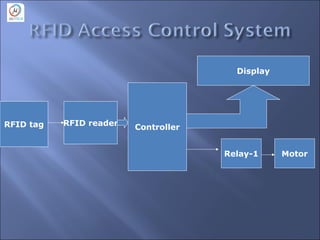
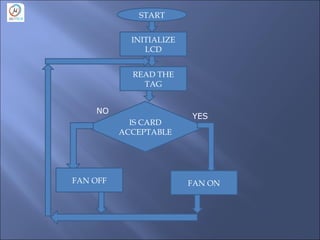
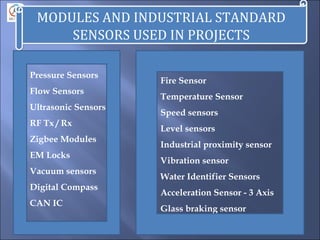
This document discusses embedded systems and provides information on:
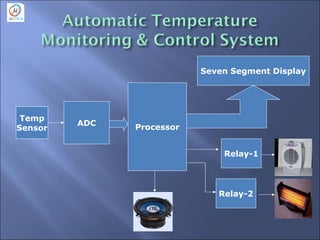
- The components of an embedded system including a processor, peripherals, and software.
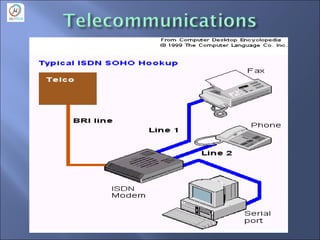
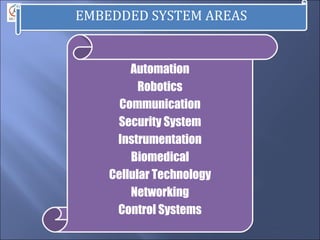
- Major application areas such as consumer electronics, automation, and networking.
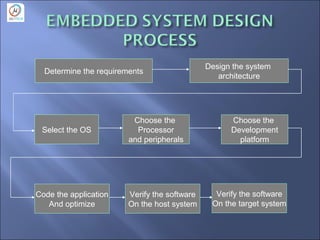
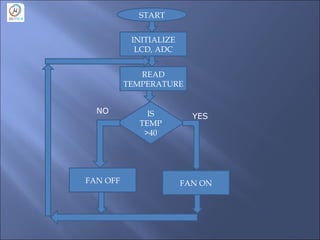
- The embedded system design process including determining requirements, designing architecture, selecting hardware and software, and testing.
- Recent trends in embedded systems including reduced size, cost and power consumption.