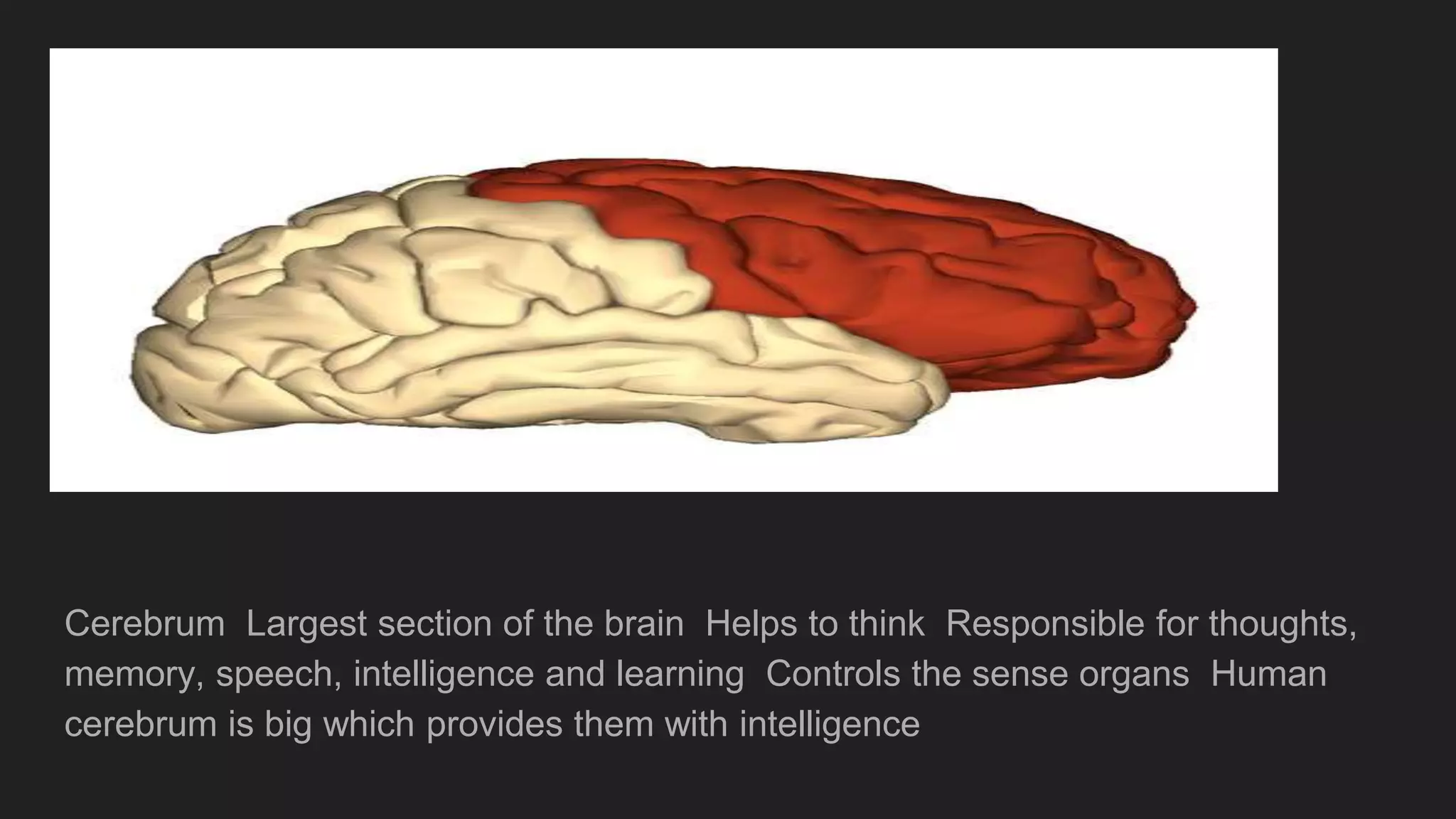
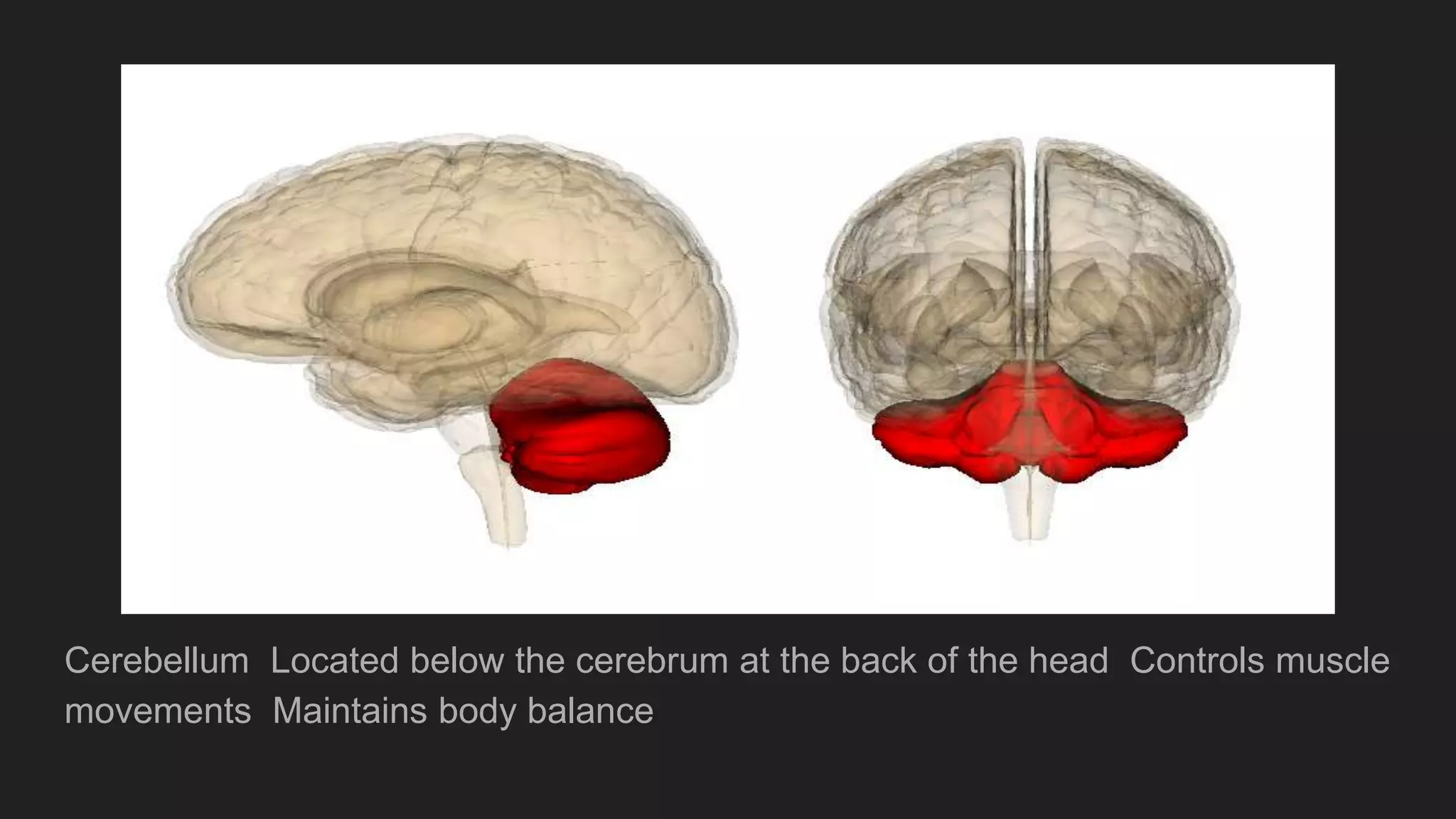
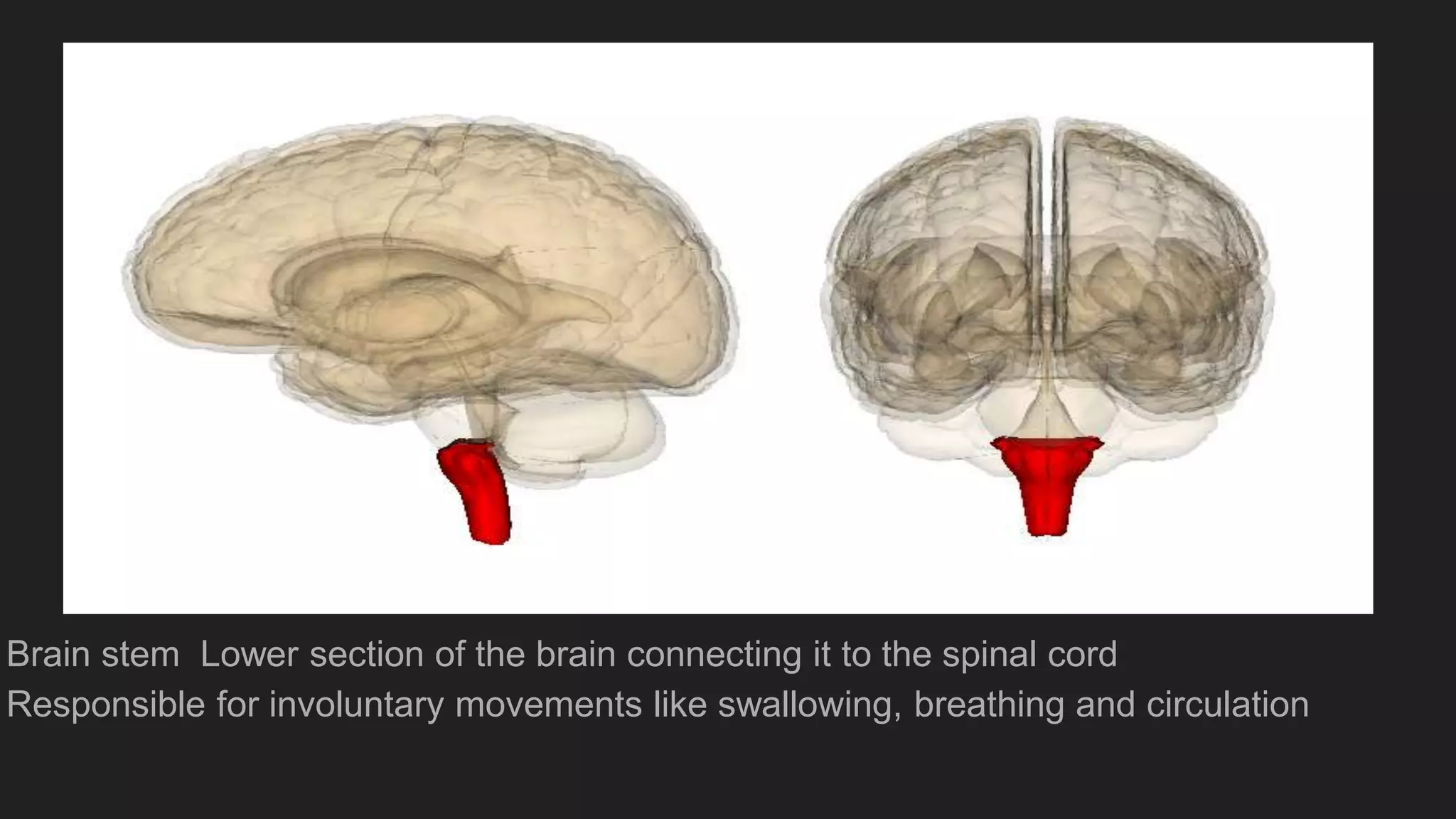
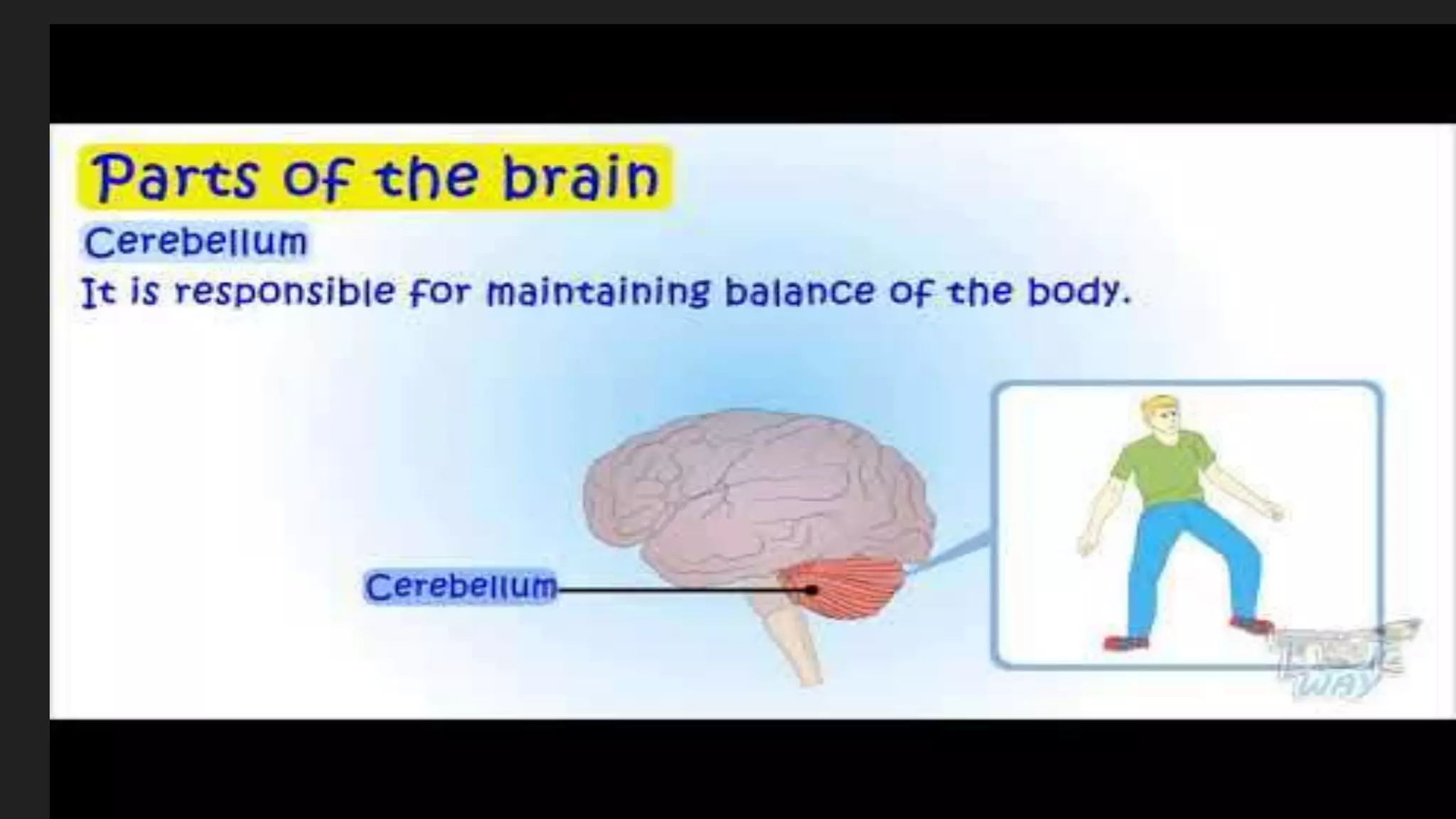
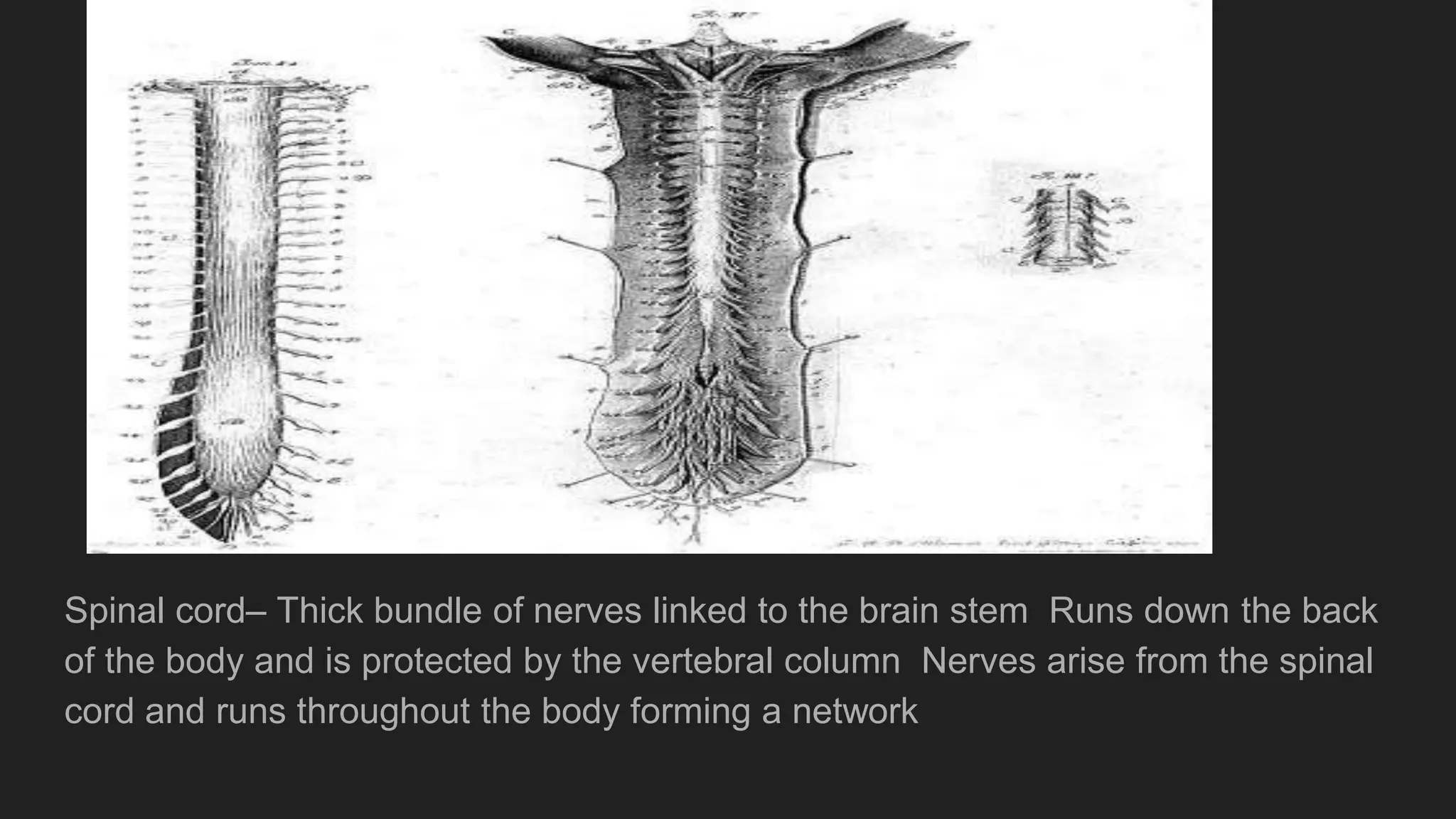
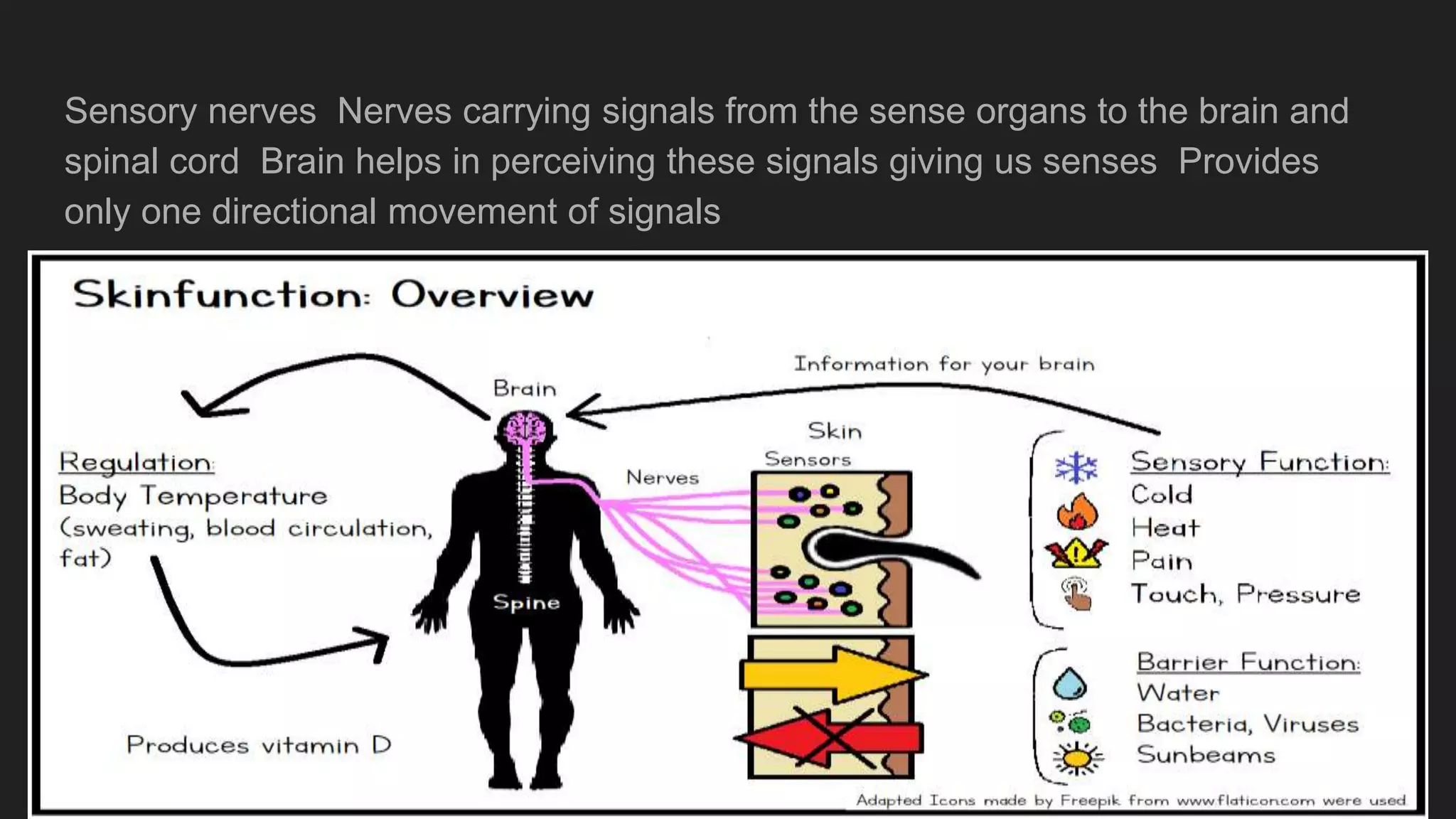
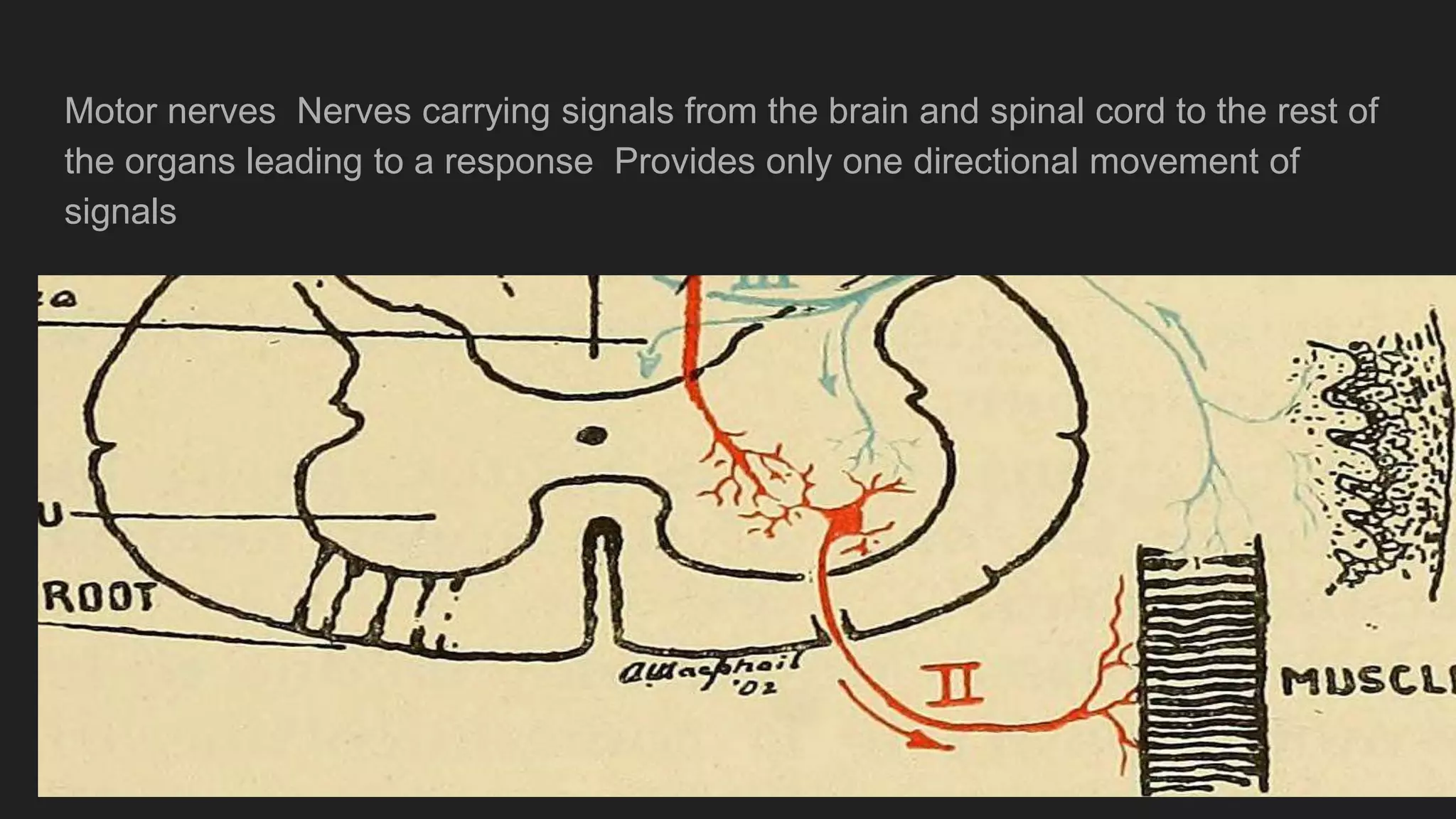
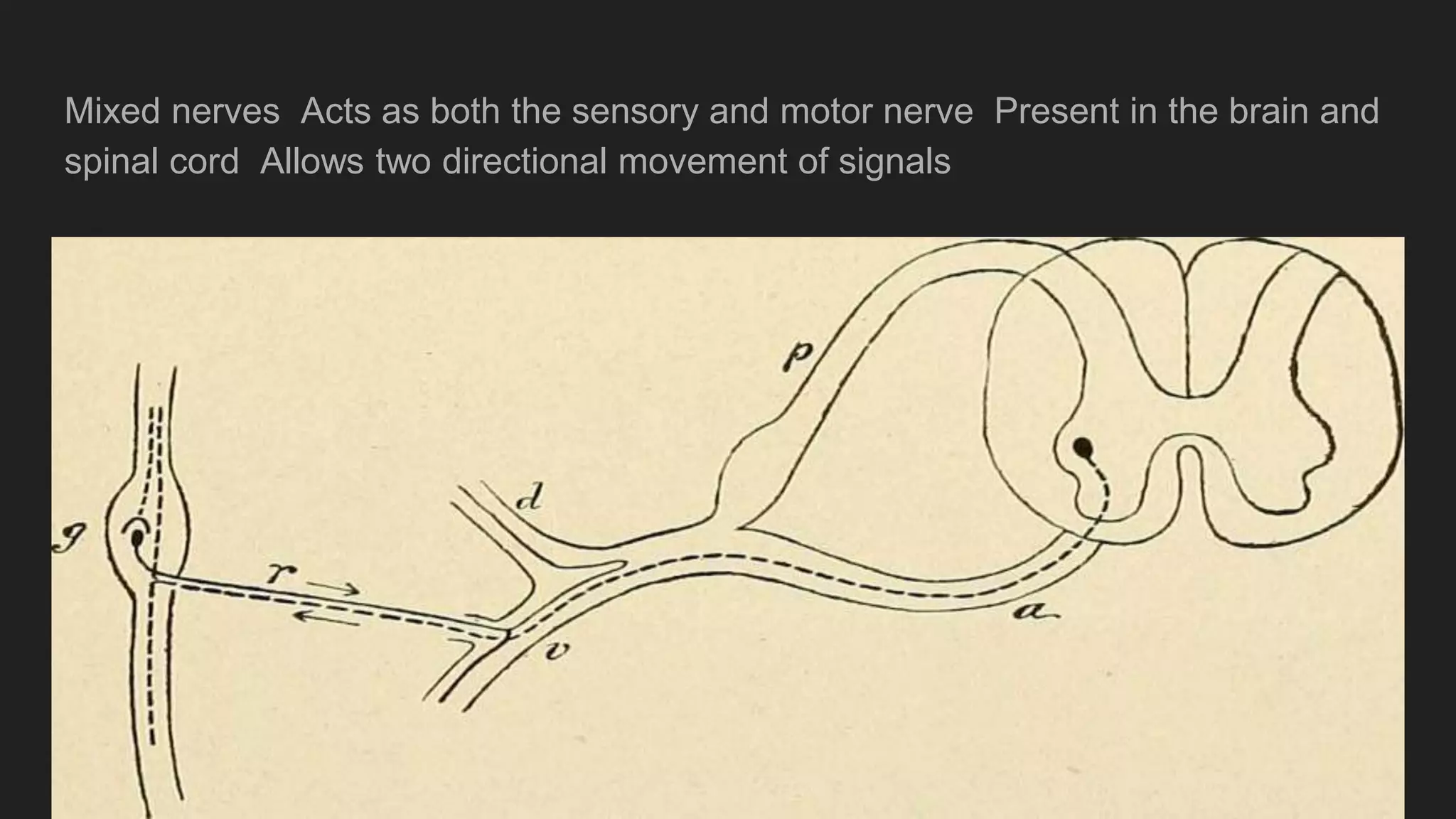
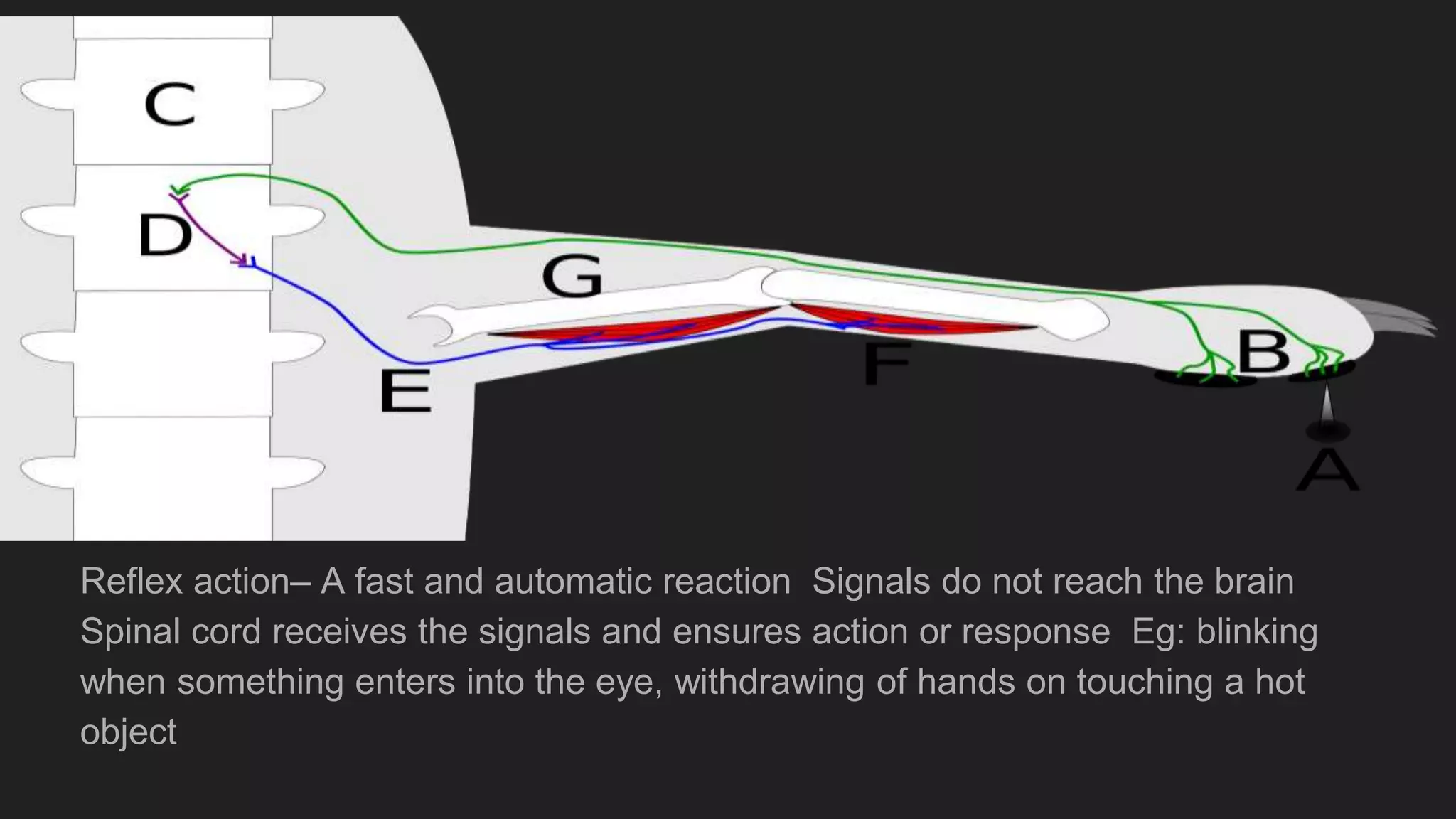
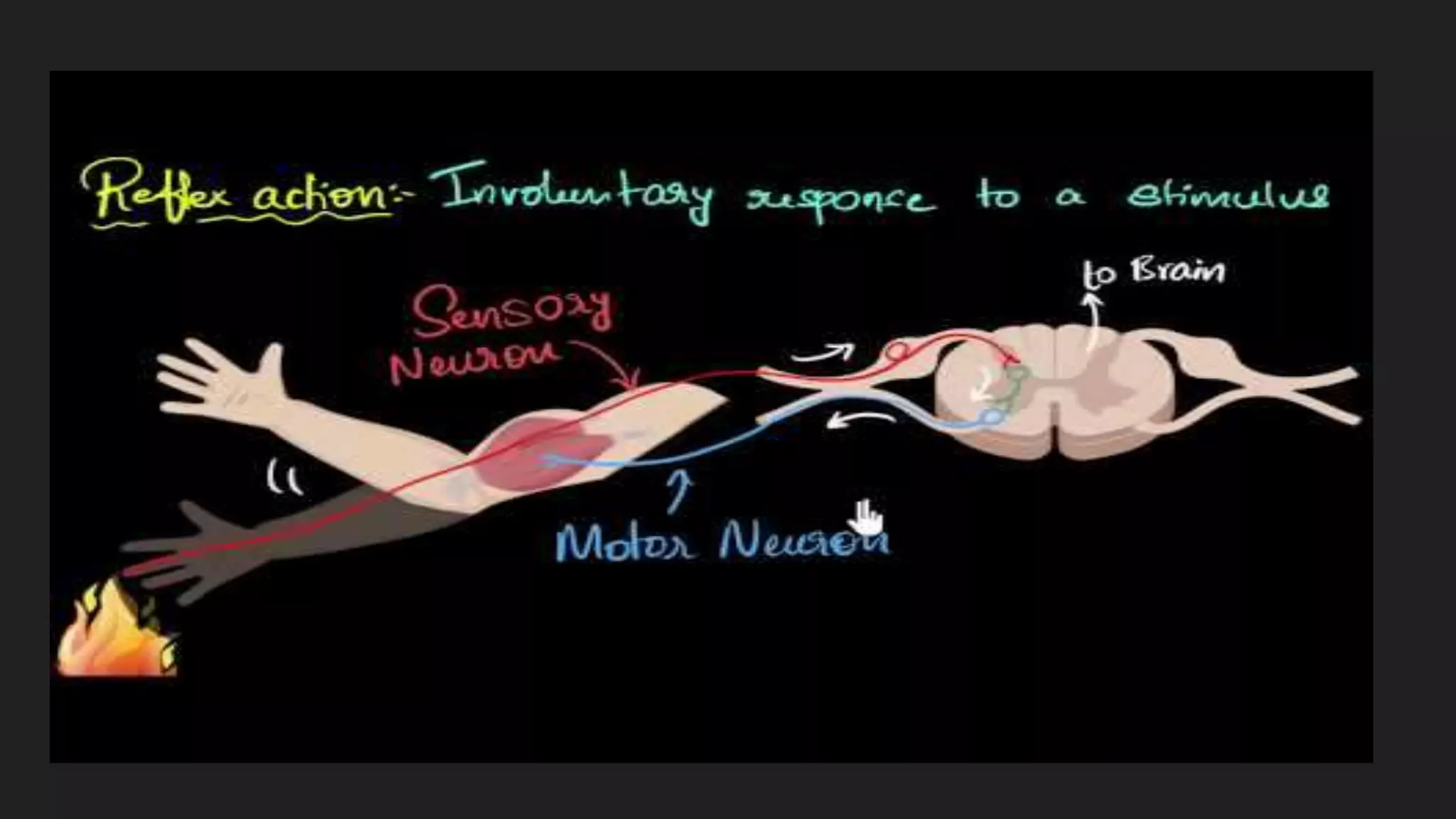
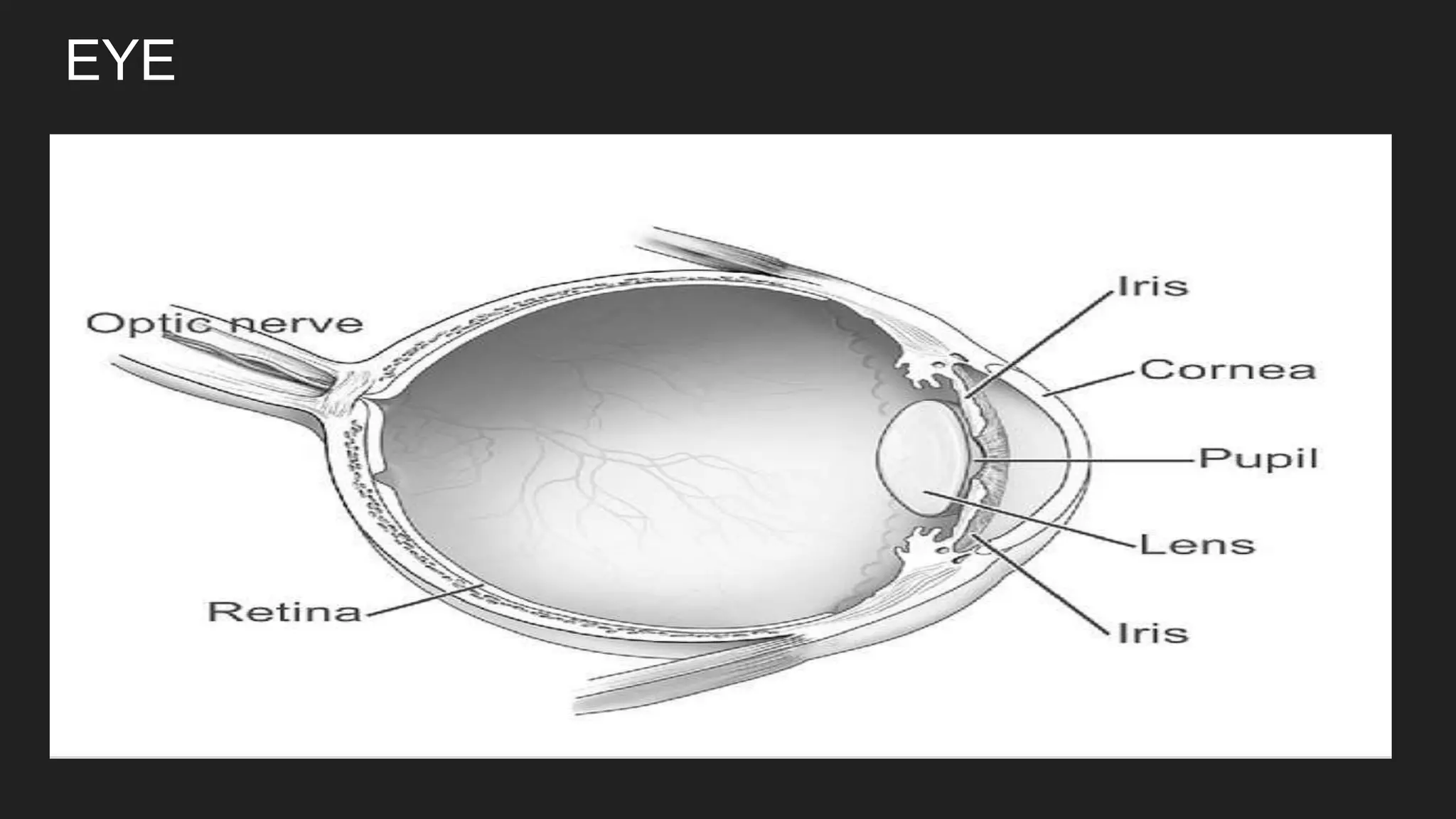
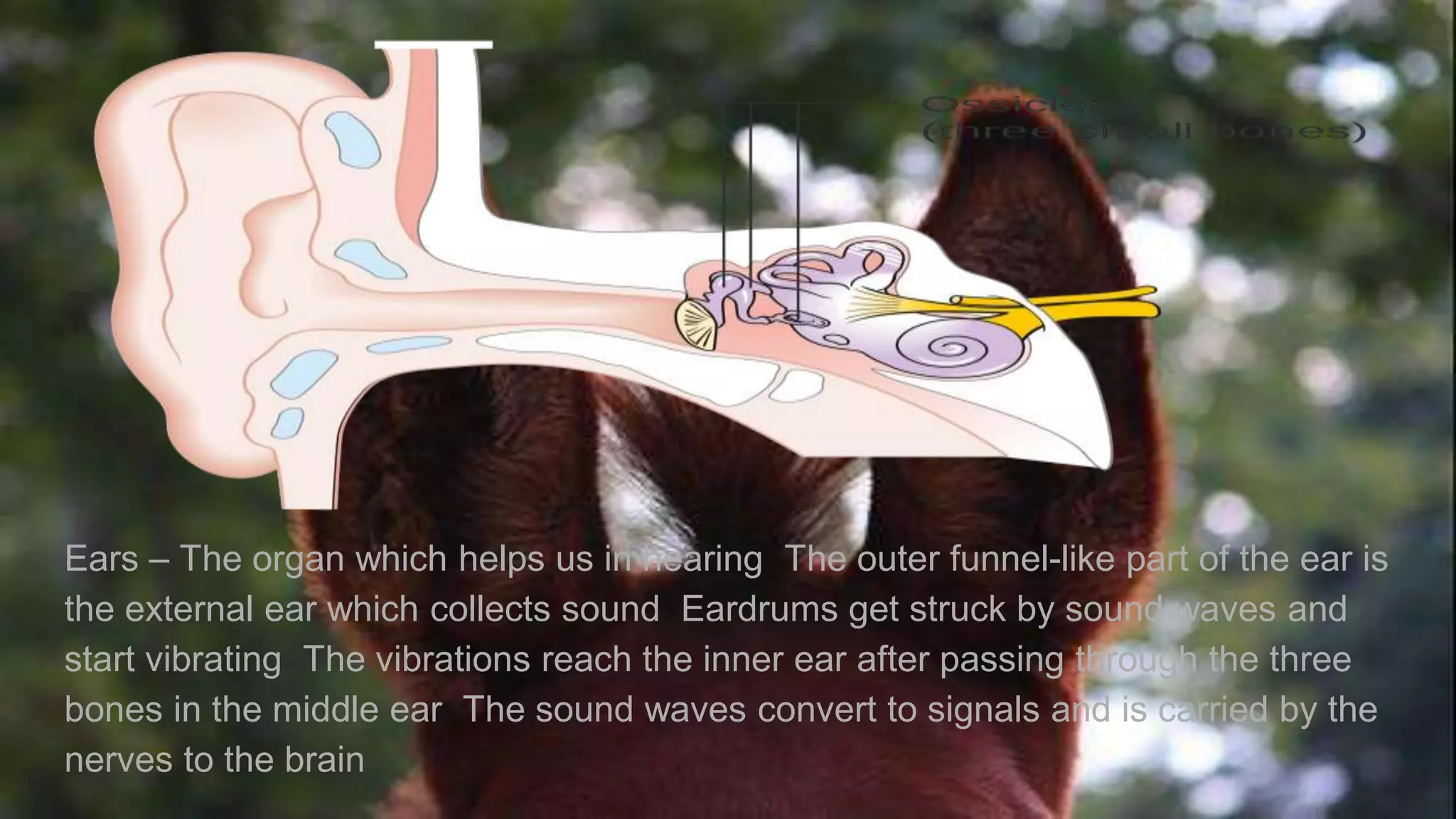
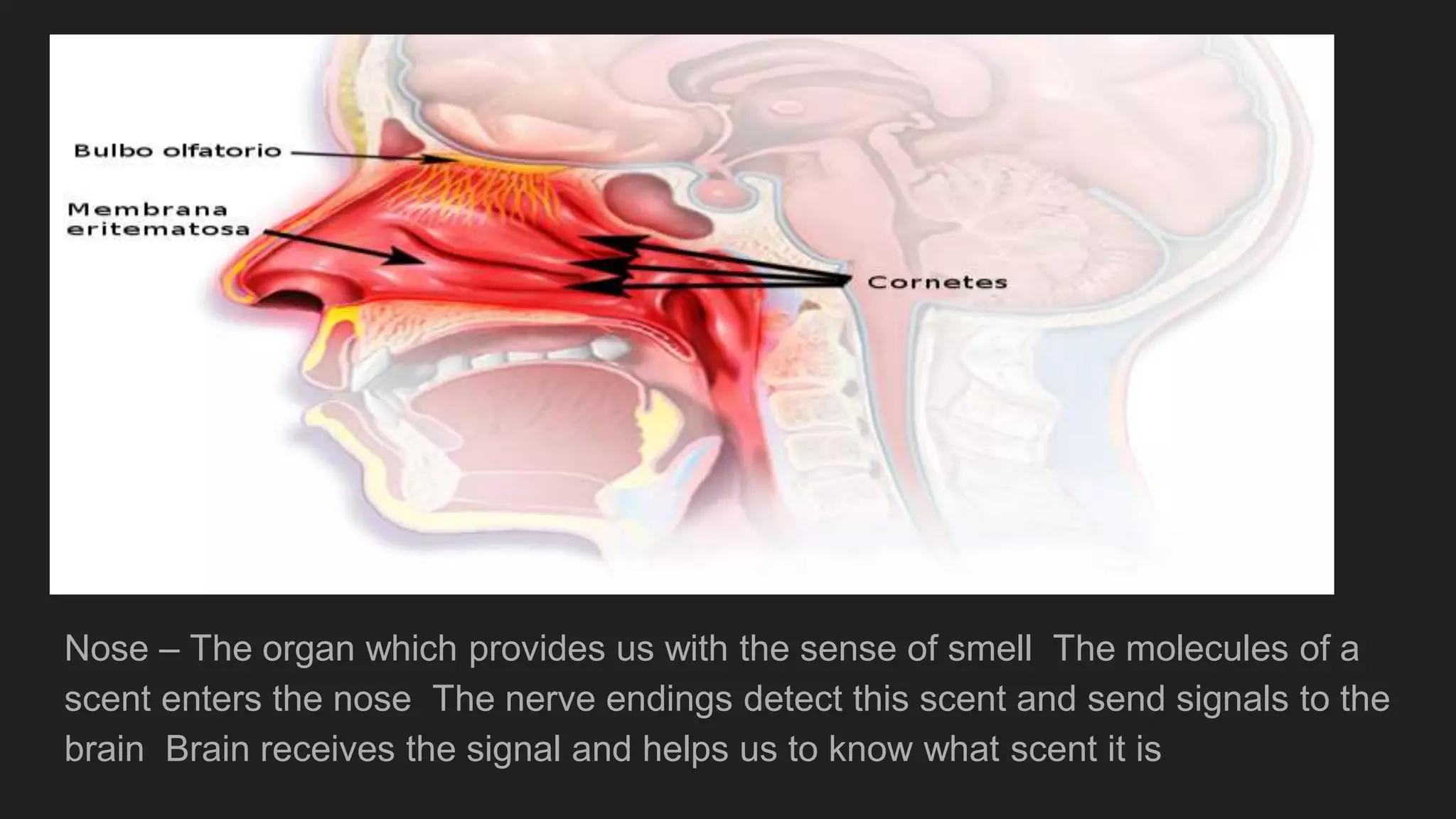
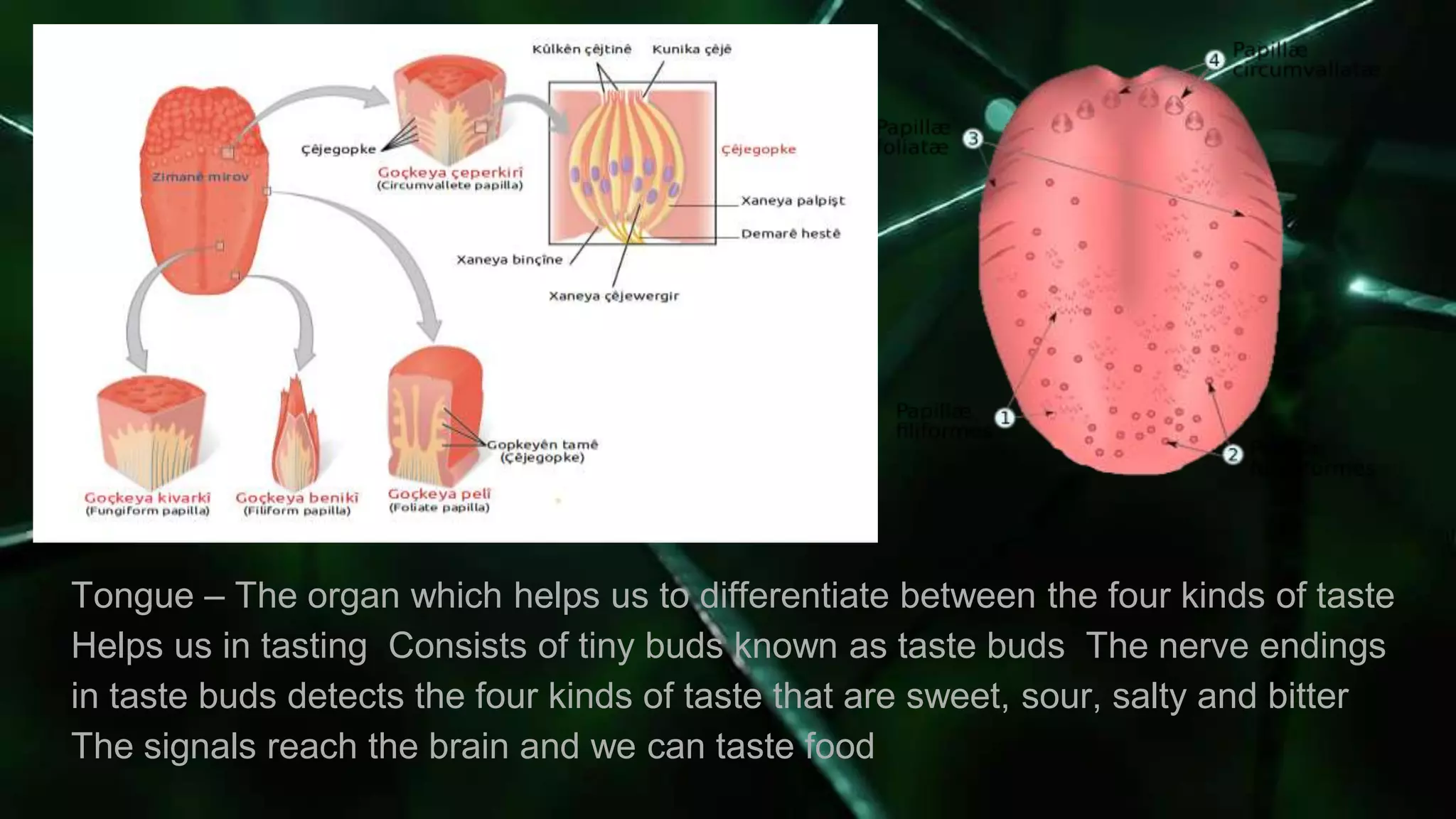
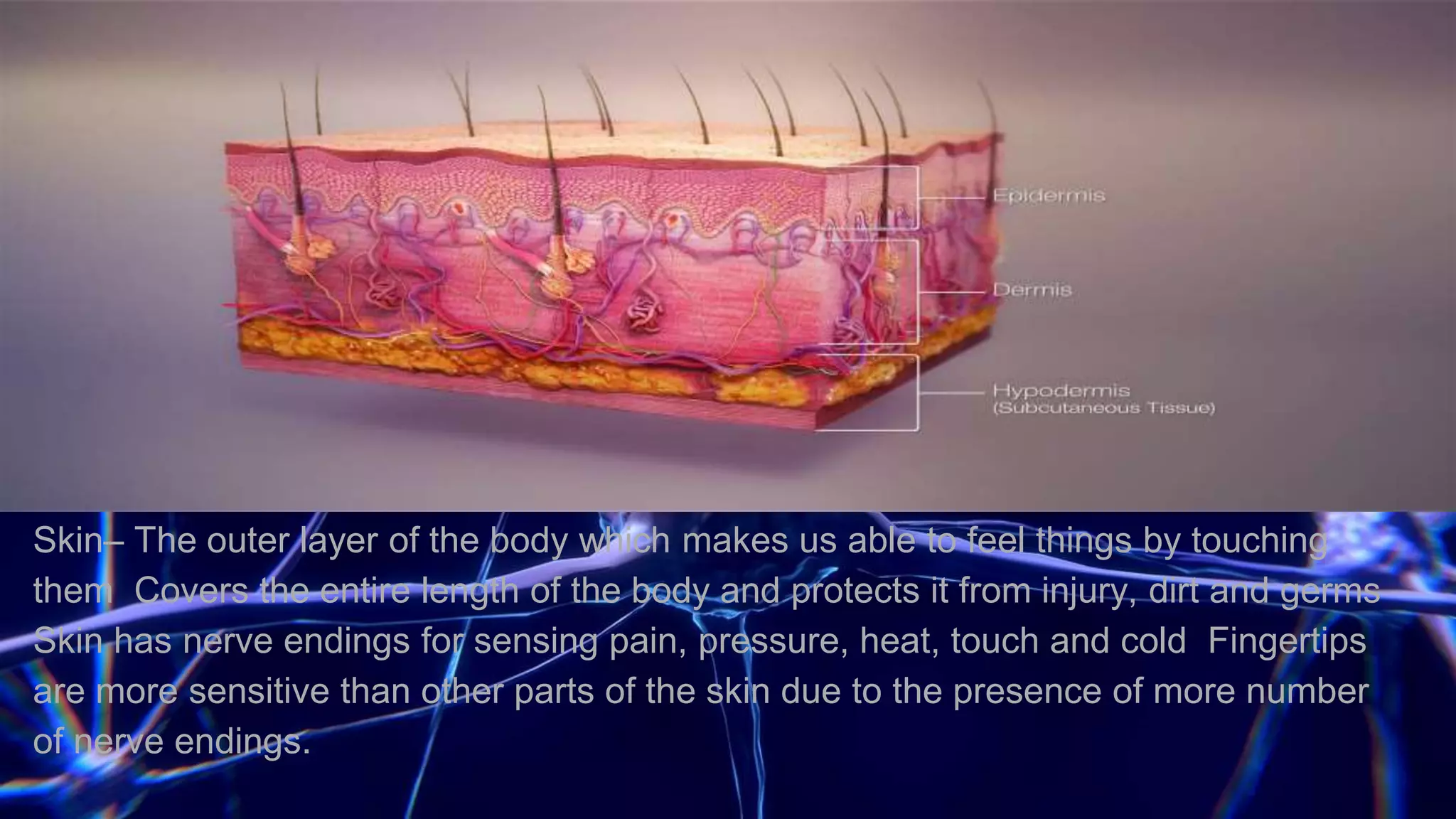
The document summarizes the main components and functions of the human nervous system. It describes the brain as the control center made up of the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem. The spinal cord connects the brain to nerves throughout the body and is responsible for involuntary movements. There are sensory nerves that carry signals to the brain and motor nerves that carry signals from the brain. The five senses - sight, hearing, smell, taste, and touch - allow humans to perceive their environment through specialized sense organs like the eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin.