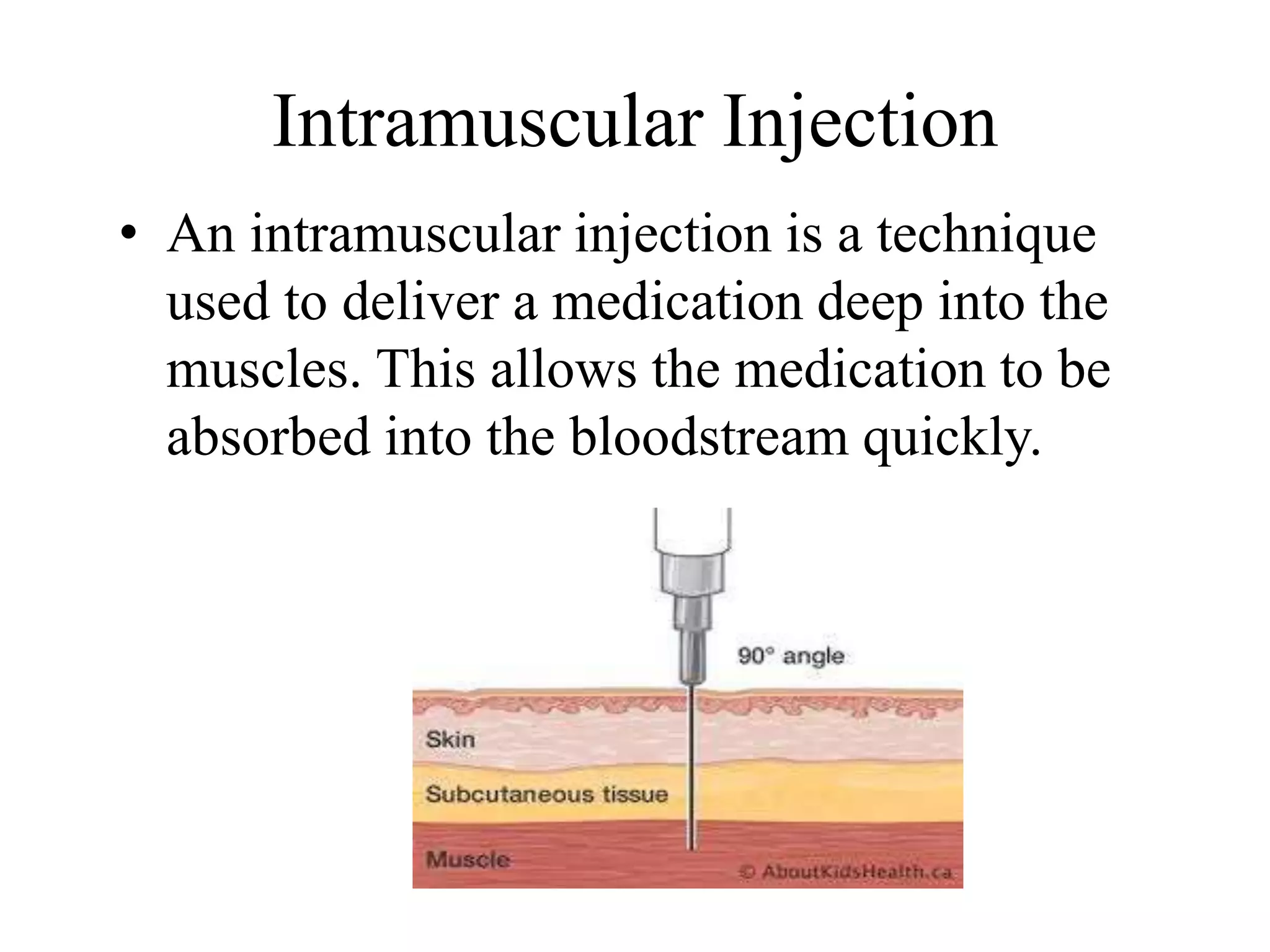
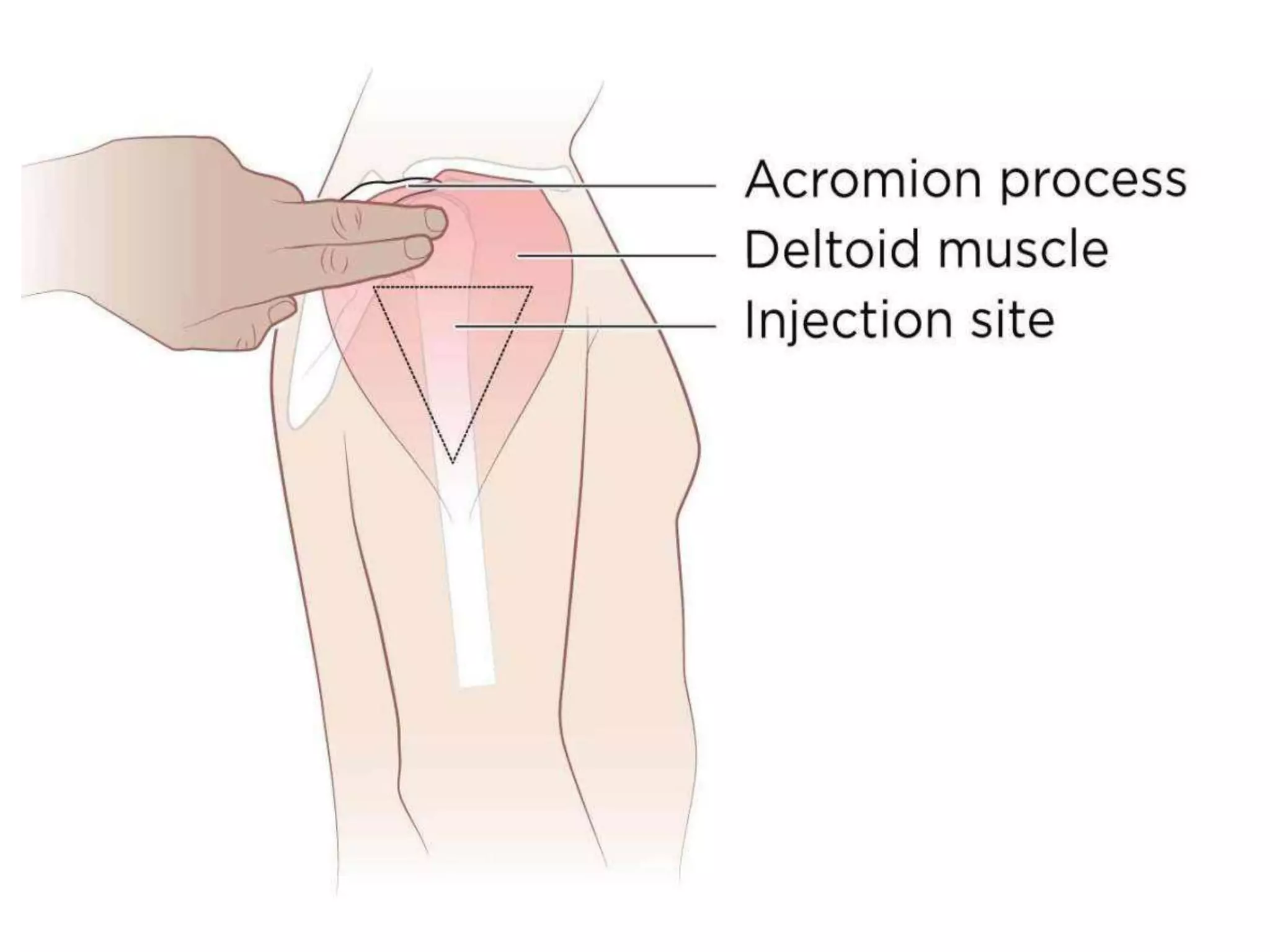
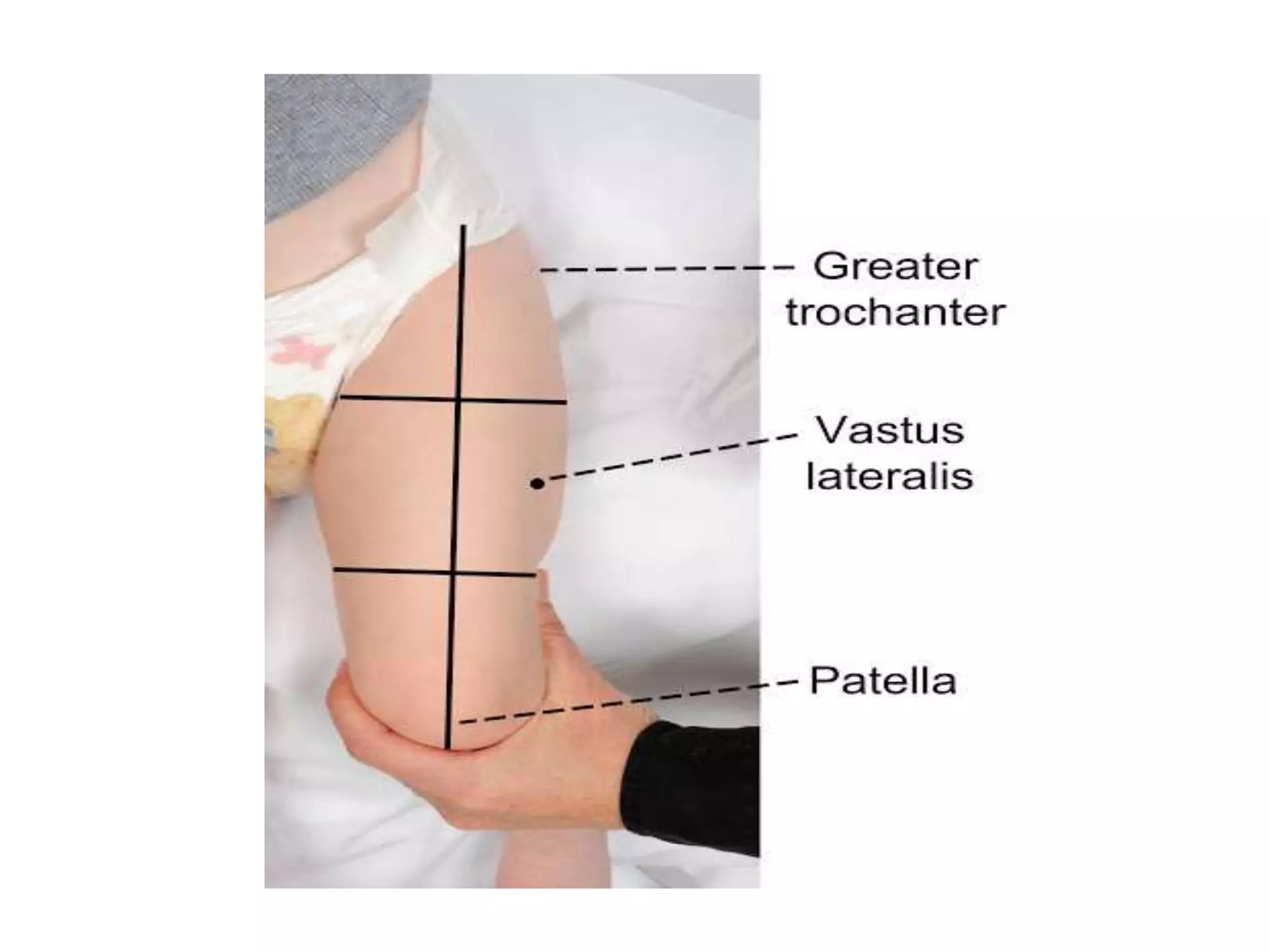
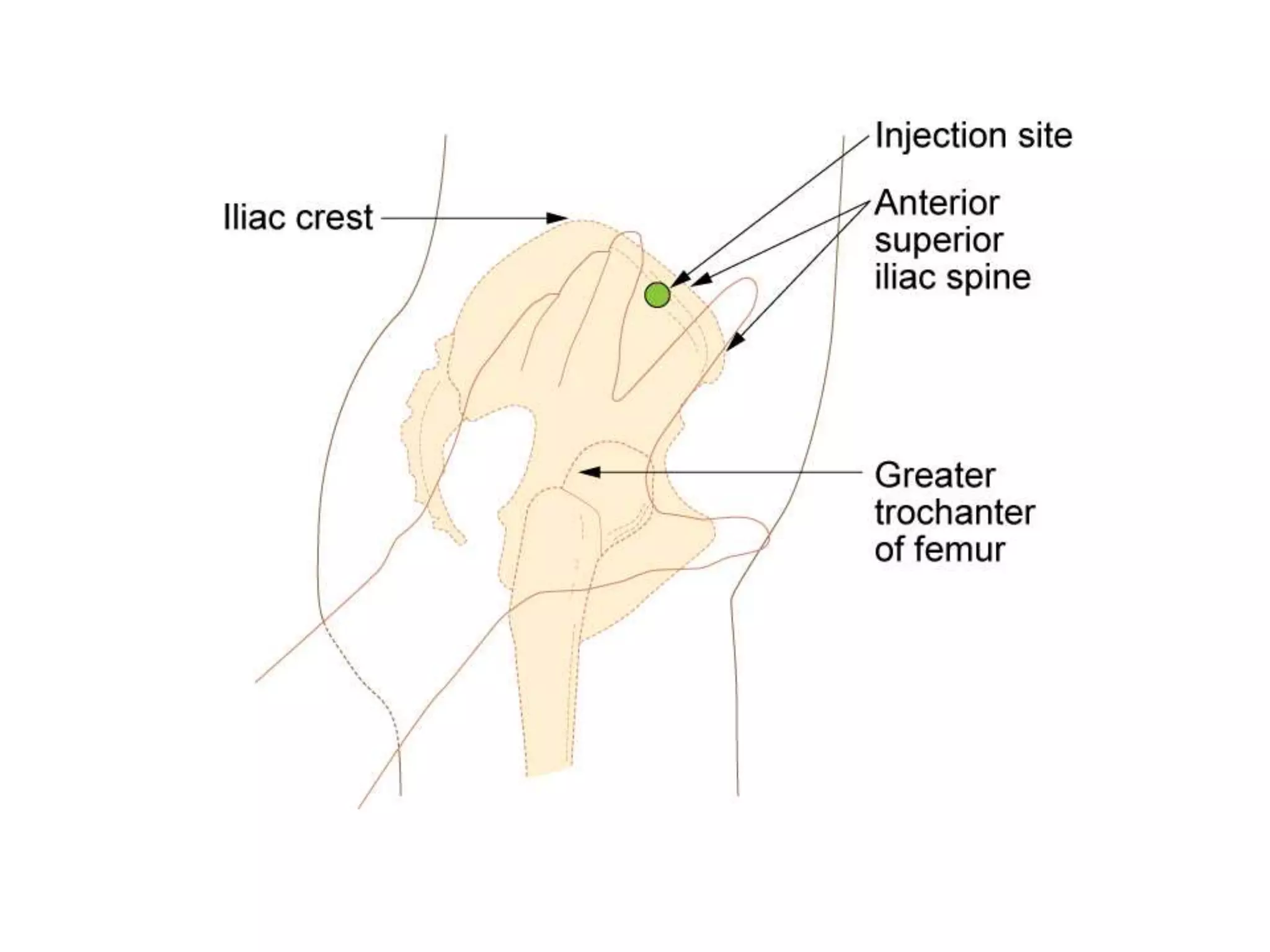
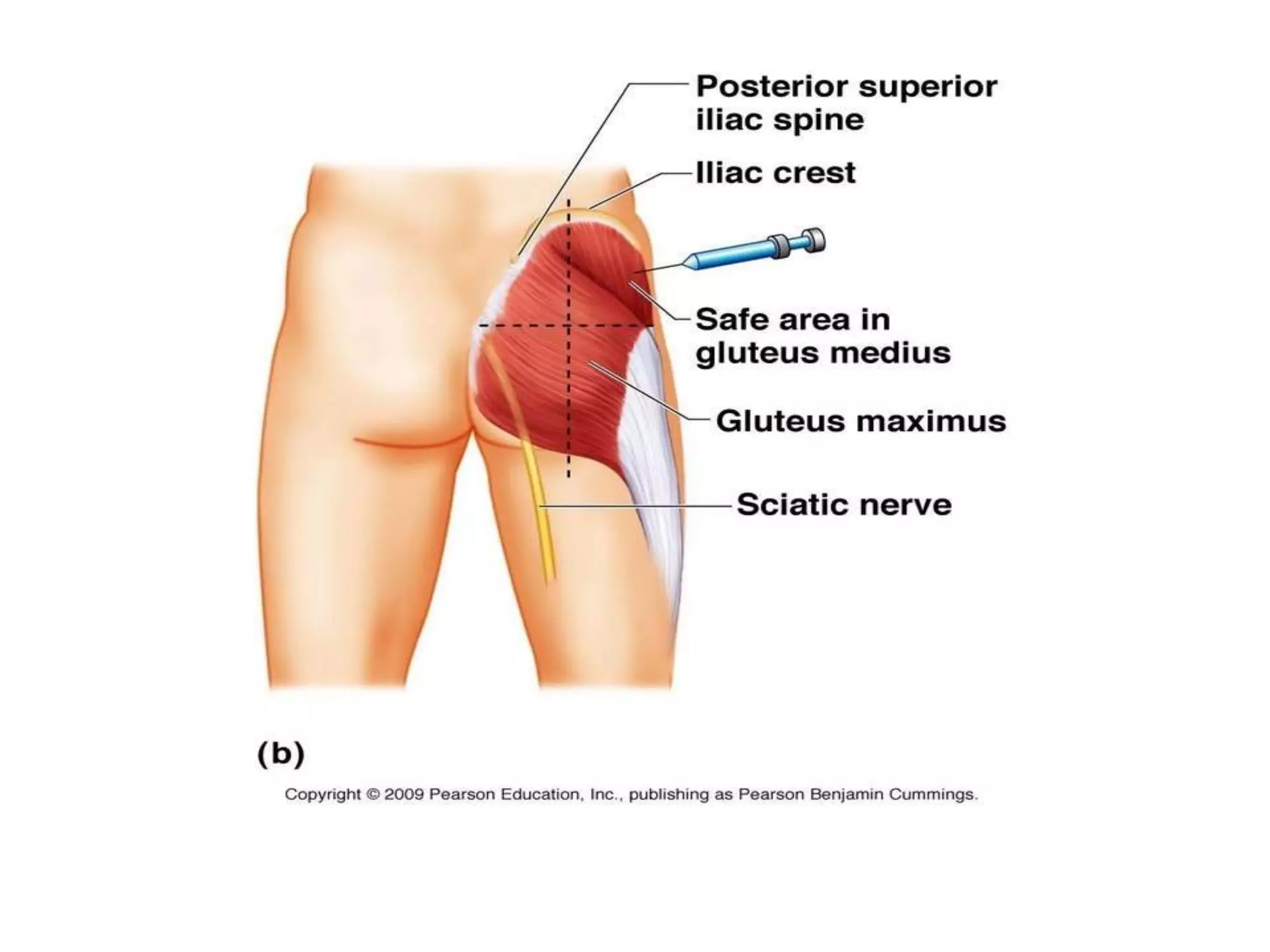
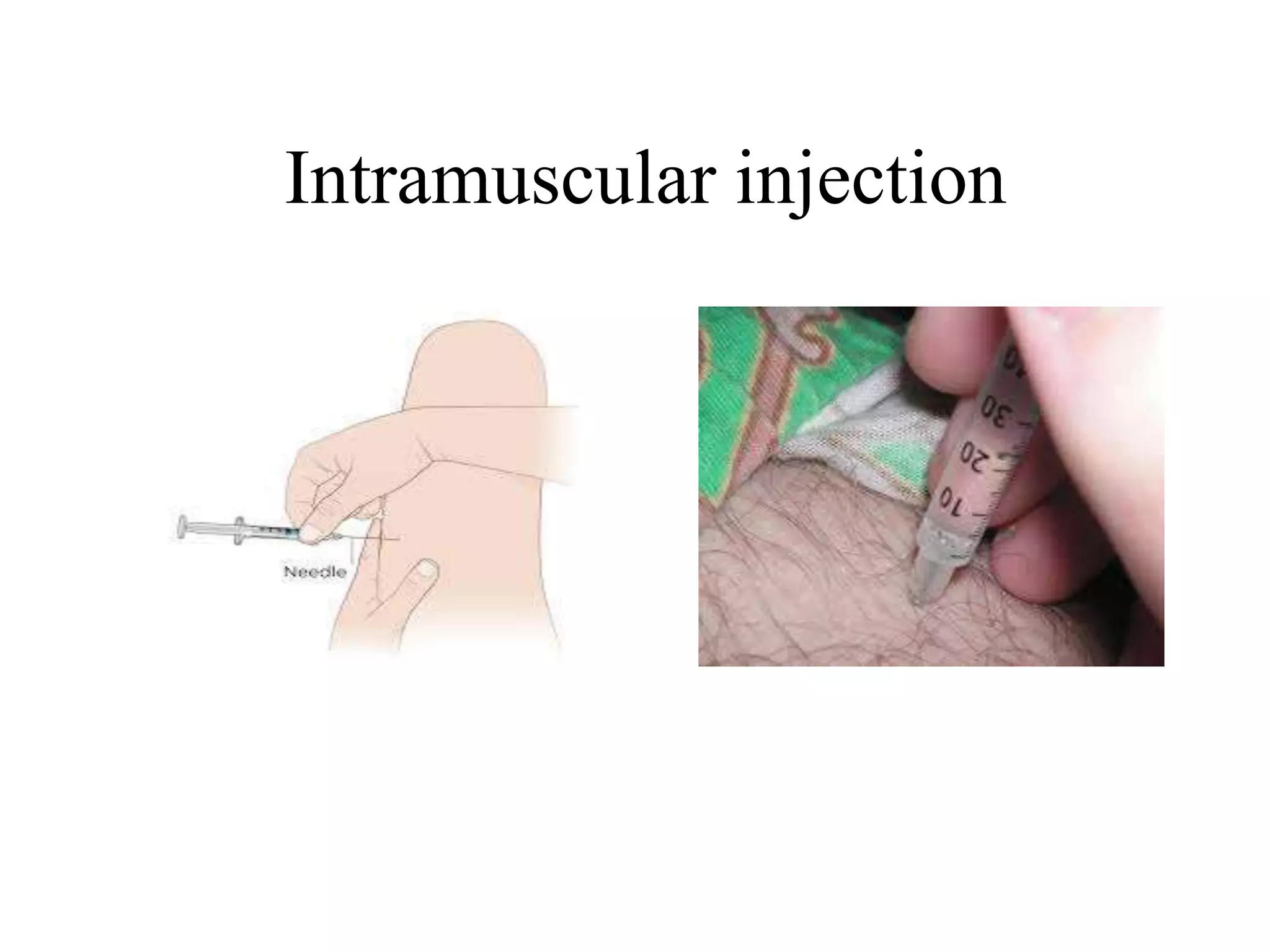
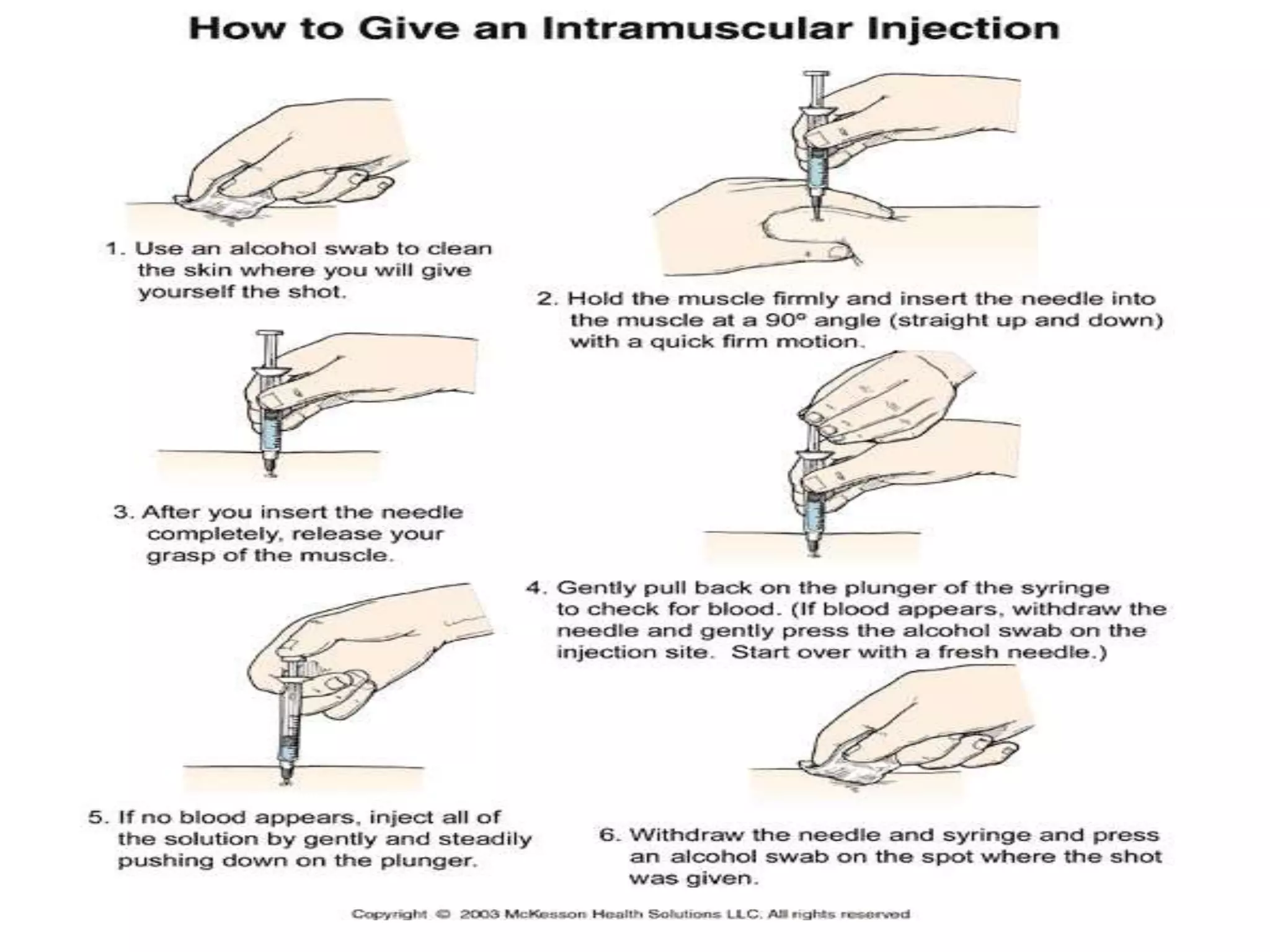
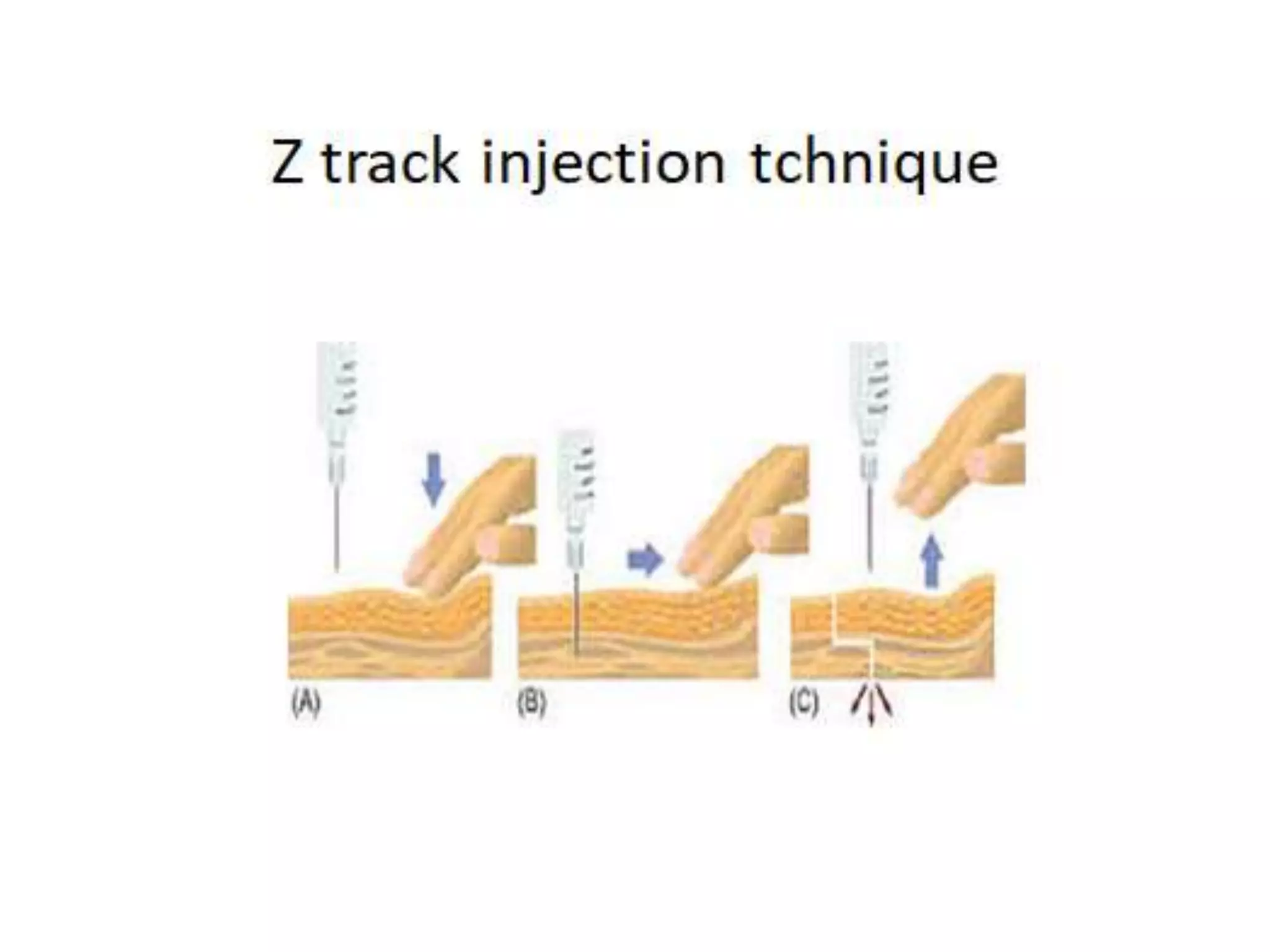
This document discusses intramuscular injections, including their purpose, sites for administration, and procedure. Intramuscular injections deliver medication into muscles to be absorbed into the bloodstream. They are used when oral or IV delivery is not recommended. Common sites are the deltoid, thigh, ventrogluteal, and dorsogluteal muscles. The procedure involves preparing the medication, positioning the patient, cleaning the site, administering the injection at a 90 degree angle, and properly disposing of supplies.