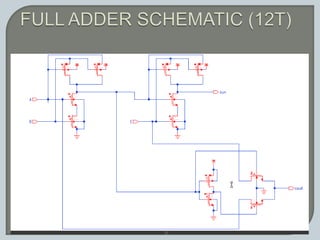
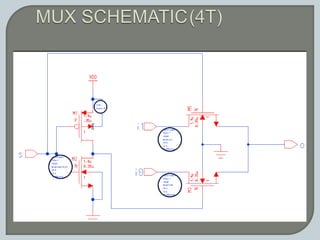
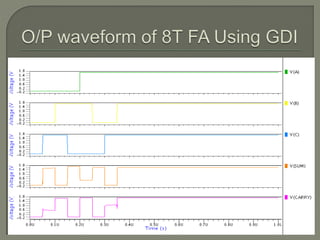
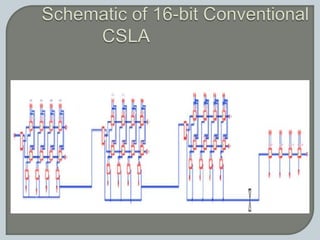
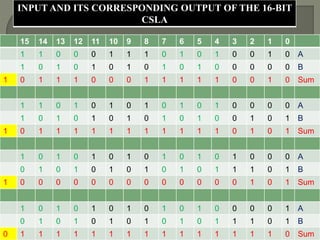
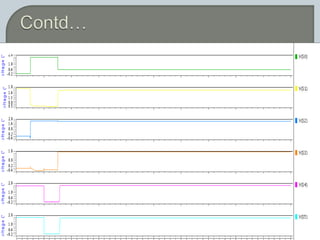
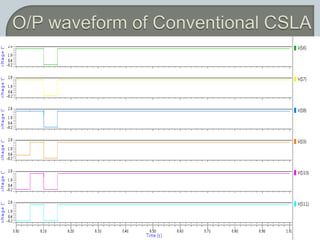
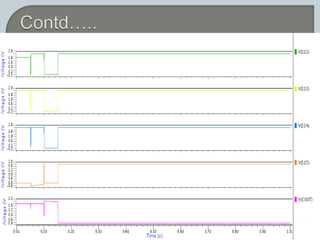
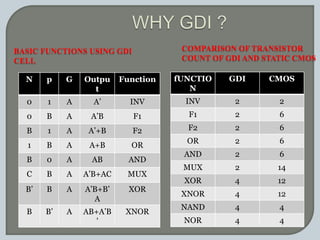
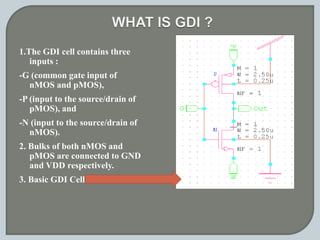
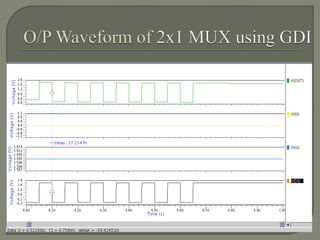
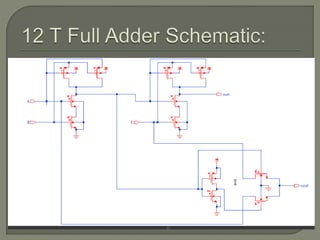
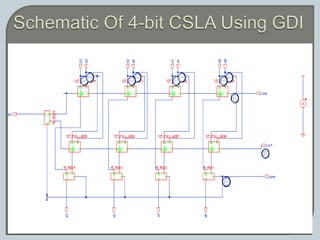
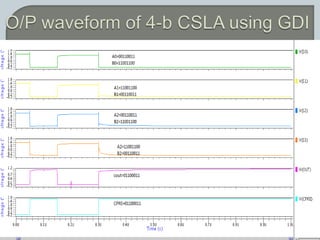
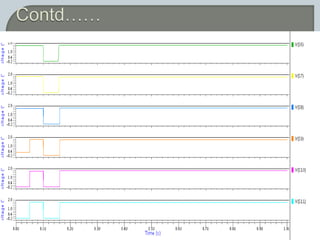
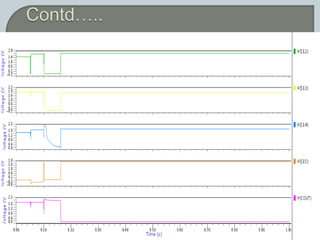
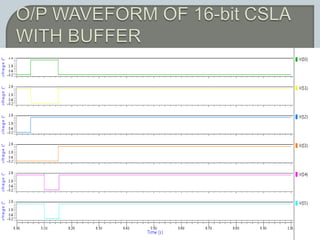
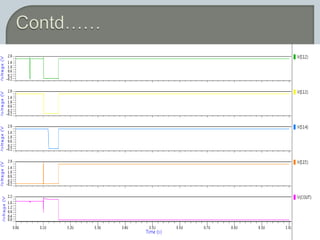
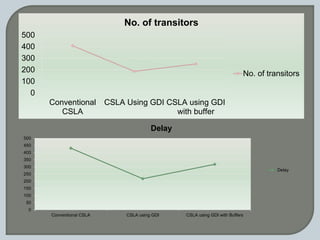
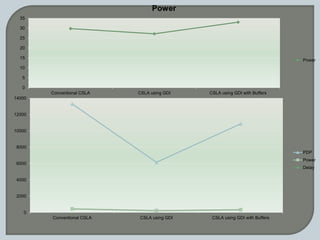
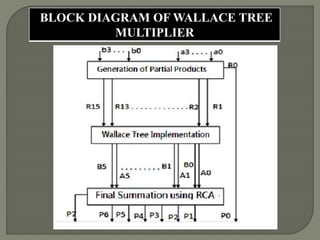
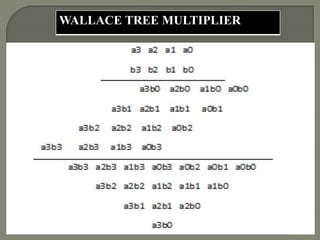
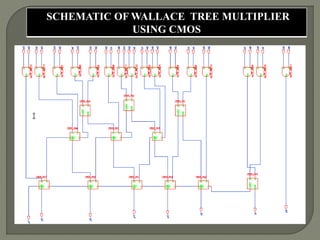
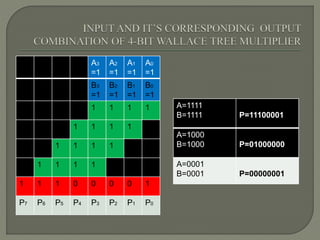
The document discusses the Carry Select Adder (CSLA), highlighting its architecture with dual Ripple Carry Adders (RCA) and multiplexers for efficient arithmetic operations. It details the implementation of low power digital designs using Gate Diffusion Input (GDI) techniques, showing comparisons in transistor count, delay, and power consumption between conventional CSLA and GDI designs. Additionally, it references various studies and conferences on advancements in low power and high-speed digital circuit designs.