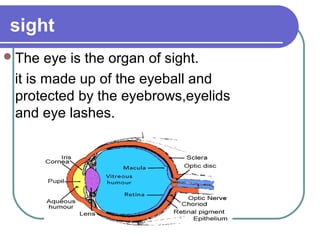
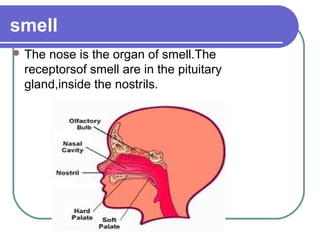
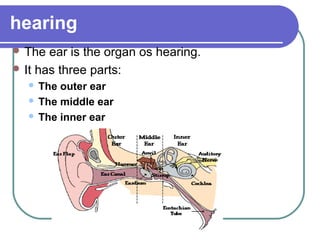
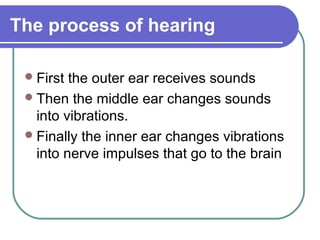
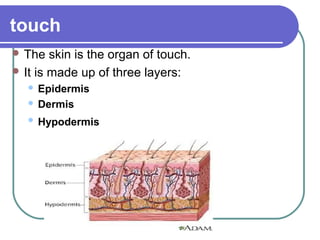
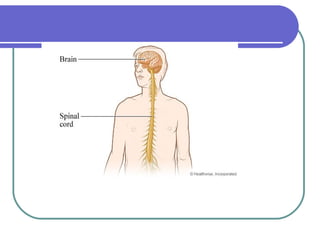
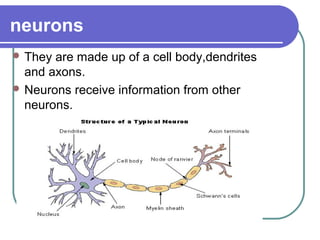
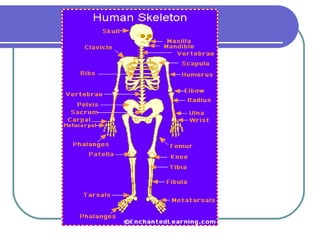
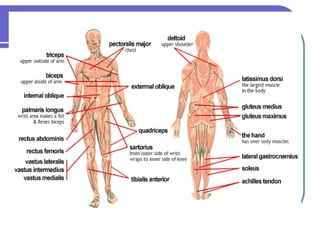
This document discusses the human body's sensory and response systems. It describes the different types of stimuli, receptors, and responses. The five senses are explained, including the organs and processes involved in sight, smell, hearing, touch, and taste. The nervous system and its role in transmitting sensory information to the brain and motor responses is outlined. Voluntary and involuntary movements are distinguished. Finally, the skeletal and muscular systems are introduced as the structures responsible for carrying out muscular responses directed by the nervous system.