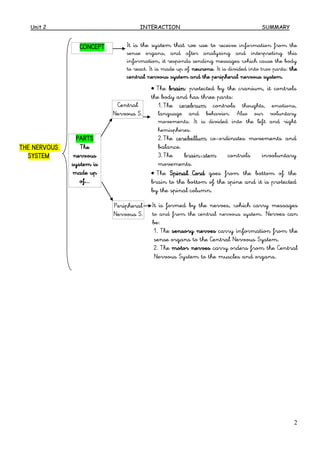
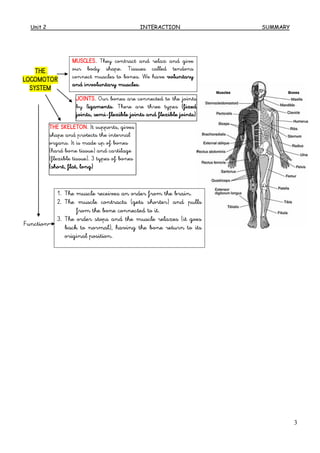
The document summarizes the key human body systems involved in interaction: the sense organs, nervous system, and locomotor system. It describes how the sense organs (sight, smell, taste, hearing, touch) detect stimuli and send this information to the brain via sensory neurons. The brain then interprets the information and sends orders to the muscles via the nervous system. Upon receiving signals, the muscles and skeleton (via joints) work together as the locomotor system to move the body and allow interaction with the environment.