1. Coagulation disorders are caused by deficiencies in clotting factors that lead to defects in normal clot formation. They can be hereditary or acquired.
2. Hereditary disorders include hemophilia A and B which are sex-linked deficiencies in factors VIII and IX respectively, and von Willebrand disease which is an autosomal disorder involving a defect in von Willebrand factor.
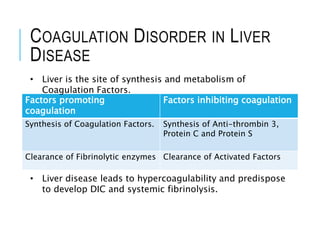
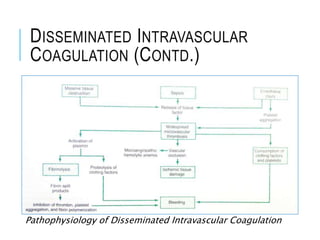
3. Acquired disorders involve deficiencies in multiple clotting factors and can result from vitamin K deficiency, liver disease, fibrinolytic defects, or disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). DIC occurs as a complication of other systemic illnesses.