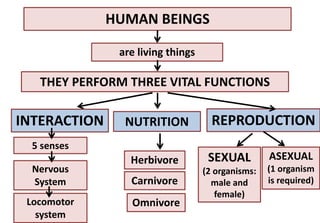
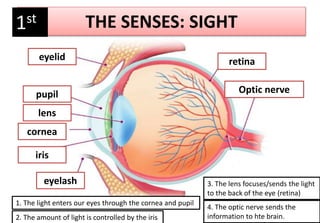
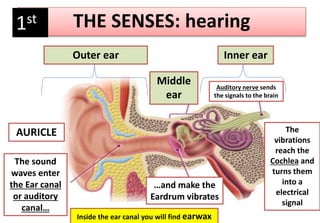
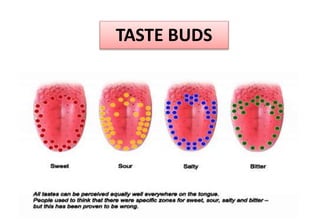
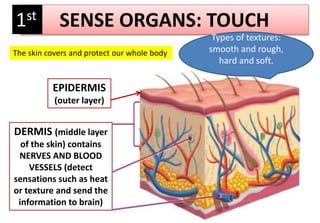
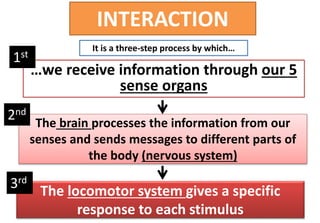
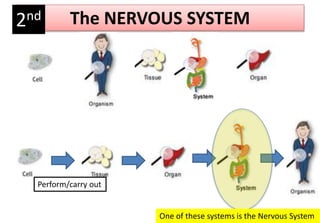
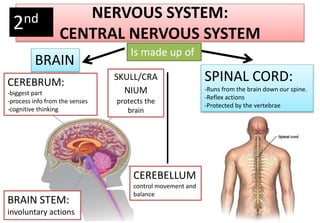
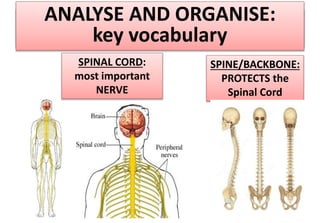
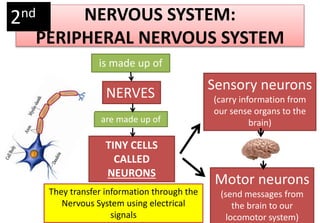
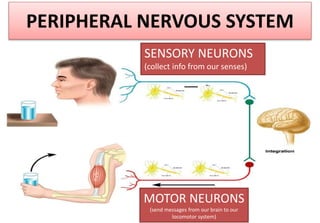
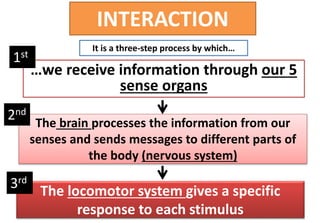
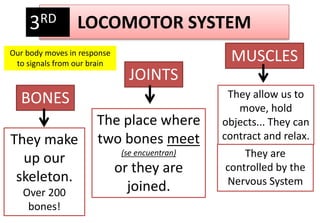
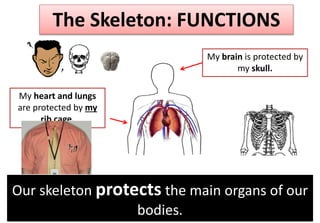
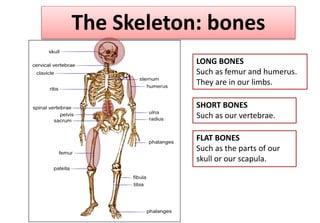
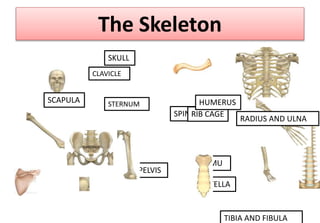
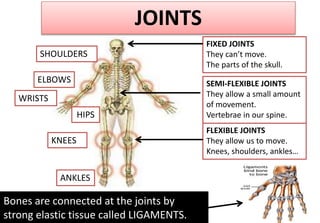
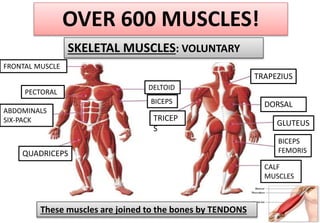
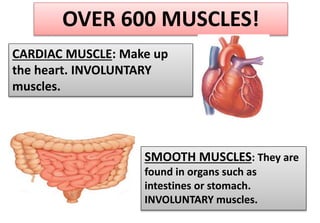
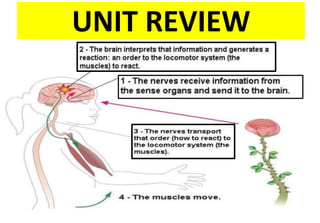
The document summarizes the key aspects of the human interaction systems. It discusses the five senses (sight, hearing, smell, taste, touch), how they receive information from the environment and send it to the brain. It then describes the nervous system, how it processes sensory information and sends signals to control the locomotor system's response. The locomotor system is made up of bones, joints and muscles that allow movement in response to brain signals. It is a three-step interactive process between the senses, nervous system and locomotor system.