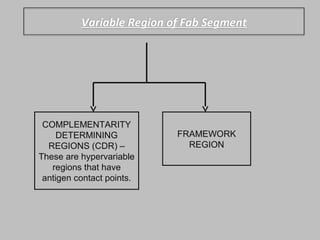
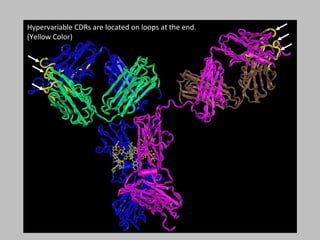
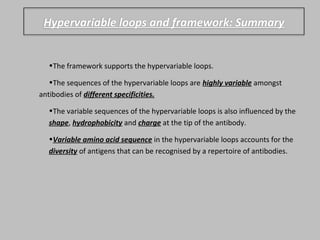
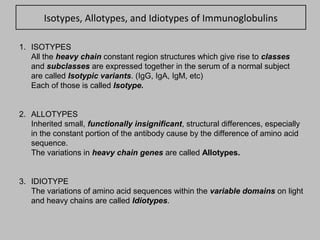
Immunoglobulin molecules have a variable region made up of light and heavy chains that provides specificity for antigens. The variable region, called the Fab segment, contains hypervariable complementarity determining regions (CDRs) that form antigen contact points and allow for recognition of a diverse range of antigens. The Fc region mediates effector functions like complement binding and interaction with immune cells. The structural basis for antibody diversity lies in the highly variable amino acid sequences of the CDR loops within the Fab segment.