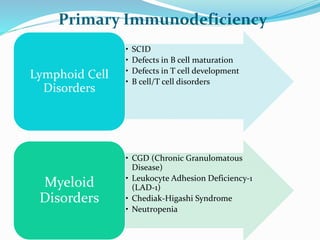
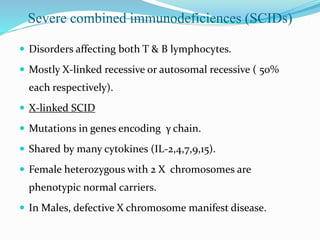
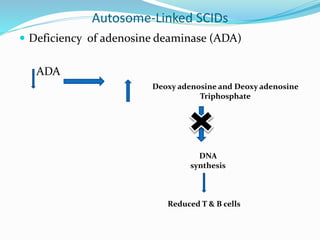
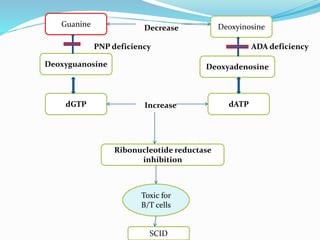
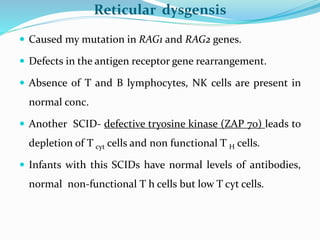
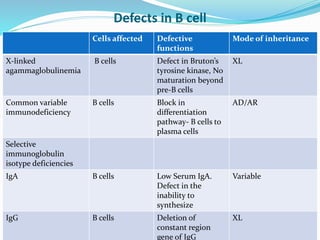
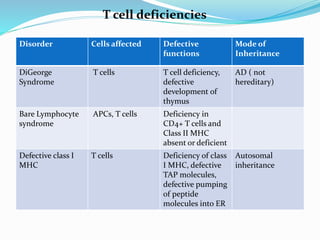
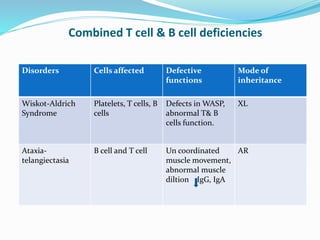
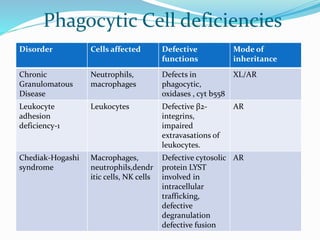
This document summarizes various primary immunodeficiencies, including severe combined immunodeficiencies (SCIDs) affecting both T and B lymphocytes. It also describes defects in B cell maturation, T cell development, and other lymphoid and myeloid disorders. Specific conditions discussed include SCID caused by mutations in the gamma chain gene (X-linked SCID), adenosine deaminase deficiency, and reticular dysgenesis. Defects in B cells, T cells, phagocytic cells, and combined T and B cell deficiencies are also summarized. The document provides information on the cells affected, defective functions, and inheritance patterns for many primary immunodeficiencies.