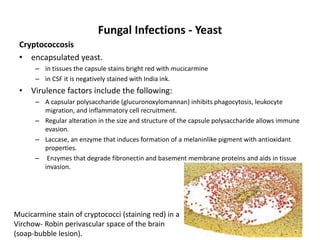
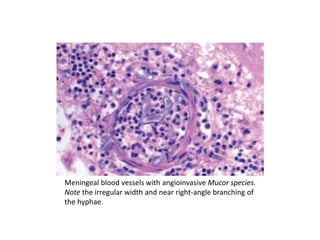
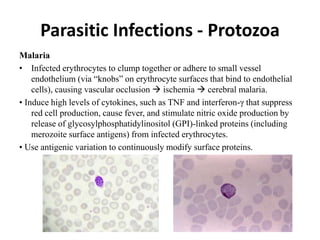
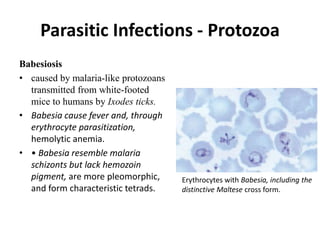
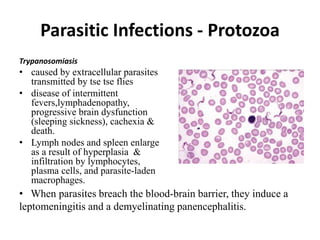
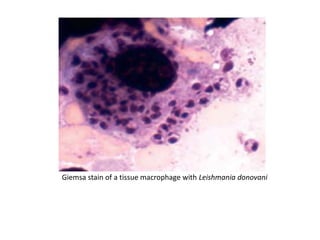
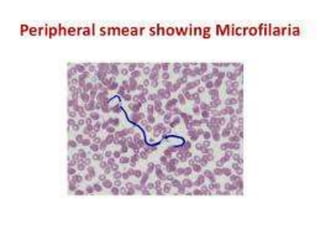
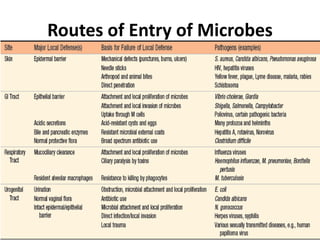
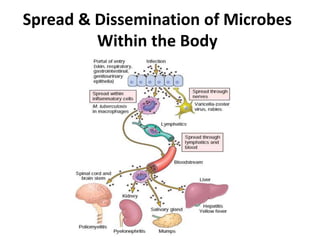
Microbes cause disease through several mechanisms: (1) attenuation of the host's normal defenses allows commensal flora to cause infections; (2) highly infectious microbes can produce disease even in healthy individuals; (3) microbes enter the body through various routes and disseminate via person-to-person contact or vectors; (4) microbes evade and manipulate the immune system through strategies like antigenic variation and resistance to antimicrobials; (5) both microbial infection and immune response can directly damage host tissues.






![Infections in People With
Immunodeficiencies
Genetic immunodeficiencies
• Antibody deficiencies
– X-linked agammaglobulinemia is associated with Streptococcus pneumoniae,
Haemophilus influenzae, Staphylococcus aureus, rotavirus, & enterovirus
infections.
• Complement proteins:
– Associated with infections due to encapsulated bacteria (e.g., S. pneumoniae
for early complement components & Neisseria meningitidis for late [C5 to C9]
elements).
• Neutrophil function:
– Infections from S. aureus, gram-negative bacteria, & fungi.
• T-cell deficiencies:
– Infections due to intracellular pathogens (e.g.viruses & some parasites); defects
in TH1 generation increase the risk of infections by atypical mycobacteria, &
defects in TH17 generation are associated with chronic mucocutaneous
candidiasis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infectiousdiseasesch8-190920170149/85/Infectious-diseases-12-320.jpg)
![Infections in People With
Immunodeficiencies
Acquired immunodeficiencies:
HIV annihilation of T-helper cells is associated with a variety of
infections
• Most organisms that infect people with AIDS were common
pathogens before the era of HIV-AIDS
• Uncommon organisms were Kaposi sarcoma herpes virus
[KSHV], cryptococcus, & Pneumocystis.
• Malnutrition also broadly impairs immune defenses.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infectiousdiseasesch8-190920170149/85/Infectious-diseases-13-320.jpg)






![Mechanisms of Bacterial Injury
Bacterial Toxins
Endotoxins (lipopolysaccharide [LPS])
• It is a cell wall component of gram-negative bacteria
composed of a common long-chain fatty acid (lipid A) & a
variable carbohydrate chain (O antigen).
• Low doses of the lipid A component elicit protective
inflammatory cell recruitment & cytokine production.
• Higher doses of the lipid A component contribute to septic
shock, disseminated intravascular coagulation, & adult
respiratory distress syndrome.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infectiousdiseasesch8-190920170149/85/Infectious-diseases-22-320.jpg)

![Mechanisms of Bacterial Injury
Bacterial Toxins
Endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide [LPS])
• It is a cell wall component of gram-negative bacteria
composed of a common long-chain fatty acid (lipid A) & a
variable carbohydrate chain (O antigen).
• Low doses of the lipid A component elicit protective
inflammatory cell recruitment & cytokine production.
• Higher doses of the lipid A component contribute to
septic shock, disseminated intravascular coagulation, &
adult respiratory distress syndrome.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infectiousdiseasesch8-190920170149/85/Infectious-diseases-25-320.jpg)

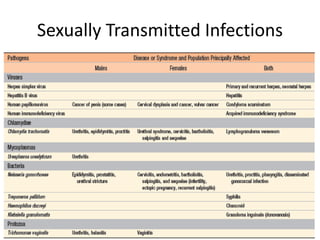
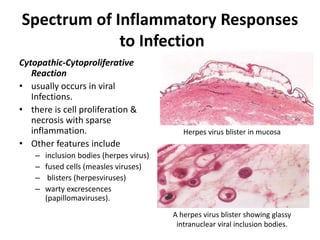

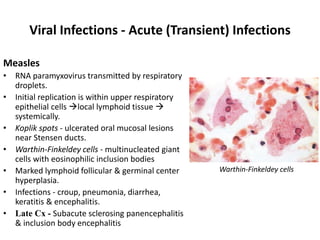




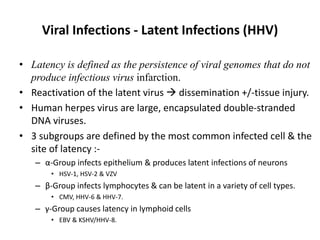

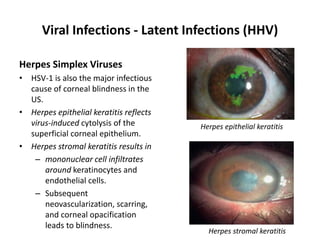

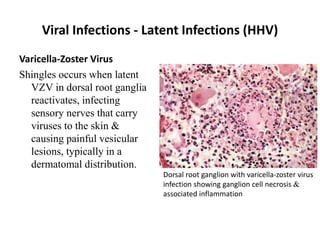
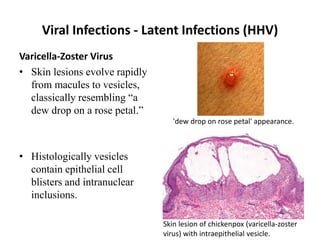

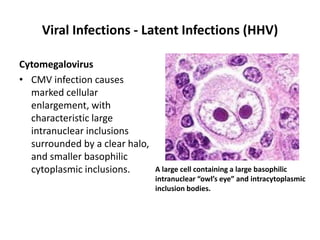



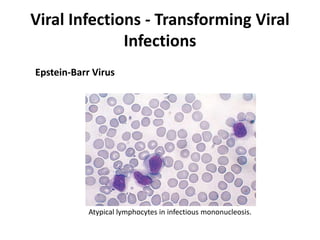










![Bacterial Infections - Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections
Neisserial Infections
• aerobic, gram-negative diplococci
• they usually have stringent in vitro growth.
• requirements (e.g., sheep blood-enriched [“chocolate”] agar).
• N. meningitidis is an important cause of bacterial meningitis,
particularly in children younger than age 2; there are 13 different
serotypes.
– Bacteria colonize the oropharynx (10% of the population is colonized at any
one time) and are spread by respiratory droplets.
– Meningitis occurs when people encounter serotypes to which they are not
previously immune (e.g., in military barracks or college dormitories).
• Neisseria gonorrhoeae is the second most common sexually transmitted
bacterial infection in the US](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infectiousdiseasesch8-190920170149/85/Infectious-diseases-63-320.jpg)









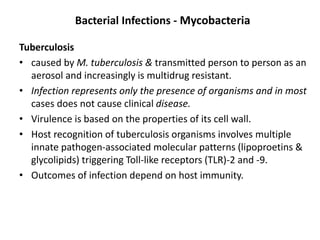




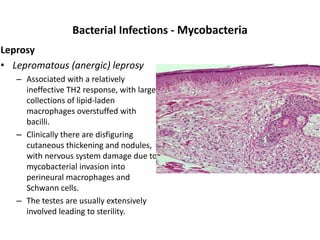
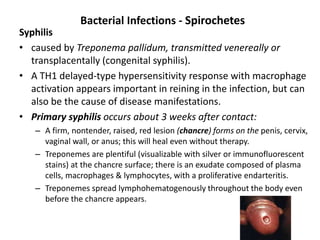
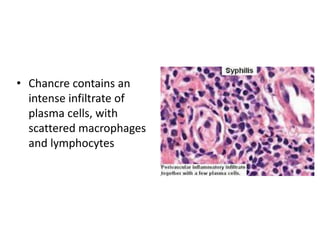
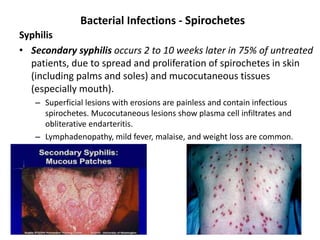
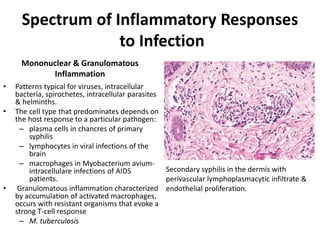
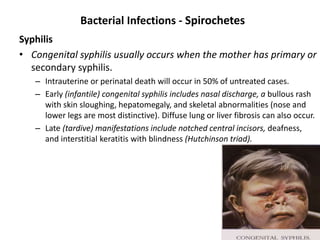
![Bacterial Infections - Spirochetes
Syphilis
• Tertiary syphilis occurs in one third of untreated patients, after a
long latent period (>5 years).
– Cardiovascular syphilis (>80% of tertiary syphilis) results in aortitis (due to
endarteritis of the aortic vasa vasorum) with aortic root and arch
aneurysms and aortic valve insufficiency.
– Neurosyphilis can be symptomatic (meningovascular disease, tabes
dorsalis, or diffuse brain parenchymal disease, so-called general paresis) or
asymptomatic (cerebrospinal fluid [CSF] abnormalities only, with
pleocytosis, increased protein, and decreased glucose).
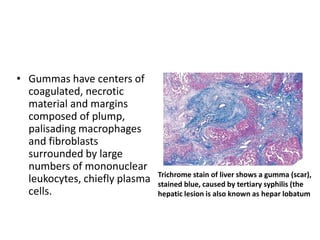
– “Benign” tertiary syphilis is associated with necrotic, rubbery masses
(gummas due to delayed-type hypersensitivity to the organisms), which
form in various sites (bone, skin, oral mucosa).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infectiousdiseasesch8-190920170149/85/Infectious-diseases-86-320.jpg)

![Bacterial Infections - Spirochetes
Syphilis
Serologic tests
• Treponemal antibody tests measure antibodies reactive with
T.Pallidum.
• Non-treponemal tests (venereal disease research laboratory
[VDRL], rapid plasma reagin [RPR]) measure antibody to
cardiolipin, a phospholipid in treponemes and normal tissues.
• Both tests become positive approximately 6 weeks after infection
but are only moderately sensitive (70% to 85%) for primary
syphilis; they are >95% sensitive for secondary syphilis.
– Nontreponemal test may become negative with time or treatment, but
treponemal antibody tests remain positive and are very sensitive for
tertiary and latent syphilis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/infectiousdiseasesch8-190920170149/85/Infectious-diseases-90-320.jpg)