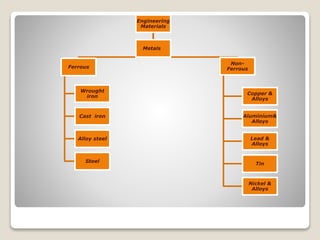
The document discusses ferrous and non-ferrous metals, detailing their properties, compositions, and applications. Ferrous materials include wrought iron, cast iron, and various steels, while non-ferrous materials cover metals like aluminum, copper, lead, tin, and nickel. Each type of metal is highlighted for its unique characteristics and industrial uses.