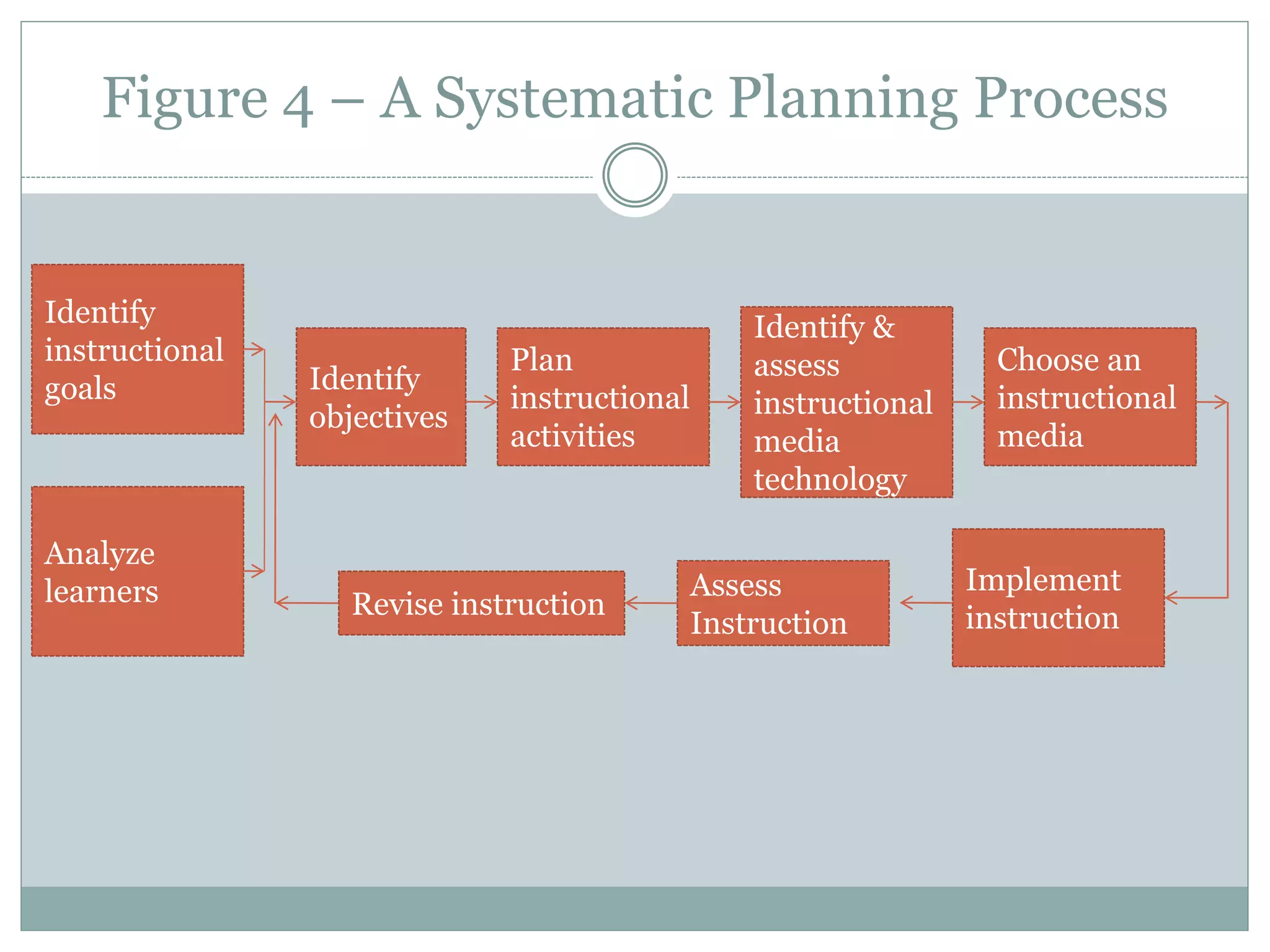
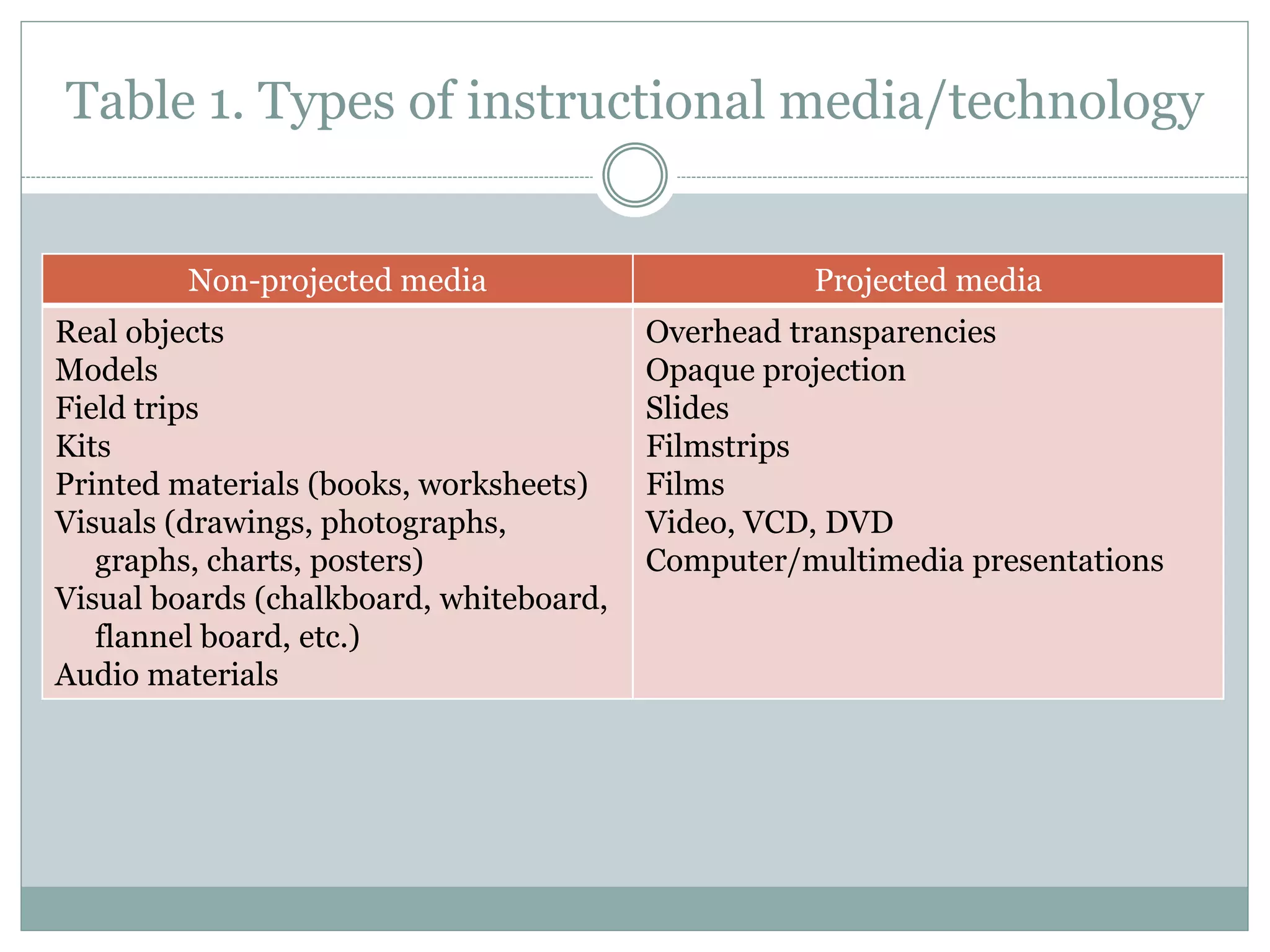
The role of technology in curriculum implementation is to aid instructional planning and delivery. In planning lessons, teachers must identify goals, analyze learners, set objectives, plan activities, and choose appropriate instructional media/technology. Technology offers various tools for learning, from non-projected media like real objects and printed materials, to projected media like videos and computer presentations. Teachers must decide which technology to use to best achieve their instructional objectives for each lesson.