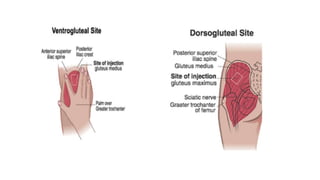
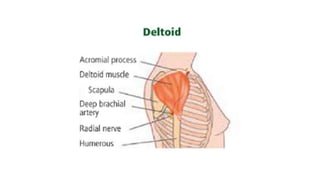
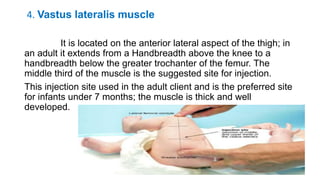
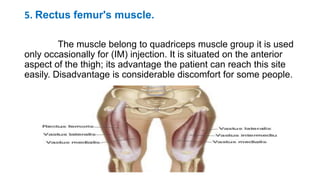
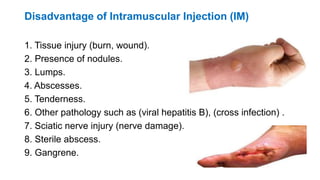
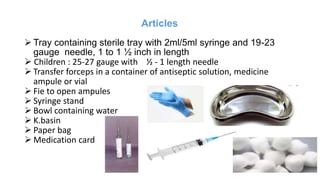
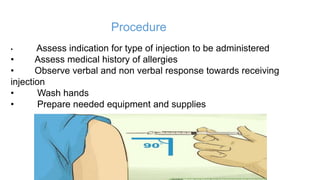
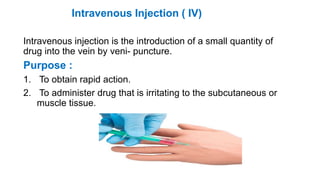
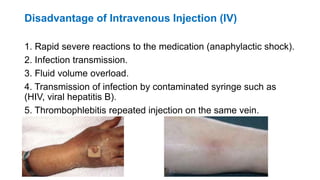
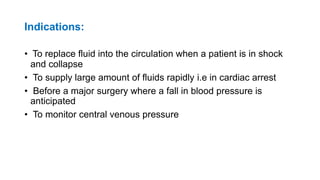
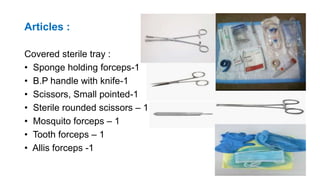
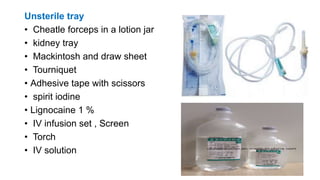
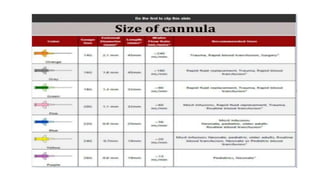
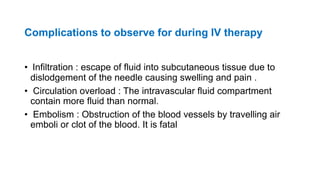
The document provides comprehensive guidelines on intramuscular (IM) and intravenous (IV) injections, detailing definitions, objectives, and step-by-step procedures for administering these injections. It covers various IM injection sites, advantages and disadvantages, IV therapy purposes, potential complications, and necessary equipment. Additionally, it emphasizes the nurse's responsibilities and procedures for venesection when veins are inaccessible.
![INTRAMUSCULAR
&
INTRAVENOUS INJECTION
Prof.Saranya.R,M.sc(N),[Ph.D],
Associate Dean
Dhanalakshmik Srinivasan University](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imiv-240503081312-a0a9ea2a/75/Intramuscular-Intravenous-Injection-pptx-1-2048.jpg)