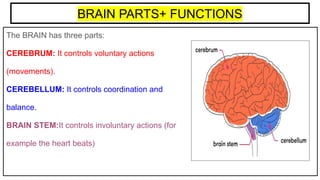
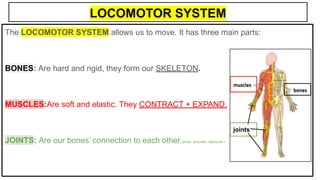
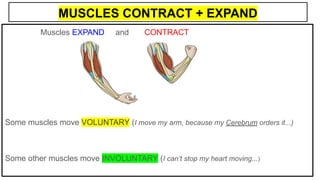
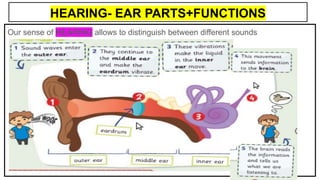
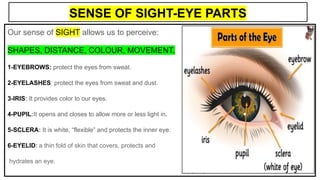
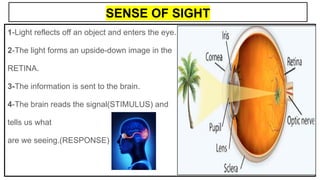
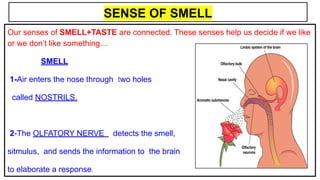
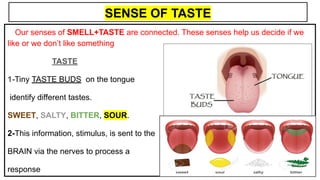
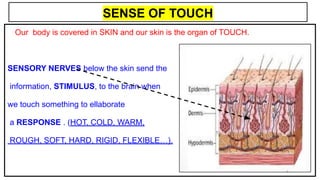
This document provides an overview of the five senses and how they work. It discusses the main parts of the brain and their functions in processing sensory information and controlling voluntary and involuntary actions. The three main parts of the locomotor system that allow movement are also outlined. Additionally, the key parts and functions of the eye, ear, nose, tongue, and skin that enable sight, hearing, smell, taste, and touch are summarized. The process of a sense organ receiving a stimulus, sending the information to the brain, and the brain responding is explained.