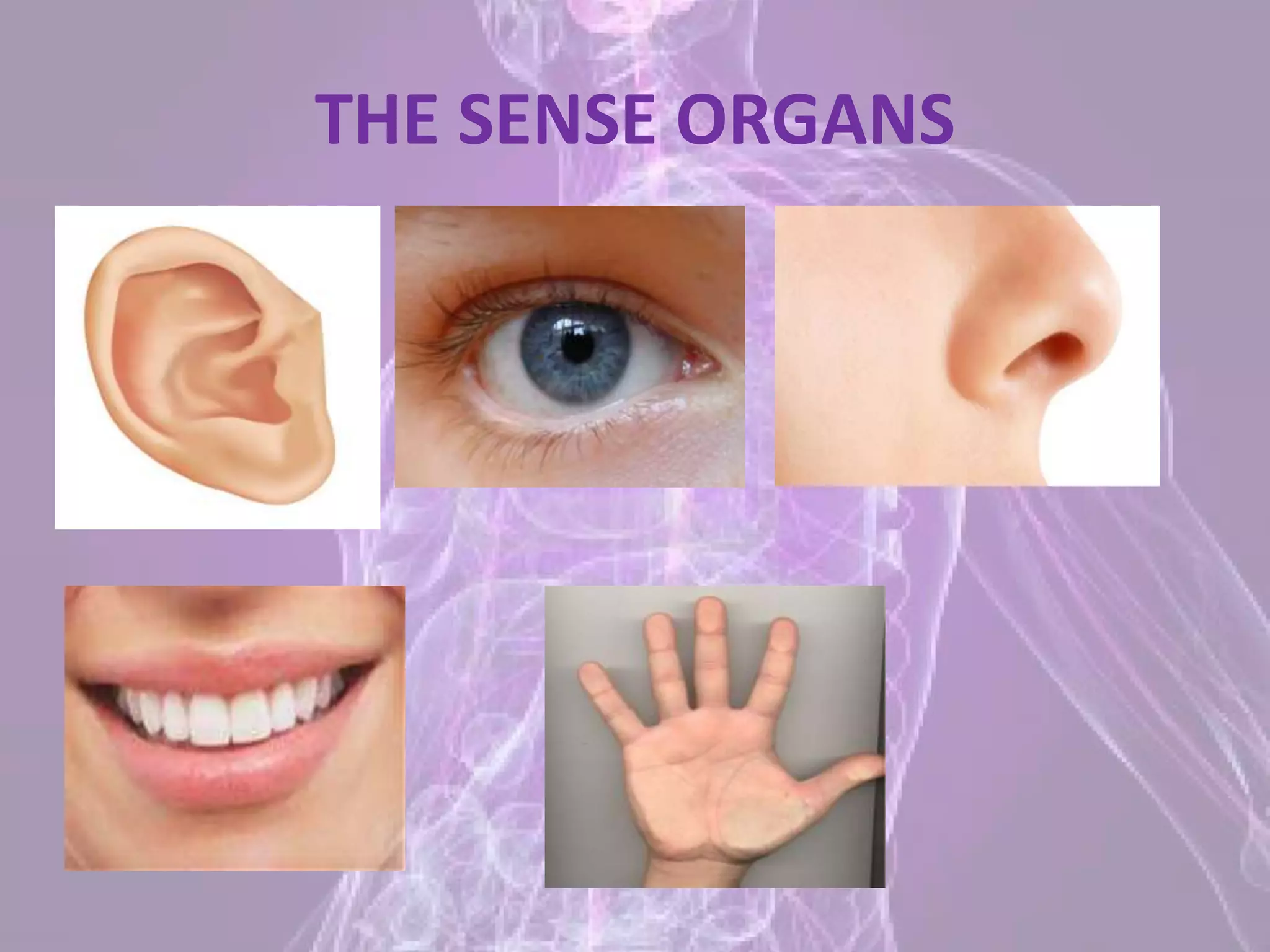
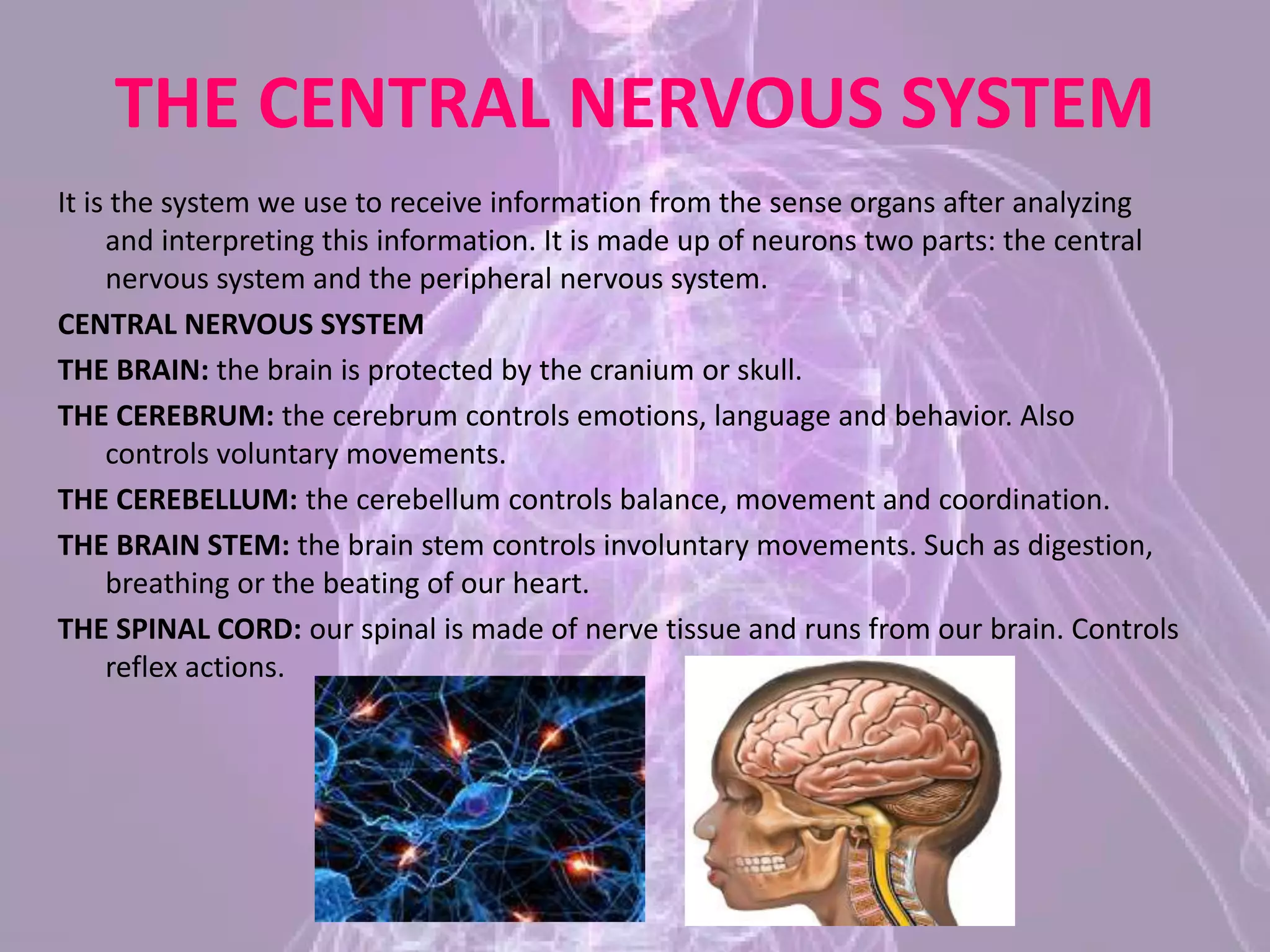
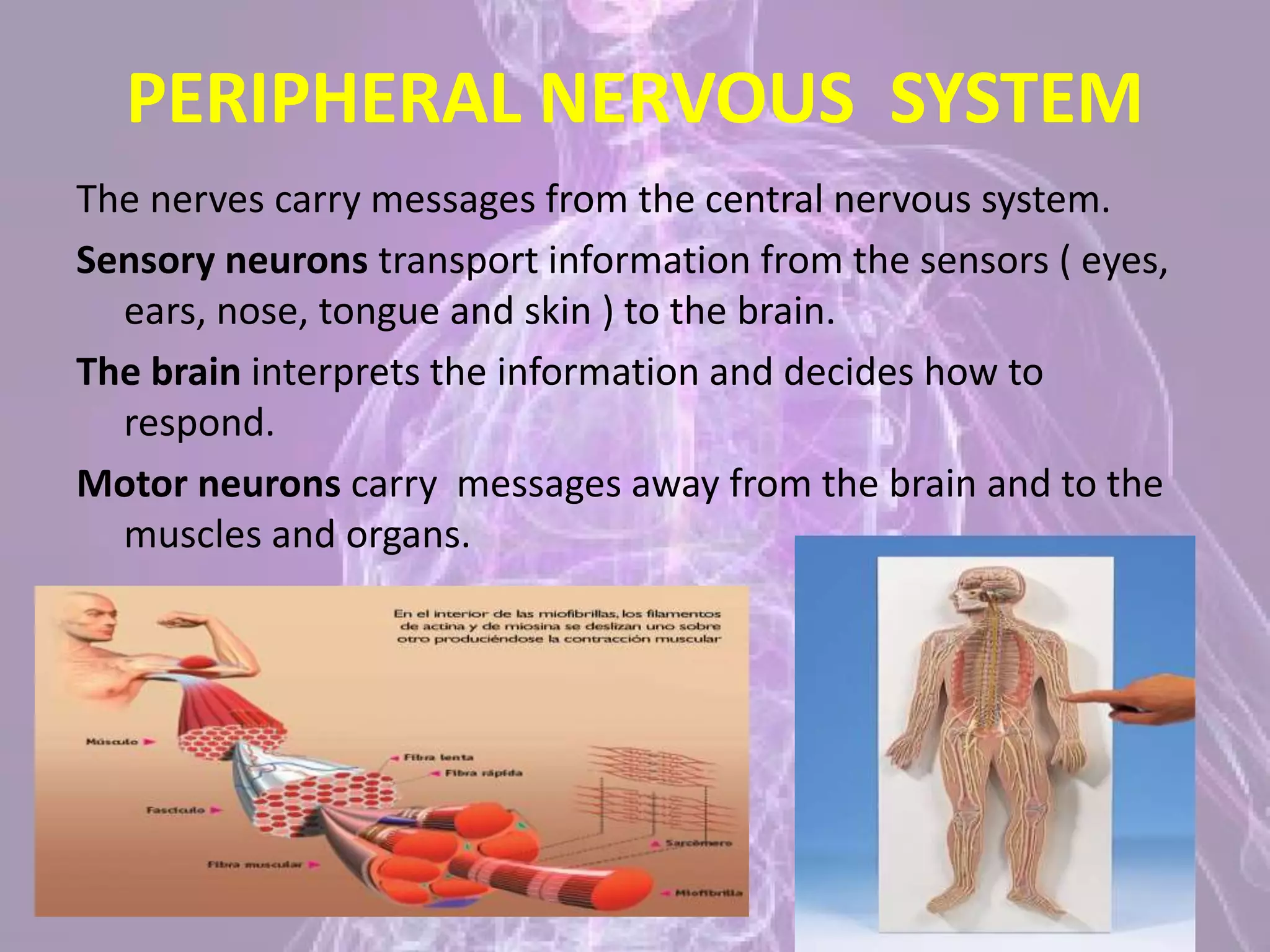
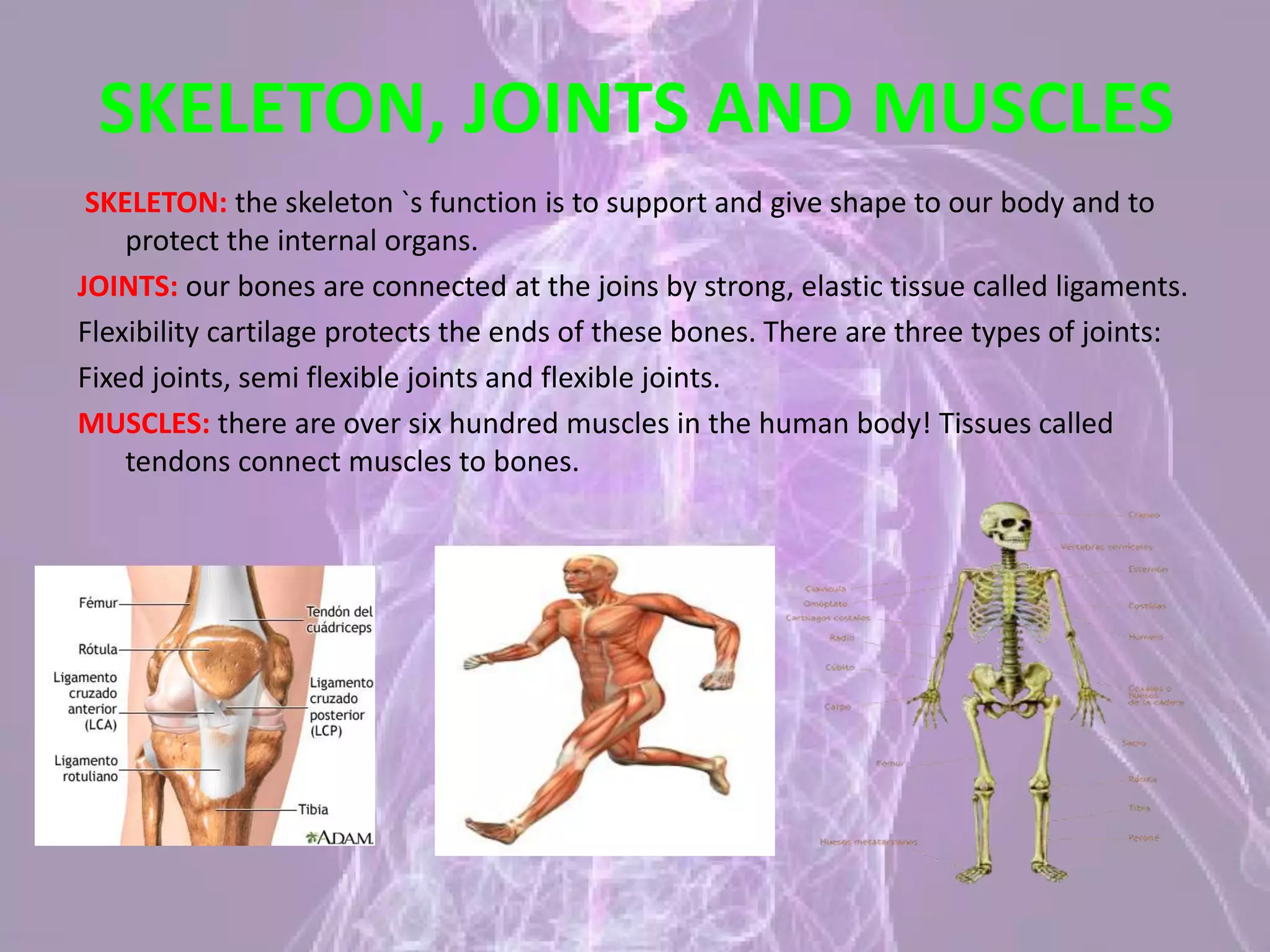
The document summarizes the five senses - sight, hearing, smell, taste, and touch - and describes how each sense works and the organs involved. It then discusses the central nervous system, including the brain, cerebellum, brain stem, and spinal cord. Finally, it briefly outlines the peripheral nervous system, skeleton, joints, and muscles. The key points are that the five senses detect stimuli and send signals to the brain for processing, and that the central and peripheral nervous systems work together to receive sensory information and control the body's responses.