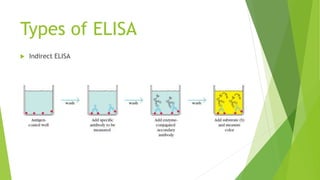
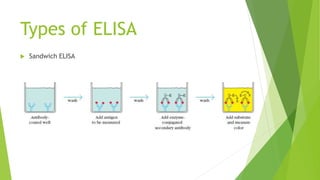
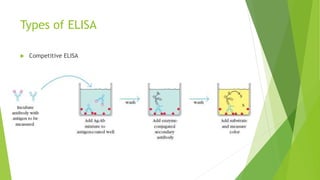
The document discusses enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), including its introduction, principle, equipment, procedure, types, advantages, and disadvantages. ELISA is a qualitative or quantitative immunological procedure that detects antigens or antibodies using enzyme-labeled antibodies and chromogenic substrates. It relies on antibody-antigen interactions and uses an enzyme-labeled antibody to generate a colored reaction, allowing detection of a particular antigen. The document outlines the basic equipment, general procedure involving coating wells with antibodies and adding samples and enzyme-labeled antibodies, and the three main types of ELISA - indirect, sandwich, and competitive.