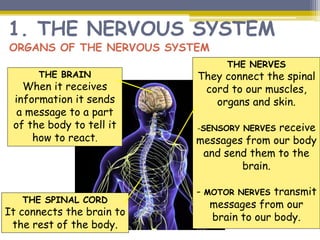
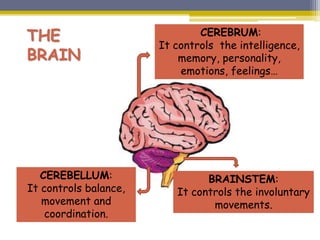
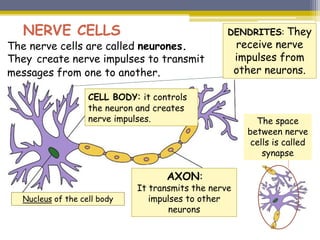
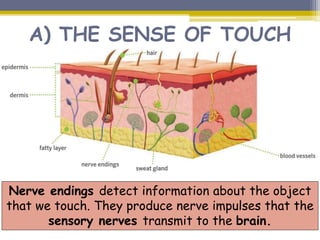
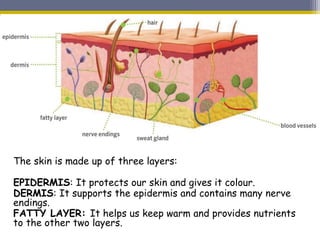
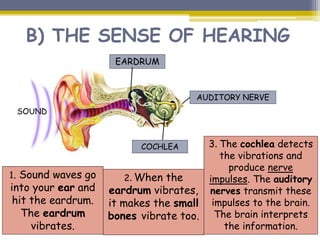
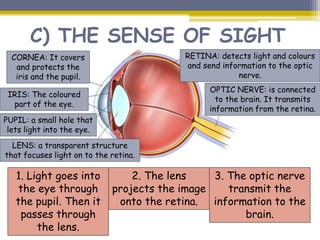
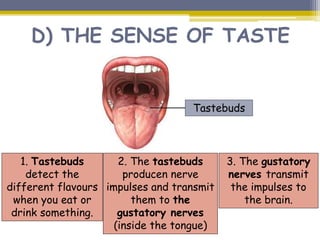
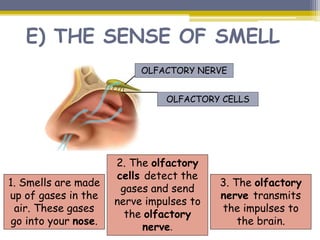
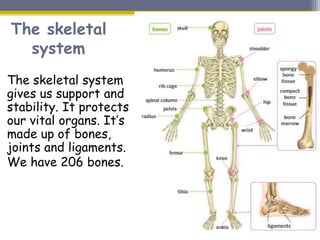
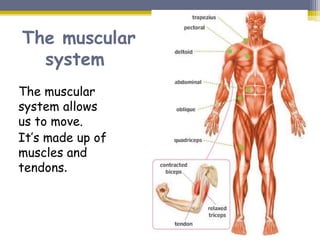
This document provides information about the nervous system and locomotor system. It discusses the main organs of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. It describes how the nervous system allows for interaction with the environment through the five senses of touch, hearing, sight, taste, and smell. The document also explains that the locomotor system consists of the skeletal and muscular systems which provide structure, protection, and enable movement.