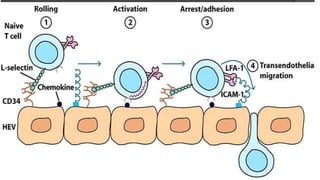
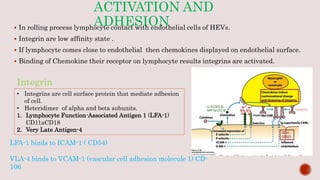
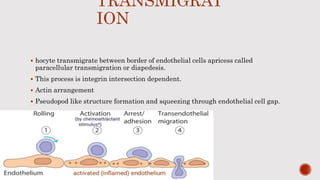
Lymphocytes continuously recirculate between the vascular system and tissues, which is essential for immune system homeostasis and function. This migration is regulated by cell adhesion molecules and chemokines. Chemokines play a key role in lymphocyte trafficking by facilitating adhesion to and transmigration through vascular endothelium. The process involves lymphocytes first rolling along endothelial cells, then becoming activated and firmly adhering via integrins when they encounter chemokines, and finally transmigrating between endothelial cells into tissues.