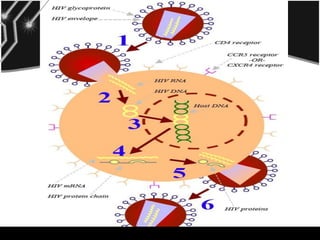
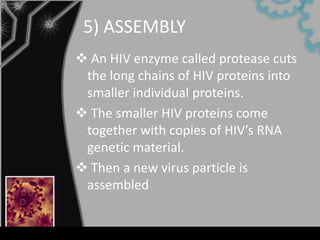
HIV enters the host cell by binding to CD4 receptors and co-receptors on T-cells. It then fuses with and releases its RNA into the cell. The RNA is converted to DNA by reverse transcriptase and integrated into the host cell's DNA by integrase. The integrated DNA is then transcribed to produce new HIV proteins which assemble and bud from the host cell to infect others.