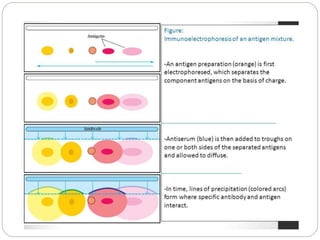
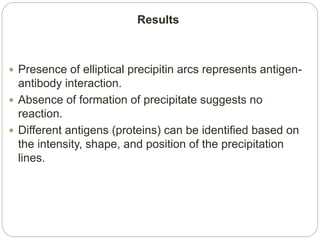
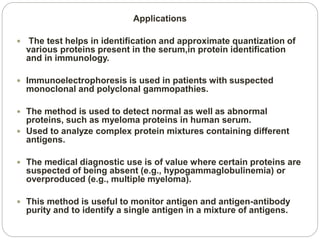
Immunoelectrophoresis is a technique that combines electrophoresis and immunodiffusion to separate and identify antigen components in a mixture. It involves applying an electric current to separate antigens in agar gel wells, then allowing the antigens to diffuse and react with antibodies placed in troughs cut into the gel. This results in the formation of precipitin lines that indicate reactions between individual antigens and antibodies, allowing different antigens to be identified based on the lines' position and shape. Immunoelectrophoresis is used in medical diagnostics to detect abnormal proteins and monitor antigen purity.