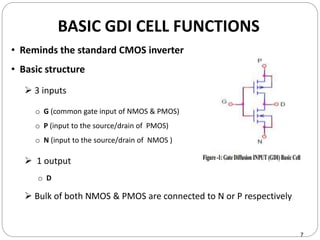
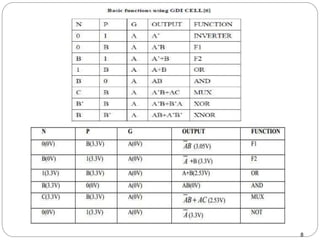
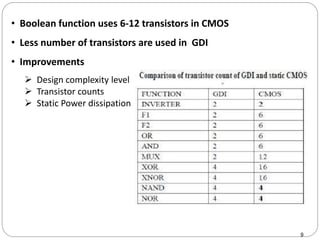
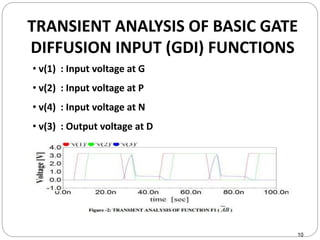
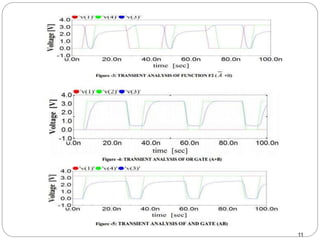
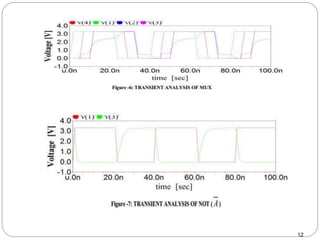
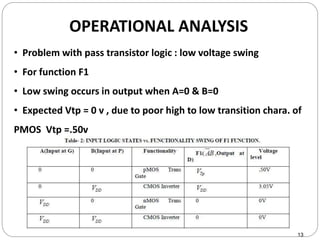
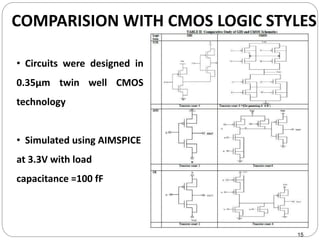
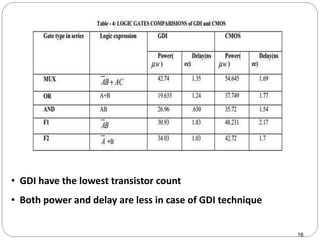
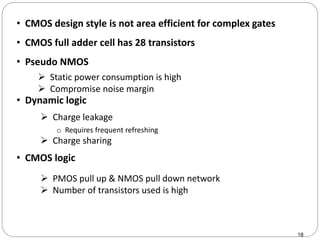
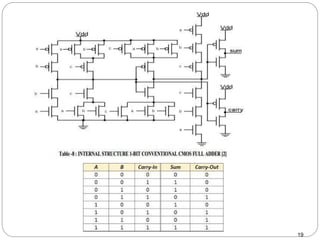
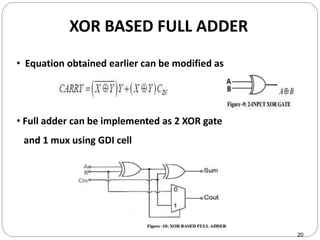
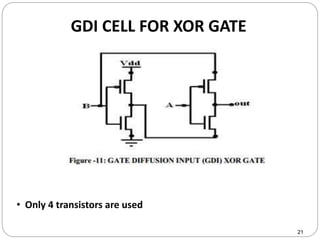
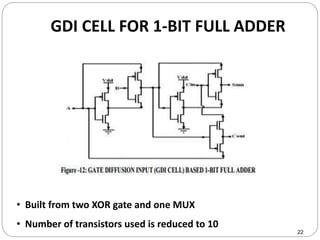
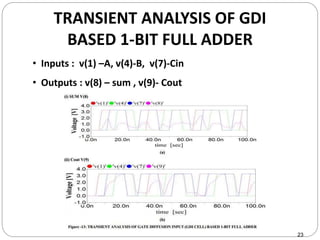
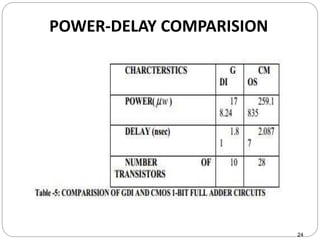
This document discusses the implementation of a 1-bit full adder circuit using the Gate Diffusion Input (GDI) technique. GDI is introduced as a low-power logic design style that can reduce transistor counts, power consumption, and propagation delay compared to traditional CMOS designs. The document first reviews the advantages of GDI and the basic GDI cell functions. It then describes how a conventional CMOS 1-bit full adder works before presenting the design of a XOR-based and GDI-based 1-bit full adder. Transient analysis and comparisons show that the GDI full adder uses fewer transistors and has lower power and delay than traditional CMOS designs. The document concludes that GDI is an