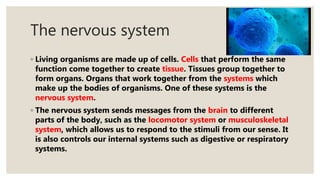
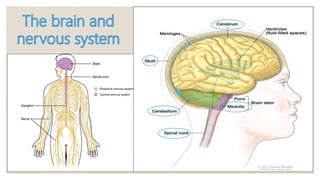
The document discusses the functions of the nervous system. It states that the nervous system sends messages from the brain to different parts of the body to allow responses to stimuli from the senses. It also controls internal systems like digestion and respiration. The brain is the most important organ as it controls the nervous system and processes information from the senses. It is made up of the cerebrum, cerebellum and brain stem which control cognitive thinking, movement and involuntary functions respectively. The spinal cord runs from the brain down the spine and controls reflex actions.