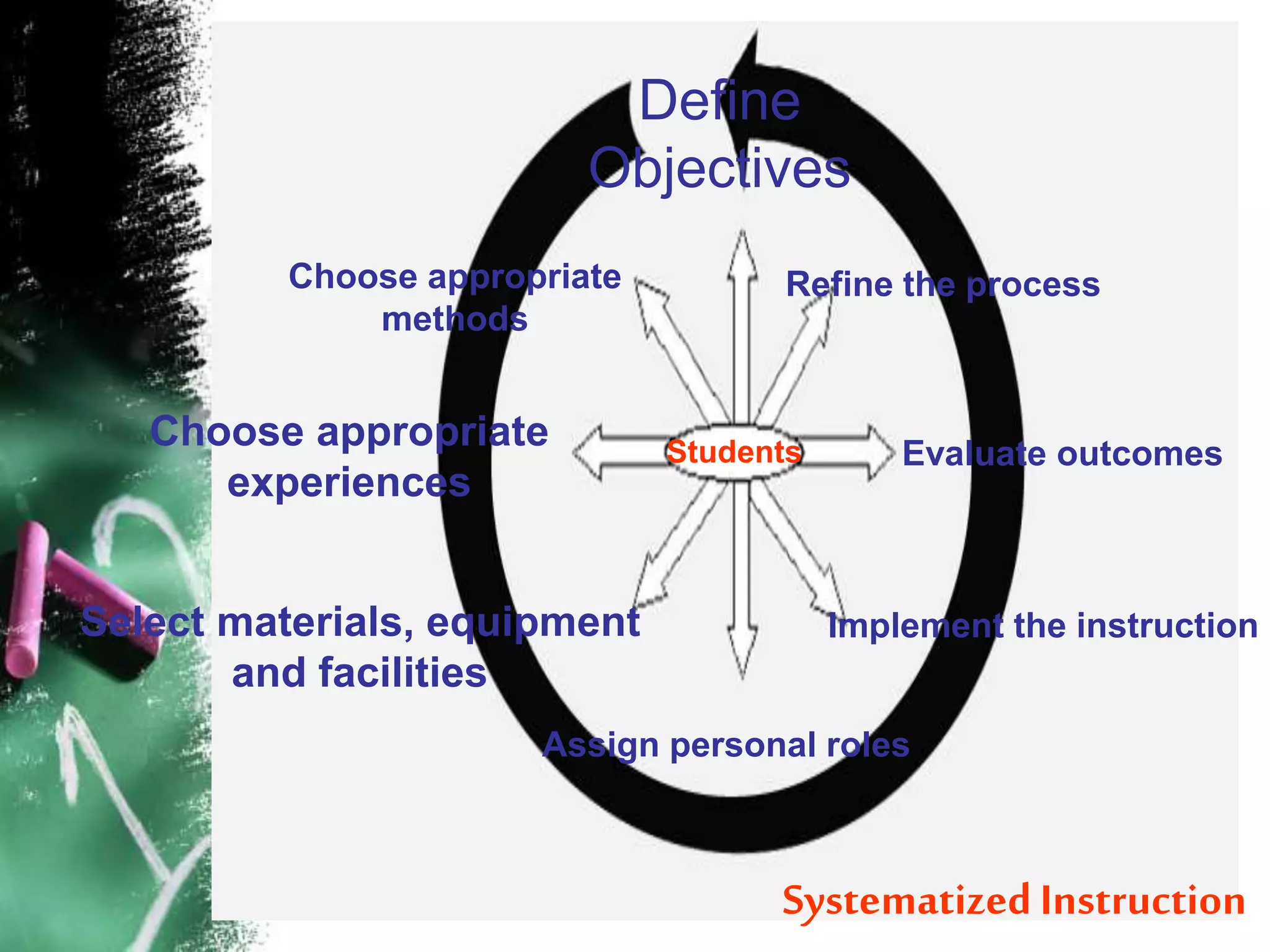
The document discusses the systematic approach to teaching, which views the entire educational program as an interconnected system. It involves defining student-centered objectives, selecting appropriate teaching methods and learning experiences, and refining the process based on evaluations to achieve the objectives. The key aspects are: (1) focusing on students and their needs, (2) planning instruction using objectives and aligned methods/materials, and (3) evaluating and refining to improve outcomes. All elements are interrelated - if one fails, learning is affected. The goal is to harmoniously integrate all parts into an effective whole.