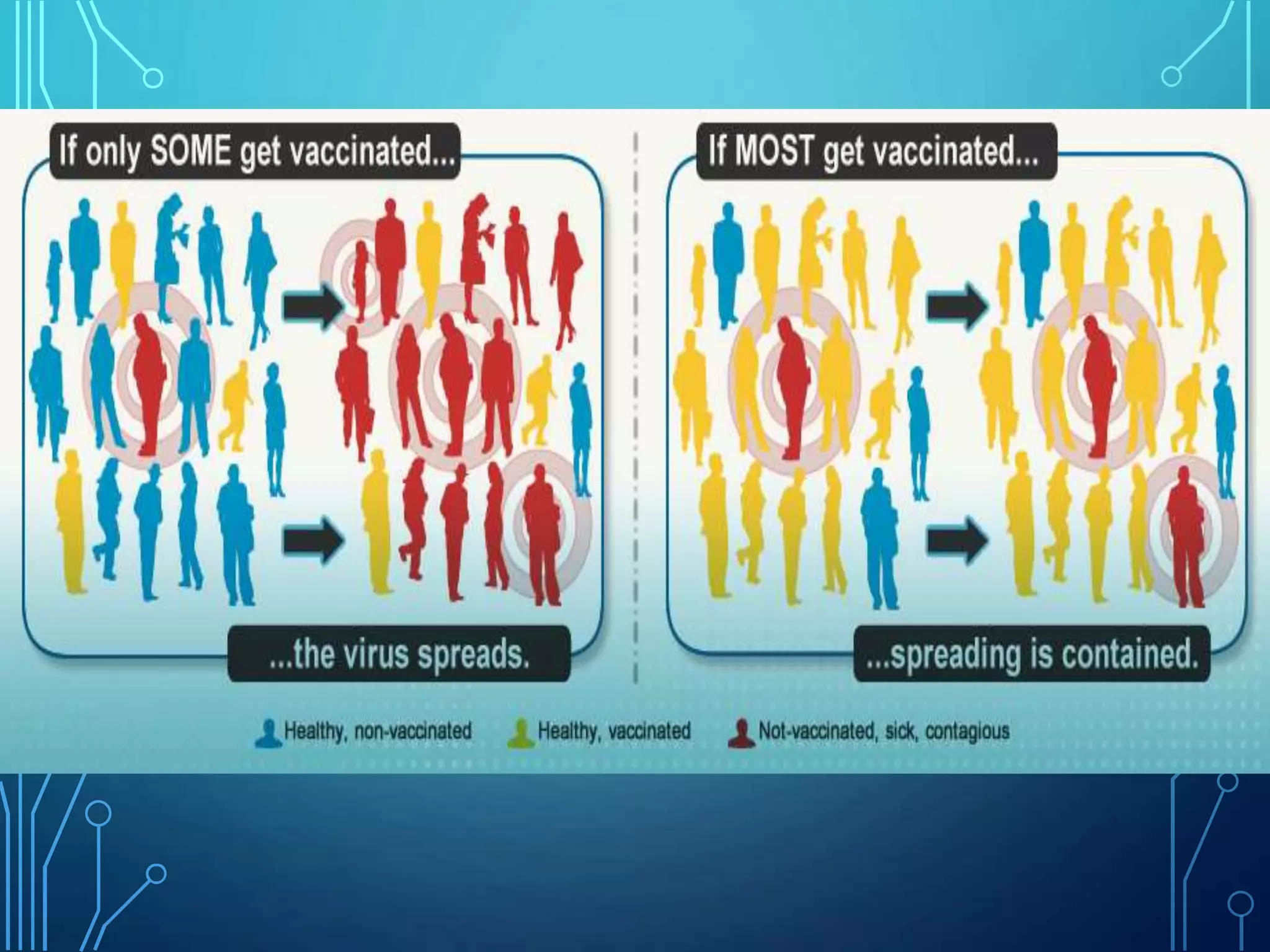
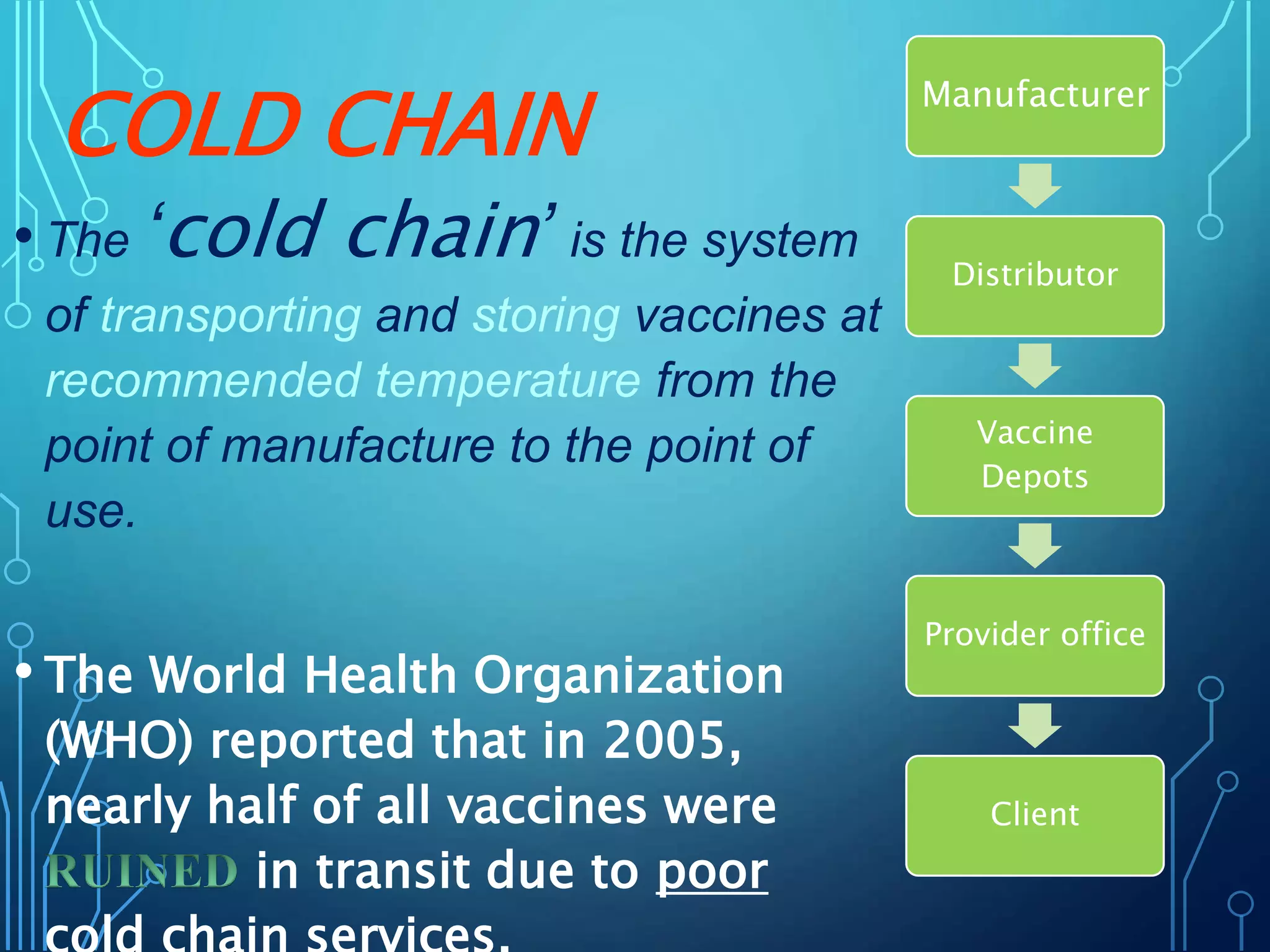
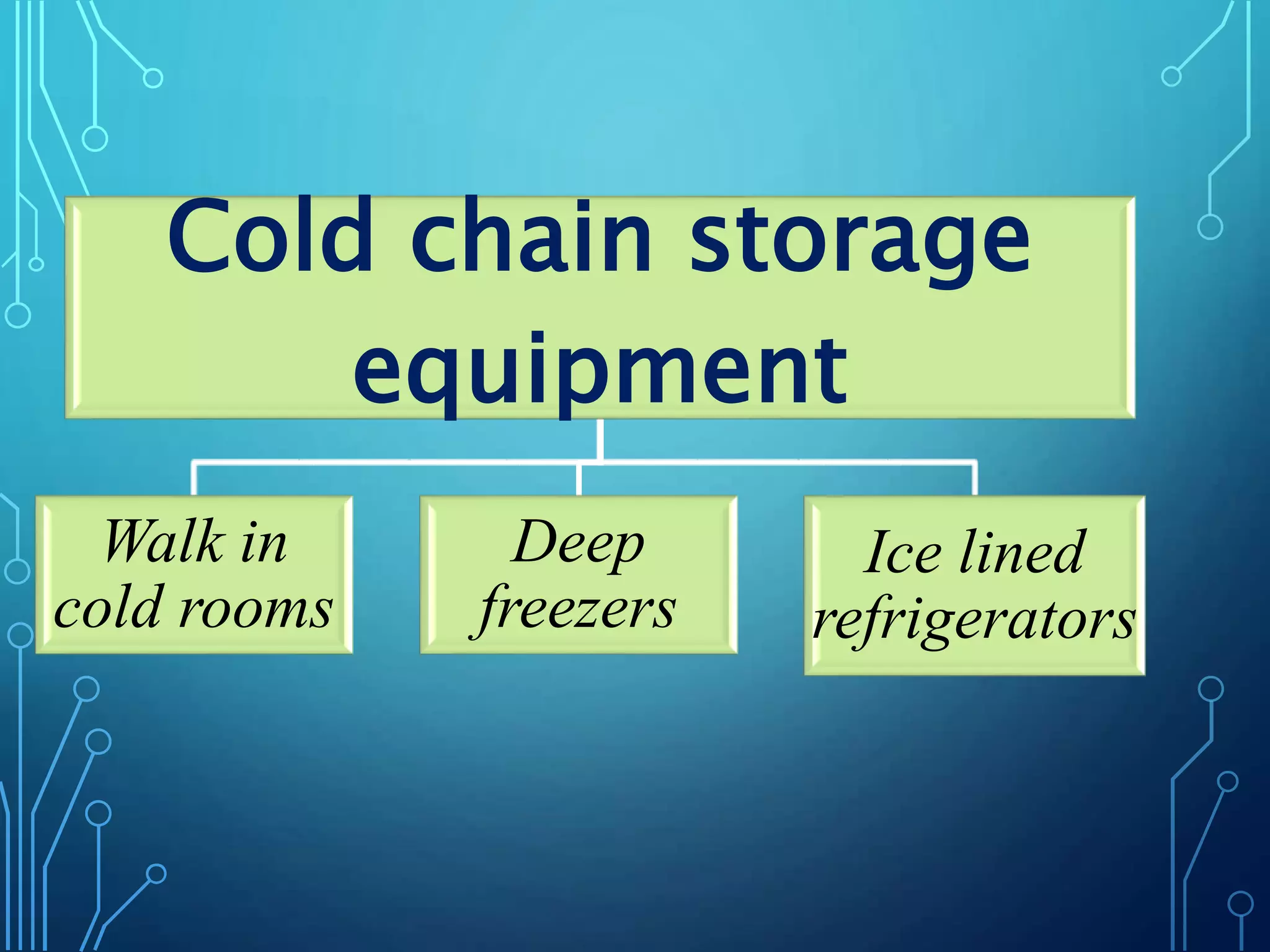
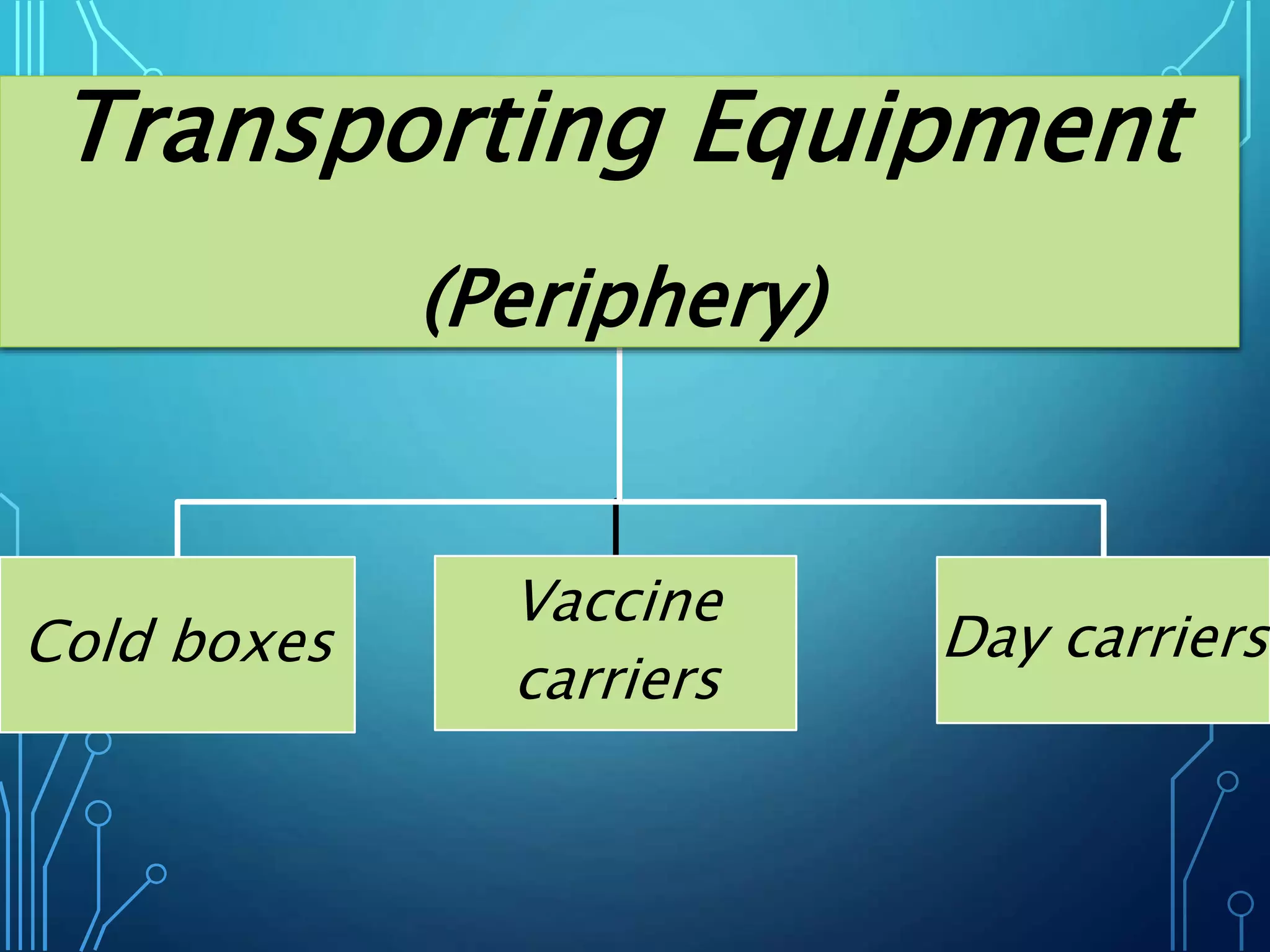
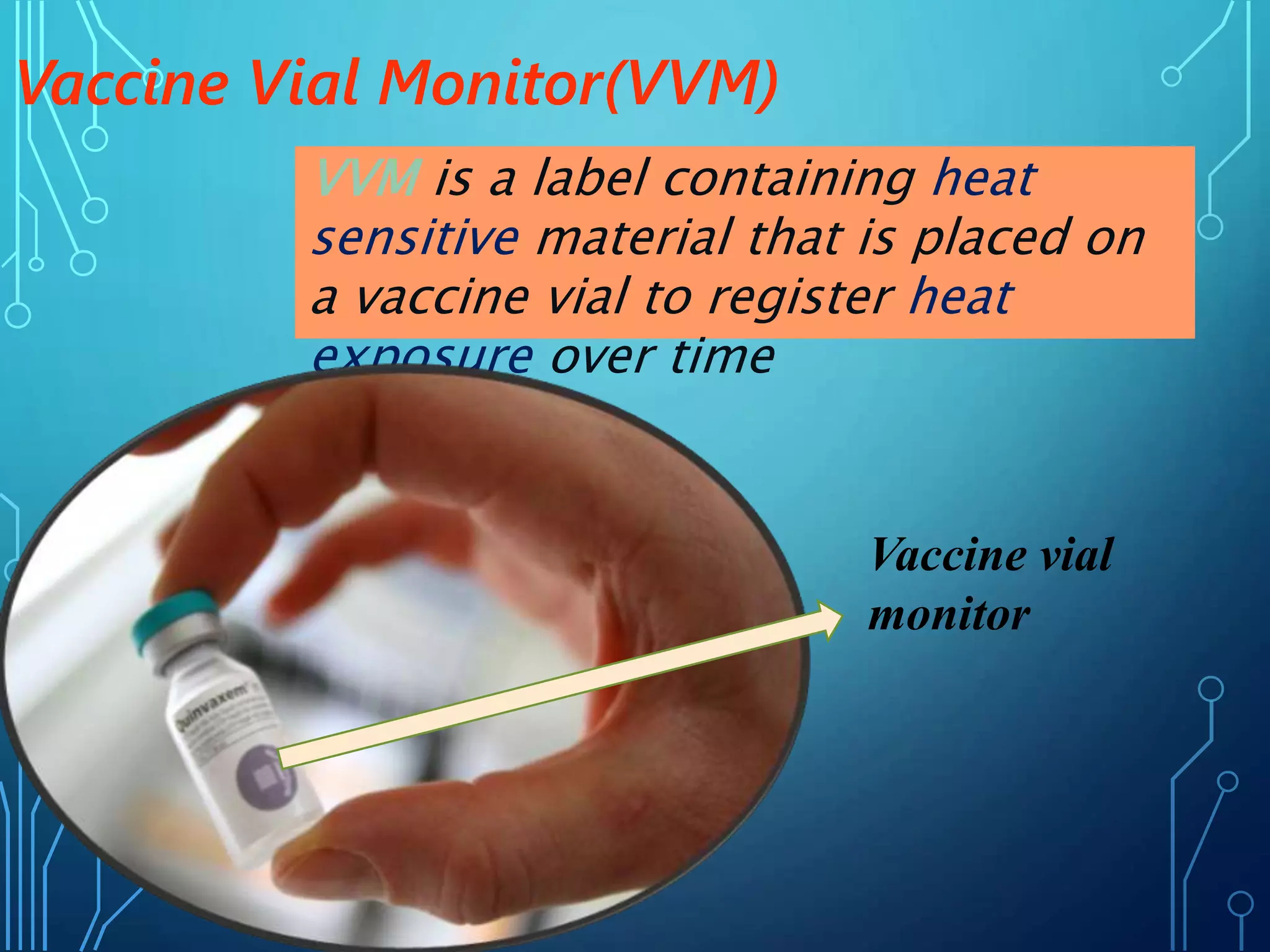
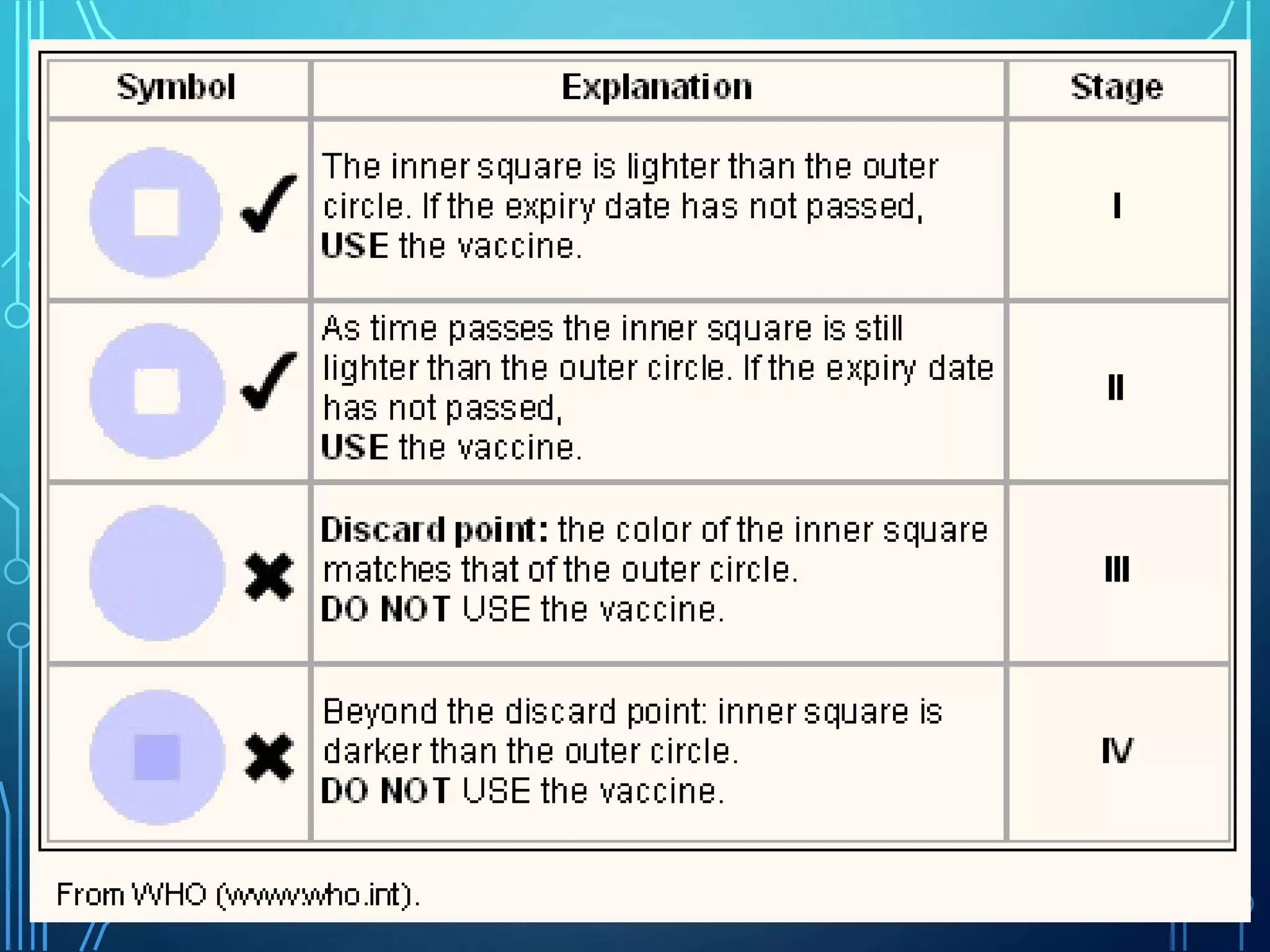
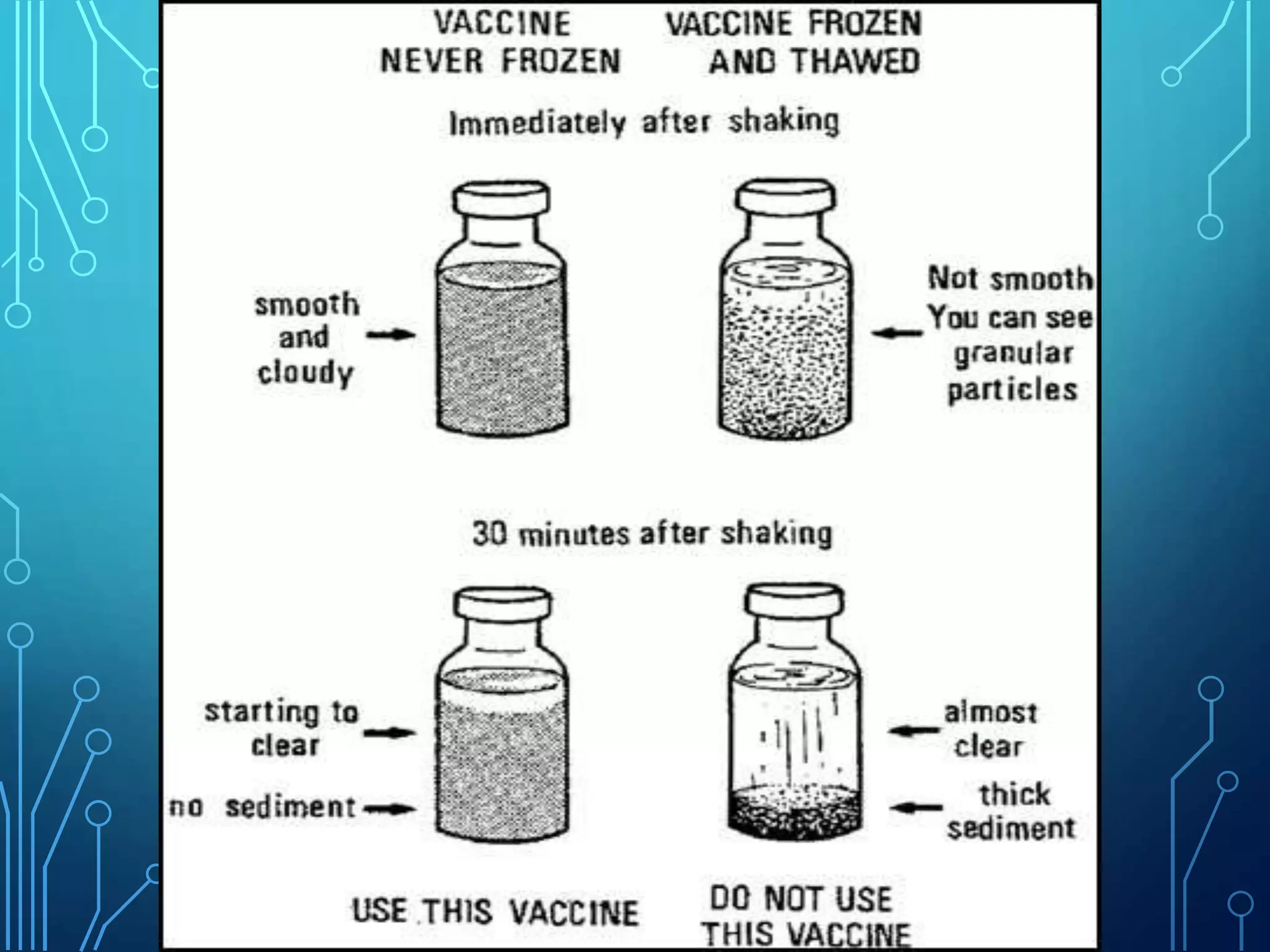
The document discusses India's immunization program, which began in 1978. It outlines key terms like immunity, immunization, vaccines, and herd immunity. It describes the national immunization schedule and strategies to reduce morbidity and mortality from vaccine-preventable diseases through vaccination. It also discusses monitoring systems and highlights the importance of maintaining the cold chain to ensure vaccine quality as the program aims to universally protect children from prevalent diseases.