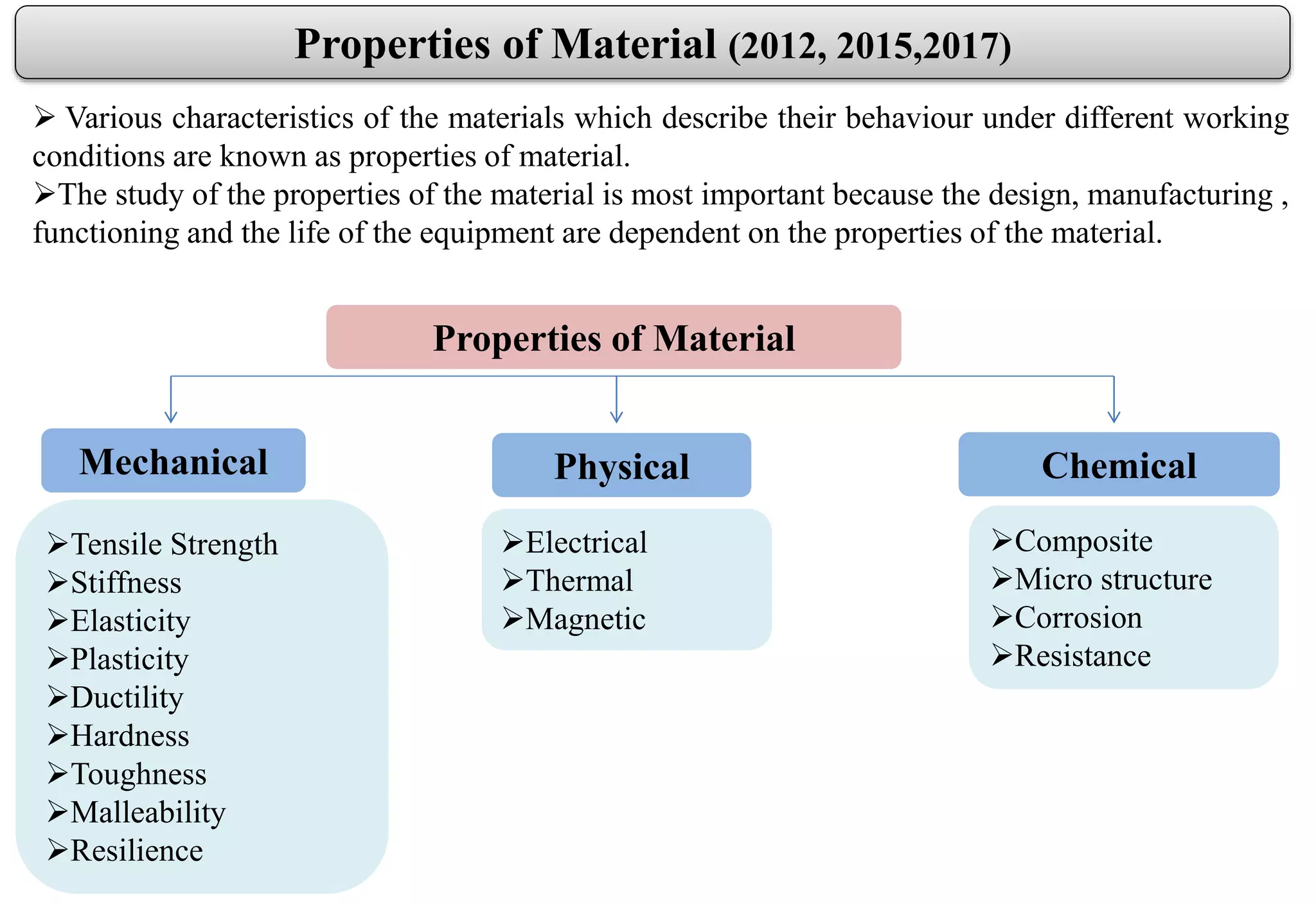
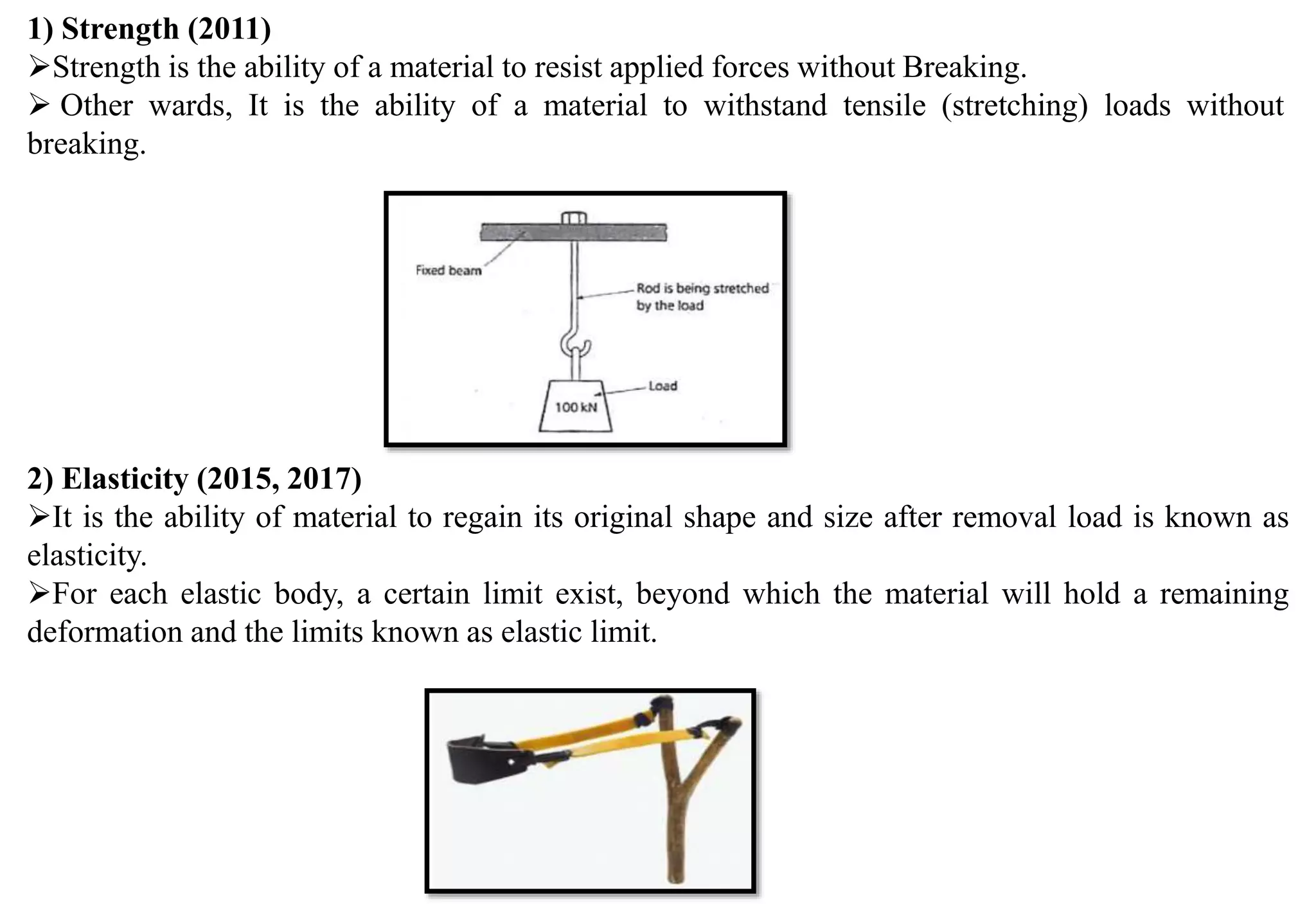
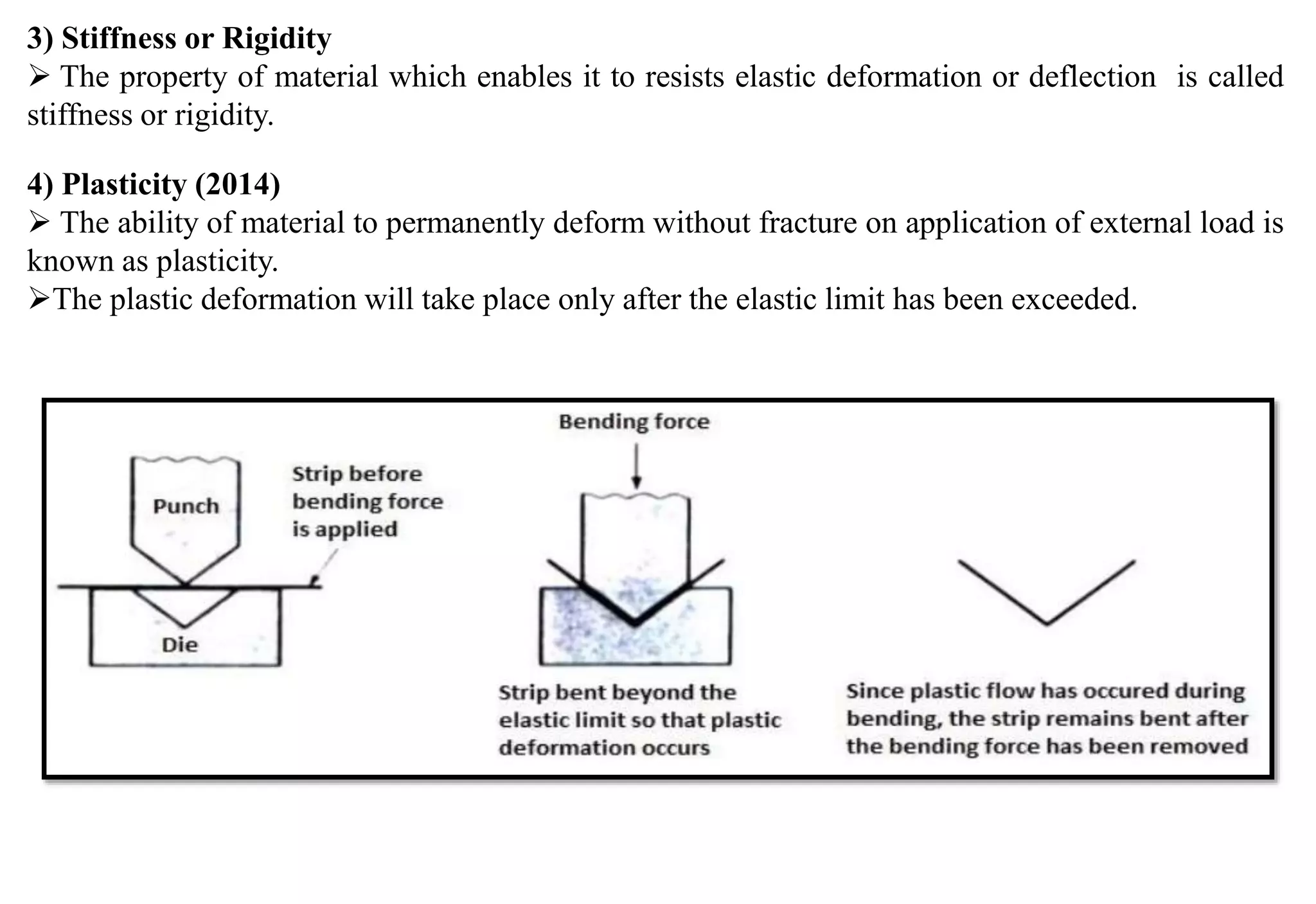
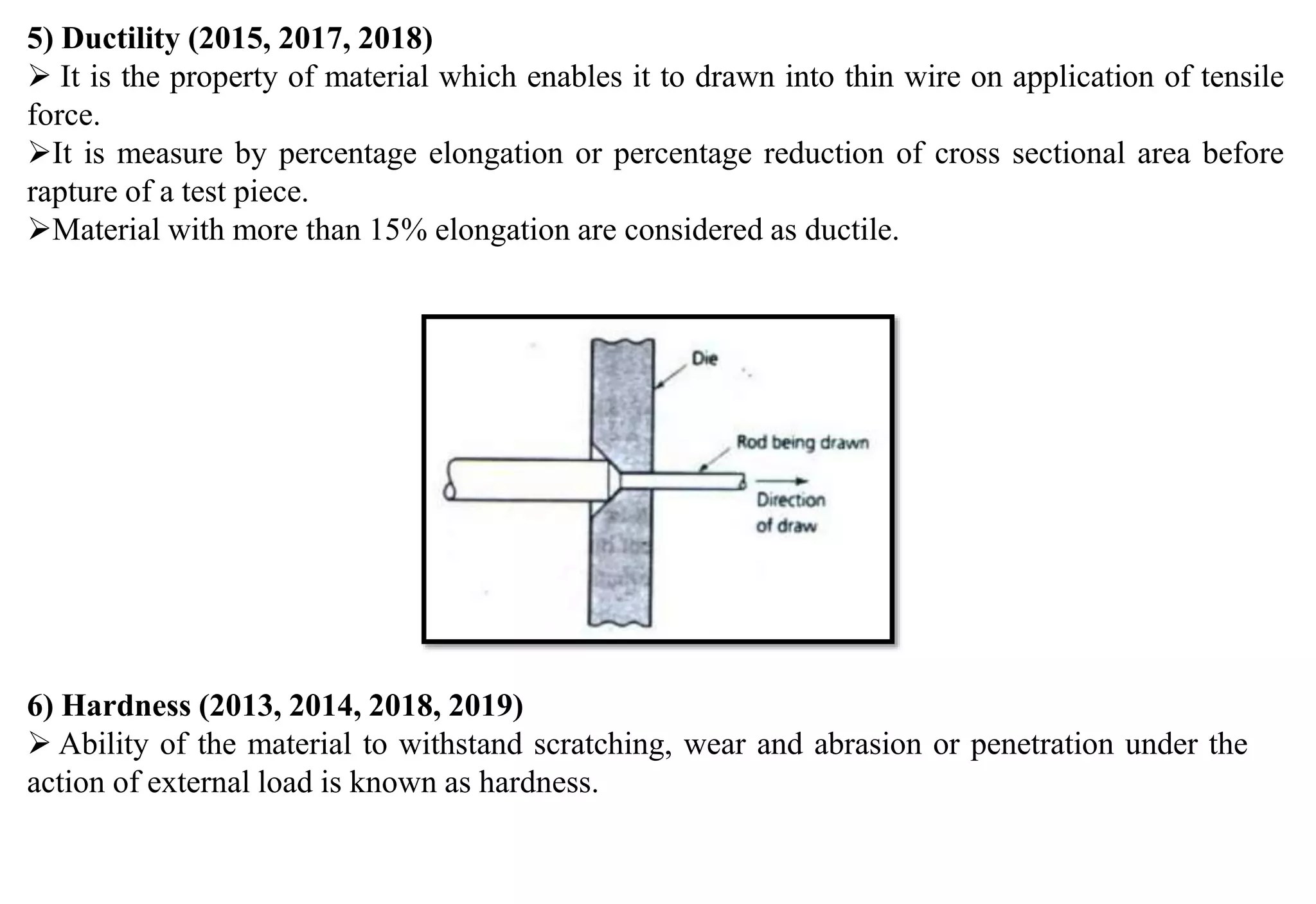
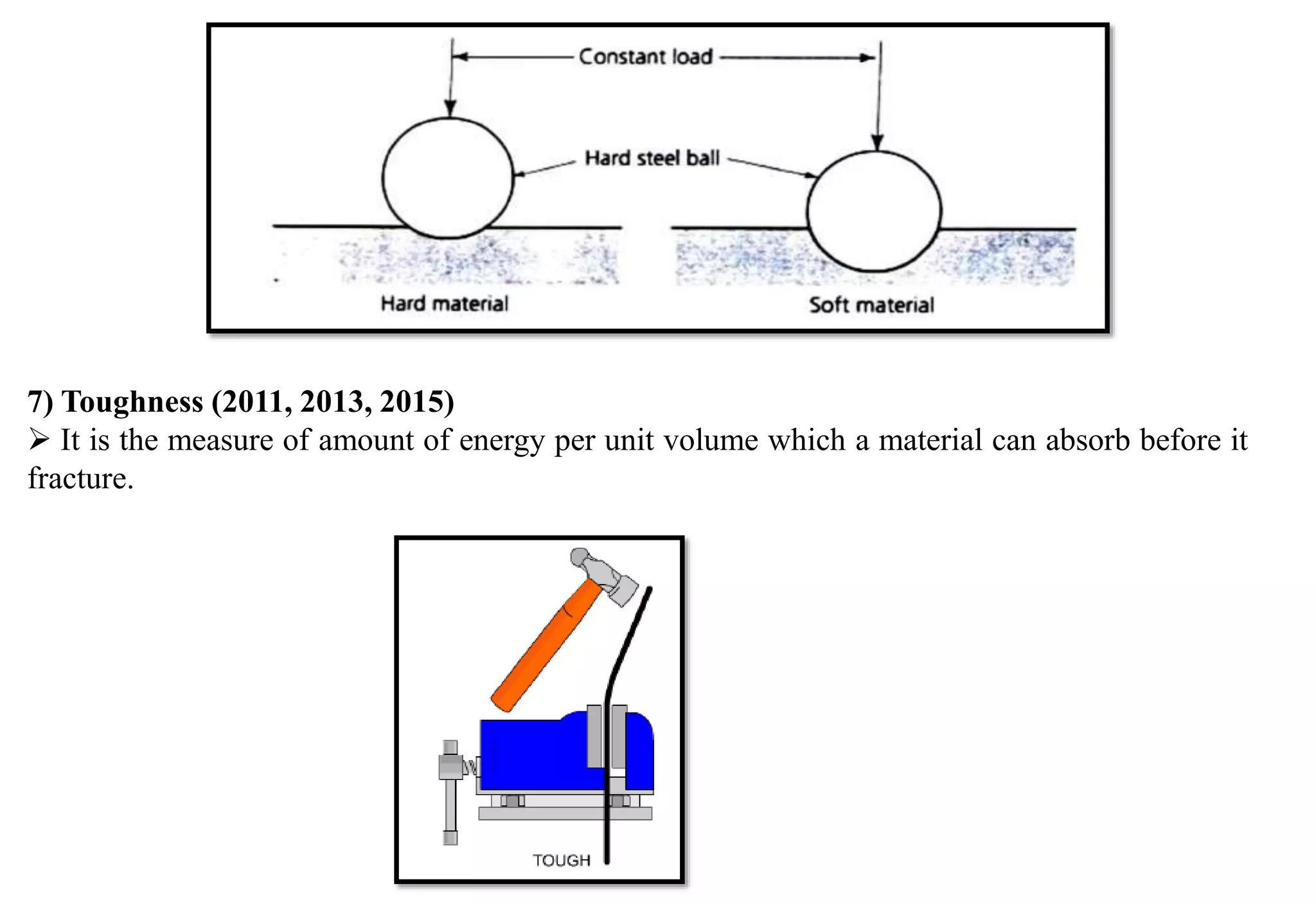
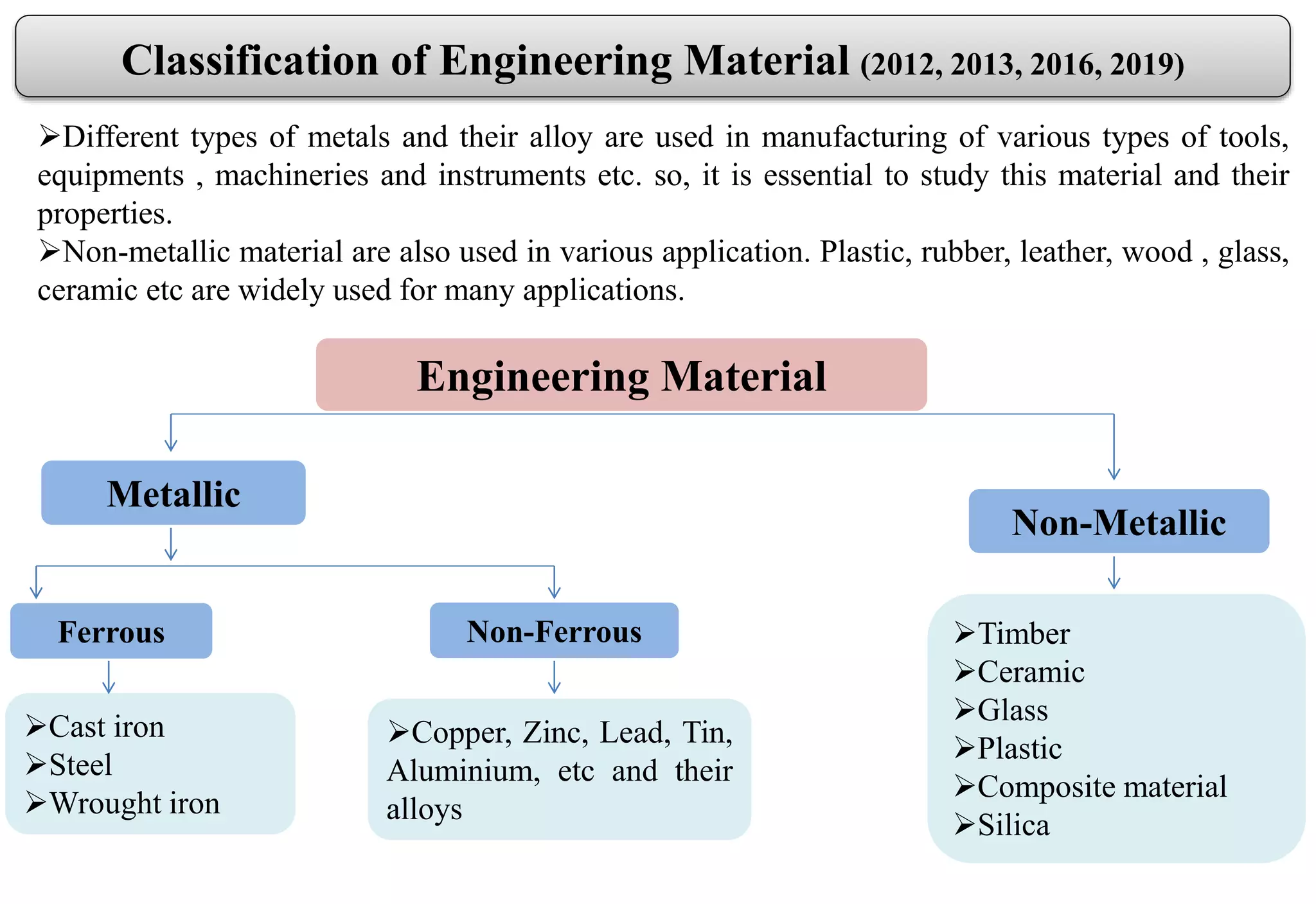
This document provides an overview of engineering materials, including their classification, properties, and applications. Metallic materials are divided into ferrous materials like iron, steel, and cast iron and non-ferrous materials like copper, aluminum, and their alloys. The properties of materials that are discussed include mechanical properties like strength, elasticity, ductility, and hardness as well as physical properties. Non-metallic materials like ceramics, polymers, wood, and composites are also introduced along with their uses.